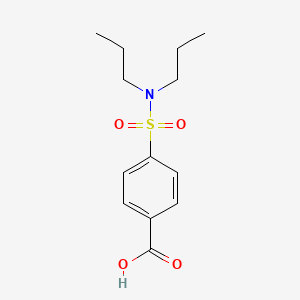

1. Benecid
2. Benemid
3. Benuryl
4. Pro-cid
5. Probecid
6. Probenecid Weimer
1. 57-66-9
2. 4-(dipropylsulfamoyl)benzoic Acid
3. Benemid
4. Probenecid Acid
5. Probecid
6. Probalan
7. Benecid
8. Probenemid
9. Benuryl
10. Probexin
11. Prolongine
12. Tubophan
13. Uricosid
14. Apurina
15. P-(dipropylsulfamoyl)benzoic Acid
16. Proben
17. Synergid R
18. Probenecidum
19. Probenecida
20. Probenecide
21. 4-[(dipropylamino)sulfonyl]benzoic Acid
22. 4-((dipropylamino)sulfonyl)benzoic Acid
23. 4-(di-n-propylsulfamoyl)benzoesaeure
24. 4-(n,n-dipropylsulfamoyl)benzoesaeure
25. Nci-c56097
26. Benzoic Acid, 4-[(dipropylamino)sulfonyl]-
27. Benzoic Acid, P-(dipropylsulfamoyl)-
28. Probenate
29. 4-(n,n-dipropylsulfamoyl)benzoic Acid
30. P-(dipropylsulfamyl)benzoic Acid
31. Benzoic Acid, 4-((dipropylamino)sulfonyl)-
32. Nsc 18786
33. Chebi:8426
34. Probenecid (benemid)
35. Nsc-18786
36. Chembl897
37. Mls000028496
38. 4-dipropylsulfamoyl-benzoic Acid
39. Benemide
40. Probenid
41. Robenecid
42. Polycillin-brb
43. Po572z7917
44. Cas-57-66-9
45. Probenicid
46. Ncgc00016251-08
47. Smr000058280
48. Dsstox_cid_1188
49. Dsstox_rid_75998
50. Dsstox_gsid_21188
51. Probenecide [inn-french]
52. Probenecidum [inn-latin]
53. Probenecida [inn-spanish]
54. Benemid (tn)
55. Ccris 3643
56. Hsdb 3387
57. Sr-01000003108
58. Einecs 200-344-3
59. Mfcd00038402
60. Brn 2815775
61. Ai3-50078
62. Unii-po572z7917
63. Probenecid [usp:inn:ban:jan]
64. Prestwick_809
65. Spectrum_000834
66. Colbenemid (salt/mix)
67. Opera_id_677
68. Probenecid [mi]
69. Probenecid [inn]
70. Probenecid [jan]
71. Prestwick0_000542
72. Prestwick1_000542
73. Prestwick2_000542
74. Prestwick3_000542
75. Spectrum2_001294
76. Spectrum3_000554
77. Spectrum4_000486
78. Spectrum5_001419
79. Probenecid [hsdb]
80. Benemid; Benecid; Benuryl
81. Epitope Id:180853
82. Probenecid [mart.]
83. Schembl3663
84. Polycillin-prb (salt/mix)
85. Probenecid [usp-rs]
86. Probenecid [who-dd]
87. Probenecid [who-ip]
88. Bidd:pxr0092
89. Oprea1_416955
90. Wln: Qvr Dswn3&3
91. Bspbio_000583
92. Bspbio_002227
93. Kbiogr_000971
94. Kbioss_001314
95. Mls001076472
96. Bidd:gt0626
97. Divk1c_000056
98. Spectrum1500502
99. Spbio_001327
100. Spbio_002504
101. Bpbio1_000643
102. Gtpl4357
103. Probenecid (jp17/usp/inn)
104. Zinc1982
105. Dtxsid9021188
106. Probenecid [ep Impurity]
107. Probenecid [orange Book]
108. Hms500c18
109. Kbio1_000056
110. Kbio2_001314
111. Kbio2_003882
112. Kbio2_006450
113. Kbio3_001727
114. Amy8947
115. Probenecid [ep Monograph]
116. Probenecid [usp Impurity]
117. Ninds_000056
118. Hms1569n05
119. Hms1920j22
120. Hms2092c03
121. Hms2096n05
122. Hms2233n05
123. Hms3259g04
124. Hms3369l18
125. Hms3652o17
126. Hms3713n05
127. Hms3743e07
128. Hms3885i18
129. P-(dipropylsulfamoyl) Benzoic Acid
130. Pharmakon1600-01500502
131. Probenecid [usp Monograph]
132. Albb-025846
133. Bcp21785
134. Hy-b0545
135. Nsc18786
136. Probenecidum [who-ip Latin]
137. Str06053
138. Proben-c Component Probenecid
139. Tox21_110328
140. Tox21_202110
141. Tox21_302928
142. Bdbm50206509
143. Ccg-39232
144. Nsc757292
145. S4022
146. Stl229614
147. Colbenemid Component Probenecid
148. 4-dipropylsulfamoyl-benzoic Acid Anion
149. Akos000165123
150. Probampacin Component Probenecid
151. Tox21_110328_1
152. Ac-2023
153. Db01032
154. Hc 5006
155. Nc00530
156. Nsc-757292
157. Sb17360
158. Idi1_000056
159. Probenecid Component Of Proben-c
160. Ncgc00016251-01
161. Ncgc00016251-02
162. Ncgc00016251-03
163. Ncgc00016251-04
164. Ncgc00016251-05
165. Ncgc00016251-06
166. Ncgc00016251-07
167. Ncgc00016251-09
168. Ncgc00016251-10
169. Ncgc00016251-13
170. Ncgc00016251-17
171. Ncgc00023829-03
172. Ncgc00023829-04
173. Ncgc00023829-05
174. Ncgc00023829-06
175. Ncgc00023829-07
176. Ncgc00256441-01
177. Ncgc00259659-01
178. Probenecid Component Of Colbenemid
179. Bp166195
180. Col-probenecid Component Probenecid
181. Probenecid Component Of Probampacin
182. 4-(n,n-dipropylaminosulphonyl)benzoic Acid
183. Sbi-0051492.p003
184. 4-dipropylsulfamoyl-benzoic Acid(probenecid)
185. Ab00052080
186. P1975
187. Probenecid Component Of Col-probenecid
188. Sw196943-3
189. En300-69677
190. C07372
191. D00475
192. D92177
193. Ab00052080_15
194. Ab00052080_16
195. 038p402
196. Q900898
197. Q-201621
198. Sr-01000003108-2
199. Sr-01000003108-3
200. Brd-k95237249-001-05-9
201. Brd-k95237249-001-15-8
202. Z53037954
203. Probenecid, European Pharmacopoeia (ep) Reference Standard
204. Probenecid, United States Pharmacopeia (usp) Reference Standard
| Molecular Weight | 285.36 g/mol |
|---|---|
| Molecular Formula | C13H19NO4S |
| XLogP3 | 3.2 |
| Hydrogen Bond Donor Count | 1 |
| Hydrogen Bond Acceptor Count | 5 |
| Rotatable Bond Count | 7 |
| Exact Mass | 285.10347926 g/mol |
| Monoisotopic Mass | 285.10347926 g/mol |
| Topological Polar Surface Area | 83.1 Ų |
| Heavy Atom Count | 19 |
| Formal Charge | 0 |
| Complexity | 374 |
| Isotope Atom Count | 0 |
| Defined Atom Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Undefined Atom Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Defined Bond Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Undefined Bond Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Covalently Bonded Unit Count | 1 |
| 1 of 4 | |
|---|---|
| Drug Name | Probalan |
| PubMed Health | Probenecid (By mouth) |
| Drug Classes | Antigout |
| Drug Label | Probenecid is a uricosuric and renal tubular transport blocking agent.The chemical name for probenecid is 4-[(dipropylamino) sulfonyl] benzoic acid (molecular weight 285.37). It has the following structural formula:C13H19NO4SProbenecid, USP is a whit... |
| Active Ingredient | Probenecid |
| Dosage Form | Tablet |
| Route | Oral |
| Strength | 500mg |
| Market Status | Prescription |
| Company | Lannett |
| 2 of 4 | |
|---|---|
| Drug Name | Probenecid |
| Active Ingredient | Probenecid |
| Dosage Form | Tablet |
| Route | Oral |
| Strength | 500mg |
| Market Status | Prescription |
| Company | Watson Labs; Mylan |
| 3 of 4 | |
|---|---|
| Drug Name | Probalan |
| PubMed Health | Probenecid (By mouth) |
| Drug Classes | Antigout |
| Drug Label | Probenecid is a uricosuric and renal tubular transport blocking agent.The chemical name for probenecid is 4-[(dipropylamino) sulfonyl] benzoic acid (molecular weight 285.37). It has the following structural formula:C13H19NO4SProbenecid, USP is a whit... |
| Active Ingredient | Probenecid |
| Dosage Form | Tablet |
| Route | Oral |
| Strength | 500mg |
| Market Status | Prescription |
| Company | Lannett |
| 4 of 4 | |
|---|---|
| Drug Name | Probenecid |
| Active Ingredient | Probenecid |
| Dosage Form | Tablet |
| Route | Oral |
| Strength | 500mg |
| Market Status | Prescription |
| Company | Watson Labs; Mylan |
Renal Agents; Uricosuric Agents
National Library of Medicine's Medical Subject Headings online file (MeSH, 1999)
IT HAS BEEN WIDELY USED IN LAB & CLINICAL INVESTIGATION OF EXCRETION OF A NUMBER OF SUBSTANCES. ... IT IS POTENT INHIBITOR OF CERTAIN GLYCINE CONJUGASES. HOWEVER, ITS THERAPEUTIC APPLICATIONS HAVE BEEN LIMITED PRINCIPALLY TO MODIFICATION OF RENAL EXCRETION OF PENICILLIN & URIC ACID.
Goodman, L.S., and A. Gilman. (eds.) The Pharmacological Basis of Therapeutics. 5th ed. New York: Macmillan Publishing Co., Inc., 1975., p. 862
... URICOSURIC AGENT FOR TREATMENT OF GOUT & GOUTY ARTHRITIS. ... /SRP: THEORETICAL (BUT NOT PRACTICAL) USE/ AS ADJUVANT THERAPY WITH PENICILLIN G, O OR V OR WITH AMPICILLIN, METHICILLIN, OXACILLIN, CLOXACILLIN, OR NAFCILLIN, FOR ELEVATION & PROLONGATION OF PENICILLIN PLASMA LEVELS BY ... ROUTE ANTIBIOTIC IS GIVEN.
Osol, A. and J.E. Hoover, et al. (eds.). Remington's Pharmaceutical Sciences. 15th ed. Easton, Pennsylvania: Mack Publishing Co., 1975., p. 873
ITS SUPPRESSION OF RENAL CLEARANCE OF PHENOLSULFONPHTHALEIN (PHENOL RED) IS OF SIGNIFICANCE IN APPLICATION OF THAT KIDNEY EXCRETION TEST AS CLINICAL GUIDE TO EFFECTIVENESS OF PROBENECID. ... /IT/ IS WELL TOLERATED /BY MOST PATIENTS ... .
Osol, A. and J.E. Hoover, et al. (eds.). Remington's Pharmaceutical Sciences. 15th ed. Easton, Pennsylvania: Mack Publishing Co., 1975., p. 873
For more Therapeutic Uses (Complete) data for PROBENECID (12 total), please visit the HSDB record page.
SINCE ... /1955/ A SINGLE FATALITY HAS BEEN ATTRIBUTED TO HYPERSENSITIVITY TO PROBENECID. IN THIS PATIENTS, JAUNDICE, ASTHMA, SKIN RASH & EOSINOPHILIA PRECEDEDMASSIVE HEPATIC NECROSIS. PATHOLOGY RESEMBLED FEW REPORTED CASES OF HEPATIC NECROSIS FROM SULFONAMIDES.
Gosselin, R.E., R.P. Smith, H.C. Hodge. Clinical Toxicology of Commercial Products. 5th ed. Baltimore: Williams and Wilkins, 1984., p. II-405
USE OF PROBENECID & COLCHICINE IN TABLET COMBINATION (COLBENEMID) SHOULD BE AVOIDED IN TREATMENT OF INITIAL ATTACK OF GOUT, SINCE ACUTE LOWERING OF URIC ACID LEVEL MAY PERPETUATE ATTACK. RATIONALE FOR LONG TERM THERAPY ... IS QUESTIONABLE.
Miller, R. R., and D. J. Greenblatt. Handbook of Drug Therapy. New York: Elsevier North Holland, 1979., p. 482
CAUTION IS WARRANTED WHEN PROBENECID IS GIVEN TO ACHIEVE HIGHER SERUM PENICILLIN LEVELS, SINCE THE CAUSE OF SUBSEQUENT DRUG RASH WILL BE DIFFICULT TO INTERPRET.
Miller, R. R., and D. J. Greenblatt. Handbook of Drug Therapy. New York: Elsevier North Holland, 1979., p. 482
SOME DEGREE OF GI IRRITATION IS EXPERIENCED BY AT LEAST 2% OF PATIENTS; INCIDENCE IS CONSIDERABLY HIGHER AFTER LARGE DOSES. CAUTION IS ADVISED IN ADMINISTERING PROBENECID IN PATIENTS WITH HISTORY OF PEPTIC ULCER. MOST REPORTS PLACE INCIDENCE OF HYPERSENSITIVITY REACTIONS, USUALLY MILD SKIN RASHES, BETWEEN 2 & 4%.
Gilman, A.G., T.W. Rall, A.S. Nies and P. Taylor (eds.). Goodman and Gilman's The Pharmacological Basis of Therapeutics. 8th ed. New York, NY. Pergamon Press, 1990., p. 746
For more Drug Warnings (Complete) data for PROBENECID (11 total), please visit the HSDB record page.
For the reduction of serum uric acid concentrations in chronic gouty arthritis and tophaceous gout in patients with frequent disabling gout attacks. Has also been effectively used to promote uric acid excretion in hyperuricemia secondary to the administration of thiazide and related diuretics.
Probenecid is a uricosuric and renal tubular blocking agent and is used in combination with colchicine to treat chronic gouty arthritis when complicated by frequent, recurrent acute attacks of gout. It inhibits the reabsorption of urate at the proximal convoluted tubule, thus increasing the urinary excretion of uric acid and decreasing serum urate levels. Effective uricosuria reduces the miscible urate pool, retards urate deposition, and promotes resorption of urate deposits. At the proximal and distal tubles, probenecid competitively inhibits the secretion of many weak organic acids including penicillins, most cephalosporins, and some other -lactam antibiotics. This results in an increase in the plasma concentrations of acidic drugs eliminated principally by renal secretion, but only a slight increase if the drug is eliminated mainly by filtration. Thus, the drug can be used for therapeutic advantages to increase concentrations of certain -lactam antibiotics in the treatment of gonorrhea, neurosyphilis, or pelvic inflammatory disease (PID).
Uricosuric Agents
Gout suppressants that act directly on the renal tubule to increase the excretion of uric acid, thus reducing its concentrations in plasma. (See all compounds classified as Uricosuric Agents.)
Adjuvants, Pharmaceutic
Agents that aid or increase the action of the principle drug (DRUG SYNERGISM) or that affect the absorption, mechanism of action, metabolism, or excretion of the primary drug (PHARMACOKINETICS) in such a way as to enhance its effects. (See all compounds classified as Adjuvants, Pharmaceutic.)
M - Musculo-skeletal system
M04 - Antigout preparations
M04A - Antigout preparations
M04AB - Preparations increasing uric acid excretion
M04AB01 - Probenecid
Route of Elimination
Excreted principally in the urine as monoacyl glucuronide and unchanged drug. Alkalinization of urine increases renal probenecid excretion.
PROBENECID IS COMPLETELY ABSORBED AFTER ORAL ADMIN. PEAK PLASMA CONCN ARE REACHED IN 2-4 HR. THE HALF-LIFE OF THE DRUG IN PLASMA IS DOSE DEPENDENT AND VARIES FROM LESS THAN 5 HR TO MORE THAN 8 HR.
Gilman, A.G., T.W. Rall, A.S. Nies and P. Taylor (eds.). Goodman and Gilman's The Pharmacological Basis of Therapeutics. 8th ed. New York, NY. Pergamon Press, 1990., p. 746
BETWEEN 85 & 95% OF DRUG IS BOUND TO PLASMA ALBUMIN, LARGELY TO ALBUMIN. SMALL UNBOUND PORTION GAINS ACCESS TO GLOMERULAR FILTRATE; A MUCH LARGER PORTION IS ACTIVELY SECRETED BY PROXIMAL TUBULE.
Gilman, A.G., T.W. Rall, A.S. Nies and P. Taylor (eds.). Goodman and Gilman's The Pharmacological Basis of Therapeutics. 8th ed. New York, NY. Pergamon Press, 1990., p. 746
IN SPITE OF ITS LOW PKA (3.4), HIGH LIPID SOLUBILITY OF UNDISSOCIATED FORM RESULTS IN VIRTUALLY COMPLETE ABSORPTION BY BACK DIFFUSION UNLESS URINE IS MARKEDLY ALKALINE. SMALL AMOUNT OF PROBENECID GLUCURONIDE APPEARS IN URINE.
Gilman, A.G., T.W. Rall, A.S. Nies and P. Taylor (eds.). Goodman and Gilman's The Pharmacological Basis of Therapeutics. 8th ed. New York, NY. Pergamon Press, 1990., p. 746
... /ORG ACID CMPD SUCH AS PROBENECID /ARE/ NOT TAKEN UP SO AVIDLY BY /PARENCHYMATOUS OR RETICULO-ENDOTHELIAL TISSUES/ & EXHIBIT HIGHER PLASMA CONCN ... .
LaDu, B.N., H.G. Mandel, and E.L. Way. Fundamentals of Drug Metabolism and Disposition. Baltimore: Williams and Wilkins, 1971., p. 372
For more Absorption, Distribution and Excretion (Complete) data for PROBENECID (8 total), please visit the HSDB record page.
YIELDS P-DIPROPYLSULFAMOYLBENZOYL-BETA-D-GLUCURONIC ACID; P-(2-HYDROXYPROPYL N-PROPYLSULFAMOYL) BENZOIC ACID; P-(3-HYDROXYPROPYL N-PROPYLSULFAMOYL) BENZOIC ACID; & P-PROPYLSULFAMOYLBENZOIC ACID IN MAN. /FROM TABLE/
Goodwin, B.L. Handbook of Intermediary Metabolism of Aromatic Compounds. New York: Wiley, 1976., p. D-100
STRUCTURES OF ALL OF METAB OF PROBENECID IN RAT BILE & HUMAN URINE HAVE BEEN ELUCIDATED. PROPIONIC ACID HAS NOW BEEN IDENTIFIED AS ANOTHER PROBENECID METAB. MAJOR METABOLIC PATHWAYS INVOLVE SIDE-CHAIN OXIDATION & GLUCURONIDE CONJUGATION ... .
The Chemical Society. Foreign Compound Metabolism in Mammals Volume 3. London: The Chemical Society, 1975., p. 288
... BETA-GLUCURONIDES OF 2- & 3-HYDROXYLATED METAB & ACYL GLUCURONIDE OF PROBENECID PER SE HAVE NOW BEEN IDENTIFIED. ... THERE IS CONSIDERABLE SPECIES DIFFERENCE IN METABOLISM. IN RATS & MONKEYS OXIDATION IS FAVORED. ... IN DOGS CONJUGATION ... /IS/ MAJOR PATHWAY, WHEREAS IN MAN, OXIDATIVE ... PATHWAY ... IS AS IMPORTANT AS GLUCURONIDATION.
The Chemical Society. Foreign Compound Metabolism in Mammals Volume 3. London: The Chemical Society, 1975., p. 288
CHRONIC ADMIN OF DRUGS NOT ONLY STIMULATES METAB OF OTHER CMPD, BUT IN SOME INSTANCES PHARMACOLOGICAL OR TOXIC EFFECT OF A DRUG WHEN GIVEN CHRONICALLY, DIMINISHES, BECAUSE IT STIMULATES ITS OWN METABOLISM EXAMPLE OF DRUG THAT EXERT THIS EFFECT IN DOGS ... /IS/ ... PROBENECID ... .
LaDu, B.N., H.G. Mandel, and E.L. Way. Fundamentals of Drug Metabolism and Disposition. Baltimore: Williams and Wilkins, 1971., p. 258
For more Metabolism/Metabolites (Complete) data for PROBENECID (6 total), please visit the HSDB record page.
6-12 hours
THE HALF-LIFE OF /PROBENECID/ IN PLASMA IS DOSE DEPENDENT AND VARIES FROM LESS THAN 5 HR TO MORE THAN 8 HR ... .
Gilman, A.G., T.W. Rall, A.S. Nies and P. Taylor (eds.). Goodman and Gilman's The Pharmacological Basis of Therapeutics. 8th ed. New York, NY. Pergamon Press, 1990., p. 746
Following oral administration of 2 g of probenecid, plasma half-life of the drug ranges from 4-17 hr; the half-life decreases as the dose decreases from 2 g to 500 mg.
McEvoy, G.K. (ed.). American Hospital Formulary Service - Drug Information 93. Bethesda, MD: American Society of Hospital Pharmacists, Inc., 1993 (Plus Supplements, 1993)., p. 1652
Probenecid inhibits the tubular reabsorption of urate, thus increasing the urinary excretion of uric acid and decreasing serum urate levels. Probenecid may also reduce plasma binding of urate and inhibit renal secretion of uric acid at subtherapeutic concentrations. The mechanism by which probenecid inhibits renal tubular transport is not known, but the drug may inhibit transport enzymes that require a source of high energy phosphate bonds and/or nonspecifically interfere with substrate access to protein receptor sites on the kidney tubules.
IN HIGHER DOSES THAN ARE REQUIRED FOR URICOSURIC EFFECT, PROBENECID ALSO INHIBITS TRANSPORT OF ORG ACIDS AT OTHER SITES, IE, TRANSPORT SYSTEM THAT REMOVES ORG ACIDS FROM CEREBROSPINAL FLUID.
Goodman, L.S., and A. Gilman. (eds.) The Pharmacological Basis of Therapeutics. 5th ed. New York: Macmillan Publishing Co., Inc., 1975., p. 862
IT INHIBITS TUBULAR REABSORPTION OF URATE, THUS INCR URINARY EXCRETION OF URIC ACID & DECR SERUM URIC ACID LEVELS.
Osol, A. and J.E. Hoover, et al. (eds.). Remington's Pharmaceutical Sciences. 15th ed. Easton, Pennsylvania: Mack Publishing Co., 1975., p. 873
Probenecid is a renal tubular blocking agent. The drug competitively inhibits active reabsorption of uric acid at the proximal convoluted tubule, thus promoting urinary excretion of uric acid and reducing serum urate concentrations. Probenecid may reduce plasma protein binding of urate and, in subtherapeutic doses, may inhibit renal secretion of uric acid. In healthy individuals, probenecid has no effect on the glomerular filtration rate or on the tubular reabsorption of normal urinary constituents such as glucose, arginine, urea, sodium, potassium, chloride, or phosphate.
McEvoy, G.K. (ed.). American Hospital Formulary Service - Drug Information 93. Bethesda, MD: American Society of Hospital Pharmacists, Inc., 1993 (Plus Supplements, 1993)., p. 1651
At the proximal and distal tubules, probenecid competitively inhibits the secretion of many weak organic acids including penicillins, most cephalosporins, and some other beta-lactam antibiotics. In general, the net effect of probenecid on the plasma concentration of weak acids depends on the ratio of the amount of organic acid secreted by the kidneys to that amount filtered at the glomeruli. Thus, probenecid substantially increases plasma concentrations of acidic drugs eliminated principally by renal secretion, but increases plasma concentrations only slightly if the drug is eliminated mainly by filtration. Plasma concentrations of penicillins are often more than doubled by probenecid; the concentration of penicillin in the CSF is also increased. Probenecid also substantially increases plasma concentrations of most cephalosporins and some other beta-lactam antibiotics. In addition, half-lives of the penicillins and cephalosporins are prolonged and their volumes of distribution may be reduced by probenecid. ... The cellular mechanism(s) responsible for the inhibition of renal tubular transport by probenecid is not known. The drug may inhibit transport enzymes that require a source of high energy phosphate bonds and/or nonspecifically interfere with substrate access to protein receptor sites on the kidney tubules.
McEvoy, G.K. (ed.). American Hospital Formulary Service - Drug Information 93. Bethesda, MD: American Society of Hospital Pharmacists, Inc., 1993 (Plus Supplements, 1993)., p. 1652
CSF concentrations of 5-hydroxyindoleacetic acid, homovanillic acid, cyclic adenosine monophosphate, and 4-hydroxy-3-methoxyphenylglycol are elevated following administration of probenecid. It has been proposed that probenecid blocks the active transport of these organic acids from the CSF into blood. Probenecid-induced elevations of homovanillic acid (a dopamine metabolite) in the CSF of patients with parkinsonian syndrome and of 5-hydroxyindoleacetic acid(a metabolite of serotonin) in the CSF of mentally depressed patients are substantially lower than those in healthy patients.
McEvoy, G.K. (ed.). American Hospital Formulary Service - Drug Information 93. Bethesda, MD: American Society of Hospital Pharmacists, Inc., 1993 (Plus Supplements, 1993)., p. 1652