

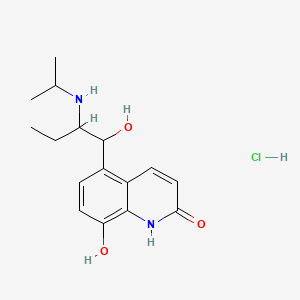

1. (r*,s*)-(+-)-8-hydroxy-5-(1-hydroxy-2-((1-methylethyl)amino)butyl)-2(1h)-quinolinone
2. Ci 888
3. Ci-888
4. Ci888
5. Hydrochloride, Procaterol
6. Monohydrochloride, Procaterol
7. Opc 2009
8. Opc-2009
9. Opc2009
10. Pro Air
11. Pro-air
12. Proair
13. Procaterol
14. Procaterol Monohydrochloride
15. Procaterol Monohydrochloride, (r*,r*)-(+)-isomer
16. Procaterol Monohydrochloride, (r*,r*)-(+-)-isomer
17. Procaterol Monohydrochloride, (r*,r*)-(-)-isomer
18. Procaterol Monohydrochloride, (r*,s*)-(+)-isomer
19. Procaterol Monohydrochloride, (r*,s*)-(-)-isomer
20. Procaterol, (r*,r*)-(+-)-isomer
21. Procaterol, (r*,s*)-(-)-isomer
1. Procaterol Hcl
2. Chebi:32056
3. 62929-91-3
4. 81262-93-3
5. Opc-2009
6. Procaterol Hydrochloride (usan)
7. Ci-888
8. 59828-07-8
9. Pro-air (tn)
10. Mls000028683
11. Schembl124726
12. Chembl1322218
13. Ccg-39328
14. Akos015967634
15. Ac-4219
16. Smr000058864
17. Db-054335
18. Ft-0630735
19. Ft-0630887
20. D02404
21. Q27114767
22. 5-(1-hydroxy-2-isopropylaminobutyl)-8-hydroxycarbostyril Hydrochloride
23. 8-hydroxy-5-(1-hydroxy-2-(isopropylamino)butyl)quinolin-2(1h)-one Hydrochloride
| Molecular Weight | 326.82 g/mol |
|---|---|
| Molecular Formula | C16H23ClN2O3 |
| Hydrogen Bond Donor Count | 5 |
| Hydrogen Bond Acceptor Count | 4 |
| Rotatable Bond Count | 5 |
| Exact Mass | 326.1397203 g/mol |
| Monoisotopic Mass | 326.1397203 g/mol |
| Topological Polar Surface Area | 81.6 Ų |
| Heavy Atom Count | 22 |
| Formal Charge | 0 |
| Complexity | 397 |
| Isotope Atom Count | 0 |
| Defined Atom Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Undefined Atom Stereocenter Count | 2 |
| Defined Bond Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Undefined Bond Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Covalently Bonded Unit Count | 2 |
Adrenergic beta-2 Receptor Agonists
Compounds bind to and activate ADRENERGIC BETA-2 RECEPTORS. (See all compounds classified as Adrenergic beta-2 Receptor Agonists.)
Bronchodilator Agents
Agents that cause an increase in the expansion of a bronchus or bronchial tubes. (See all compounds classified as Bronchodilator Agents.)
Sympathomimetics
Drugs that mimic the effects of stimulating postganglionic adrenergic sympathetic nerves. Included here are drugs that directly stimulate adrenergic receptors and drugs that act indirectly by provoking the release of adrenergic transmitters. (See all compounds classified as Sympathomimetics.)