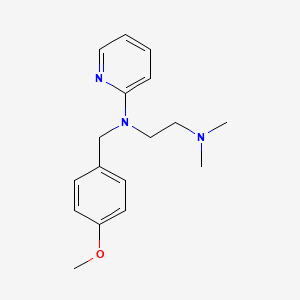

1. Anthisan
2. Boots Bite And Sting Relief
3. Kriptin
4. Maleate, Mepyramine
5. Maleate, Pyrilamine
6. Mepyramine Maleate
7. Pyranisamine
8. Pyrilamine
9. Pyrilamine Maleate
1. Pyrilamine
2. 91-84-9
3. Pyranisamine
4. Anthisan
5. Dorantamin
6. Mepiramine
7. Kriptin
8. Antalergan
9. Antallergan
10. Histapyran
11. Neoantergan
12. Anhistabs
13. Anhistol
14. Antamine
15. Copsamine
16. Coradon
17. Harvamine
18. Histacap
19. Histalon
20. Histasan
21. Maranhist
22. Mepyren
23. Nyscaps
24. Paraminyl
25. Pyramal
26. Stangen
27. Statomin
28. Thylogen
29. Dipane
30. Isamin
31. Parmal
32. Neo-bridal
33. Afko-hist
34. Mepyramin
35. Stamine
36. Pyra
37. Wait's Green Mountain Antihistamine
38. Pyrilamide
39. Rp 2786
40. Nci-c60651
41. N',n'-dimethyl-n-(p-methoxybenzyl)-n-(2-pyridyl)ethylenediamine
42. 1,2-ethanediamine, N-((4-methoxyphenyl)methyl)-n',n'-dimethyl-n-2-pyridinyl-
43. Nsc13136
44. Nsc-13136
45. Chembl511
46. Hpe317o9tl
47. N1-(4-methoxybenzyl)-n2,n2-dimethyl-n1-(pyridin-2-yl)ethane-1,2-diamine
48. Chebi:6762
49. 2-((p-methoxybenzyl)(2-(dimethylamino)ethyl)amino)pyridine
50. Pyridine, 2-((p-methoxybenzyl)(2-(dimethylamino)ethyl)amino)-
51. N-(p-methoxybenzyl)-n',n'-dimethyl-n-2-pyridyl-1,2-ethanediamine
52. Mepyramine (inn)
53. [3h]mepyramine
54. [3h]pyrilamine
55. 102206-59-7
56. Ncgc00015822-09
57. 2-((2-(dimethylamino)ethyl)-(p-methoxybenzyl)amino)pyridine
58. Pyridine, 2-((2-(dimethylamino)ethyl)(p-methoxybenzyl)amino)-
59. Mepyramine [inn]
60. Dsstox_cid_3542
61. N-[2-(dimethylamino)ethyl]-n-[(4-methoxyphenyl)methyl]pyridin-2-amine
62. 1,2-ethanediamine, N-[(4-methoxyphenyl)methyl]-n',n'-dimethyl-n-2-pyridinyl-
63. N-((4-methoxyphenyl)methyl)-n',n'-dimethyl-n-2-pyridinyl-1,2-ethanediamine
64. Dsstox_rid_77071
65. Dsstox_gsid_23542
66. Mepyramin [german]
67. P-methoxy-benzyl-.alpha.-pyridyl-dimethyl-aethylendiamin
68. 2-[[2-(dimethylamino)ethyl](p-methoxybenzyl)amino]pyridine
69. Mepiramina
70. Mepyraminum
71. Mepyramine [inn:ban]
72. Pyridine, 2-[[2-(dimethylamino)ethyl](p-methoxybenzyl)amino]-
73. N-(4-methoxybenzyl)-n',n'-dimethyl-n-pyridin-2-ylethane-1,2-diamine
74. N-(p-methoxybenzyl)-n',n'-dimethyl-n-(.alpha.-pyridyl)ethylenediamine
75. N-(p-methoxybenzyl)-n',n'-dimethyl-n-(alpha-pyridyl)ethylenediamine
76. Mepyraminum [inn-latin]
77. Mepiramina [inn-spanish]
78. N-[(4-methoxyphenyl)methyl]-n',n'-dimethyl-n-2-pyridinyl-1,2-ethanediamine
79. Cas-91-84-9
80. [11c]pyrilamine
81. [11c]-pyrilamine
82. [11c]-mepyramine
83. Ccris 4865
84. Hsdb 5187
85. Cas-59-33-6
86. Einecs 202-102-2
87. Nsc 13136
88. Unii-hpe317o9tl
89. Brn 0269019
90. 2-[(p-methoxybenzyl)[2-(dimethylamino)ethyl]amino]pyridine
91. Pyriliamine
92. Neobridal
93. 2-[[2-(dimethylamino)ethyl]-(p-methoxybenzyl)amino]pyridine
94. Pyridine, 2-[(p-methoxybenzyl)[2-(dimethylamino)ethyl]amino]-
95. Pyrlex
96. 2-((2-(dimethylamino)ethyl)(p-methoxybenzyl)amino)pyridine
97. 3h]pyrilamine
98. N,n-dimethyl-n'-{[4-(methyloxy)phenyl]methyl}-n'-pyridin-2-ylethane-1,2-diamine
99. N-[(4-methoxyphenyl)methyl]-n',n'-dimethyl-n-pyridin-2-ylethane-1,2-diamine
100. Histan (salt/mix)
101. Pymafed (salt/mix)
102. Antihist (salt/mix)
103. Minihist (salt/mix)
104. Spectrum_000904
105. Tocris-0660
106. Prefrin A (salt/mix)
107. Pyrilamine [mi]
108. N-(p-methoxybenzyl)-n',n'-dimethyl-n-2-pyridylethylenediamine
109. N-p-methoxybenzyl-n',n'-dimethyl-n-alpha-pyridylethylenediamine
110. P-methoxybenzyl-alpha-pyridyl-dimethyl-aethylendiamin [german]
111. N-(para-methoxybenzyl)-n',n'-dimethyl-n-2-pyridylethylenediamine
112. N-para-methoxybenzyl-n',n'-dimethyl-n-alpha-pyridylethylenediamine
113. Prestwick0_000289
114. Prestwick1_000289
115. Prestwick2_000289
116. Prestwick3_000289
117. Spectrum2_001306
118. Spectrum3_000605
119. Spectrum4_000493
120. Spectrum5_001264
121. Lopac-p-5514
122. Mepyramine [hsdb]
123. Pyrilamine [vandf]
124. Mepyramine [mart.]
125. Mepyramine [who-dd]
126. Lopac0_000890
127. Oprea1_317349
128. Schembl19114
129. Bspbio_000198
130. Bspbio_002110
131. Kbiogr_001005
132. Kbioss_001384
133. 5-22-08-00381 (beilstein Handbook Reference)
134. Bidd:gt0215
135. Divk1c_000175
136. P-methoxybenzyl-alpha-pyridyl-dimethyl-aethylendiamin
137. Spbio_001371
138. Spbio_002417
139. Bpbio1_000218
140. Ccris 1330 (salt/mix)
141. Gtpl1227
142. Gtpl3957
143. 2-[(2-dimethylaminoethyl)(p-methoxybenzyl)amino]pyridine
144. Dtxsid9023542
145. Bdbm22567
146. Kbio1_000175
147. Kbio2_001384
148. Kbio2_003952
149. Kbio2_006520
150. Kbio3_001610
151. Ninds_000175
152. Hms2089m19
153. Tox21_110230
154. Tox21_200978
155. Zinc19144216
156. N'-[(4-methoxyphenyl)methyl]-n,n-dimethyl-n'-pyridin-2-ylethane-1,2-diamine
157. Tox21_110230_1
158. Ccg-204972
159. Db06691
160. R.d. 2786
161. Sdccgsbi-0050865.p005
162. Idi1_000175
163. Wln: T6nj Bn2n1&1&1r Do1
164. Wln: T6nj Dn1r Do1&2n1&1
165. N-(p-methoxybenzyl)-n',2-ethanediamine
166. Ncgc00015822-01
167. Ncgc00015822-02
168. Ncgc00015822-03
169. Ncgc00015822-04
170. Ncgc00015822-05
171. Ncgc00015822-06
172. Ncgc00015822-07
173. Ncgc00015822-08
174. Ncgc00015822-10
175. Ncgc00015822-11
176. Ncgc00015822-12
177. Ncgc00015822-13
178. Ncgc00015822-15
179. Ncgc00015822-17
180. Ncgc00015822-21
181. Ncgc00023513-02
182. Ncgc00023513-04
183. Ncgc00023513-05
184. Ncgc00023513-06
185. Ncgc00258531-01
186. Sbi-0050865.p004
187. Ab00053539
188. Ft-0628211
189. D08183
190. Ab00053539-19
191. Ab00053539_20
192. Ab00053539_21
193. L000391
194. Q3800087
195. Brd-k97564742-050-04-6
196. Brd-k97564742-050-05-3
197. Brd-k97564742-103-01-9
198. 1, N-[(4-methoxyphenyl)methyl]-n',n'-dimethyl-n-2-pyridinyl-
199. Ethylenediamine, N',n'-dimethyl-n-(p-methoxybenzyl)-n-(2-pyridyl)-
200. Ethylenediamine,n'-dimethyl-n-(p-methoxybenzyl)-n-(2-pyridyl)-
201. N,n-dimethyl-n'-(4-methoxybenzyl)-n'-(2-pyridyl)ethylenediamine
202. N,n-dimethyl-n'-(p-methoxybenzyl)-n'-(2 -pyridyl)ethylenediamine
203. N-(p-methoxybenzyl)-n',n'-dimethyl-n-2-(pyridylethylene)diamine
204. N-p-methoxybenzyl-n',n'-dimethyl-n-.alpha.-pyridylethylenediamine
205. Pyridine, 2-[[2-(dimethylamino)ethyl][p-methoxybenzyl)amino]]-
206. N,n-dimethyl-n'-(4-methoxybenzyl)-n'-(.alpha.-pyridyl)-ethylenediaminene
207. N-(4-methoxybenzyl)-n ,n -dimethyl-n-pyridin-2-ylethane-1,2-diamine
208. N-dimethylamino-aethyl-n-p-methoxy-benzyl-.alpha.-amino-pyridin-maleat
209. 1,2-ethanediamine, N-[(4-methoxyphenyl)methyl]-n',n'-dimethyl-n-2-pyridyl-
| Molecular Weight | 285.4 g/mol |
|---|---|
| Molecular Formula | C17H23N3O |
| XLogP3 | 3.3 |
| Hydrogen Bond Donor Count | 0 |
| Hydrogen Bond Acceptor Count | 4 |
| Rotatable Bond Count | 7 |
| Exact Mass | 285.184112366 g/mol |
| Monoisotopic Mass | 285.184112366 g/mol |
| Topological Polar Surface Area | 28.6 Ų |
| Heavy Atom Count | 21 |
| Formal Charge | 0 |
| Complexity | 277 |
| Isotope Atom Count | 0 |
| Defined Atom Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Undefined Atom Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Defined Bond Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Undefined Bond Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Covalently Bonded Unit Count | 1 |
Anti-Allergic Agents; Histamine H1 Antagonists
National Library of Medicine's Medical Subject Headings online file (MeSH, 1999)
Antihistamines are indicated in the prophylactic and symptomatic treatment of perennial and seasonal allergic rhinitis, vasomotor rhinitis, and allergic conjunctivitis due to inhalant allergens and foods. /Antihistamines; Included in US product labeling/
USP Convention. USPDI - Drug Information for the Health Care Professional. 15 th ed. Volume 1. Rockville, MD: United States Pharmacopeial Convention, Inc., 1995. (Plus updates.), p. 303
Antihistamines are indicated for the symptomatic treatment of pruritus associated with allergic reactions and of mild, uncomplicated allergic skin manifestations of urticaria and angioedema, in dermatographism, and in urticaria associated with transfusions. /Antihistamines; Included in US product labeling/
USP Convention. USPDI - Drug Information for the Health Care Professional. 15 th ed. Volume 1. Rockville, MD: United States Pharmacopeial Convention, Inc., 1995. (Plus updates.), p. 303
Antihistamines are also used in the treatment of pruritus associated with pityriasis rosea. /Antihistamines; NOT included in US product labeling/
USP Convention. USPDI - Drug Information for the Health Care Professional. 15 th ed. Volume 1. Rockville, MD: United States Pharmacopeial Convention, Inc., 1995. (Plus updates.), p. 303
For more Therapeutic Uses (Complete) data for PYRILAMINE (11 total), please visit the HSDB record page.
Use is not recommended in newborn or premature infants because this age group has an increased susceptibility to anticholinergic side effects, such as central nervous system excitation, and an increased tendency toward convulsions. A paradoxical reaction characterized by hyperexcitability may occur in children taking antihistamines. /Antihistamines/
USP Convention. USPDI - Drug Information for the Health Care Professional. 15 th ed. Volume 1. Rockville, MD: United States Pharmacopeial Convention, Inc., 1995. (Plus updates.), p. 306
Dizziness, sedation, confusion, and hypotension may be more likely to occur in geriatric patients taking antihistamines. Geriatric patients are especially susceptible to the anticholinergic side effects, such as dryness of mouth and urinary retention (especially in males), of the antihistamines. If these side effects occur and continue or are severe, medication should probably be discontinued. /Antihistamines/
USP Convention. USPDI - Drug Information for the Health Care Professional. 15 th ed. Volume 1. Rockville, MD: United States Pharmacopeial Convention, Inc., 1995. (Plus updates.), p. 306
Prolonged use of antihistamines ... may decrease or inhibit salivary flow, thus contributing to the development of caries, periodontal disease, oral candidiasis, and discomfort. /Antihistamines/
USP Convention. USPDI - Drug Information for the Health Care Professional. 15 th ed. Volume 1. Rockville, MD: United States Pharmacopeial Convention, Inc., 1995. (Plus updates.), p. 306
H1 antagonists are most useful in acute exudative types of allergy that present with symptoms of rhinitis, urticaria, and conjunctivitis. Their effect, however, is purely palliative and confined to the suppression of symptoms attributable to the histamine-antibody reaction. The drugs do not diminish the intensity of this reaction, which is the cause of the various hypersensitivity diseases. /Histamine Antagonist: H1 Antagonists/
Gilman, A.G., T.W. Rall, A.S. Nies and P. Taylor (eds.). Goodman and Gilman's The Pharmacological Basis of Therapeutics. 8th ed. New York, NY. Pergamon Press, 1990., p. 587
For more Drug Warnings (Complete) data for PYRILAMINE (11 total), please visit the HSDB record page.
5. 5= EXTREMELY TOXIC: PROBABLE ORAL LETHAL DOSE (HUMAN) 5-50 MG/KG, BETWEEN 7 DROPS AND 1 TEASPOONFUL FOR A 70 KG (150 LB) PERSON. /MALEATE/
Gosselin, R.E., R.P. Smith, H.C. Hodge. Clinical Toxicology of Commercial Products. 5th ed. Baltimore: Williams and Wilkins, 1984., p. II-380
Indicated for the treatment of allergic conditions, symptomatic relief of hypersensitivity reaction, and treatment of pruritic skin disorders.
Sleep Aids, Pharmaceutical
Drugs used to induce SLEEP, prevent SLEEPLESSNESS, or treat SLEEP INITIATION AND MAINTENANCE DISORDERS. (See all compounds classified as Sleep Aids, Pharmaceutical.)
Anti-Allergic Agents
Agents that are used to treat allergic reactions. Most of these drugs act by preventing the release of inflammatory mediators or inhibiting the actions of released mediators on their target cells. (From AMA Drug Evaluations Annual, 1994, p475) (See all compounds classified as Anti-Allergic Agents.)
Histamine H1 Antagonists
Drugs that selectively bind to but do not activate histamine H1 receptors, thereby blocking the actions of endogenous histamine. Included here are the classical antihistaminics that antagonize or prevent the action of histamine mainly in immediate hypersensitivity. They act in the bronchi, capillaries, and some other smooth muscles, and are used to prevent or allay motion sickness, seasonal rhinitis, and allergic dermatitis and to induce somnolence. The effects of blocking central nervous system H1 receptors are not as well understood. (See all compounds classified as Histamine H1 Antagonists.)
D - Dermatologicals
D04 - Antipruritics, incl. antihistamines, anesthetics, etc.
D04A - Antipruritics, incl. antihistamines, anesthetics, etc.
D04AA - Antihistamines for topical use
D04AA02 - Mepyramine
R - Respiratory system
R06 - Antihistamines for systemic use
R06A - Antihistamines for systemic use
R06AC - Substituted ethylene diamines
R06AC01 - Mepyramine
The H1 antagonists are well absorbed from the gi tract. Following oral administration, peak plasma concn are achieved in 2 to 3 hr and effects usually last 4 to 6 hr; however, some of the drugs are much longer acting ... . /Histamine Antagonists: H1 Antagonists/
Gilman, A.G., T.W. Rall, A.S. Nies and P. Taylor (eds.). Goodman and Gilman's The Pharmacological Basis of Therapeutics. 8th ed. New York, NY. Pergamon Press, 1990., p. 584
... H1 antagonists are eliminated more rapidly by children than by adults and more slowly in those with severe liver disease. /Histamine Antagonists: H1 Antagonists/
Gilman, A.G., T.W. Rall, A.S. Nies and P. Taylor (eds.). Goodman and Gilman's The Pharmacological Basis of Therapeutics. 8th ed. New York, NY. Pergamon Press, 1990., p. 584
MAIN SITE OF METABOLIC TRANSFORMATION IS LIVER. /ANTIHISTAMINES/
Goodman, L.S., and A. Gilman. (eds.) The Pharmacological Basis of Therapeutics. 5th ed. New York: Macmillan Publishing Co., Inc., 1975., p. 607
H1 blockers are among the many drugs that induce hepatic microsomal enzymes, and they may facilitate their own metabolism. /Histamine Antagonists: H1 Antagonists/
Gilman, A.G., T.W. Rall, A.S. Nies and P. Taylor (eds.). Goodman and Gilman's The Pharmacological Basis of Therapeutics. 8th ed. New York, NY. Pergamon Press, 1990., p. 584
Mepyramine is a histamine H1 receptor inverse agonist. It binds to a G protein-coupled form of the receptor and promotes a G protein-coupled inactive state of the H1 receptor that interferes with the Gq/11-mediated signaling. Mepyramine competes with histamine for binding at H1-receptor sites on the effector cell surface, resulting in suppression of histaminic edema, flare, and pruritus. The sedative properties of Mepyramine occur at the subcortical level of the CNS.
Antihistamines used in the treatment of allergy act by competing with histamine for H1-receptor sites on effector cells. They thereby prevent, but do not reverse, responses mediated by histamine alone. Antihistamines antagonize, in varying degrees, most of the pharmacological effects of histamine, including urticaria and pruritus. Also, the anticholinergic actions of most antihistamines provide a drying effect on the nasal mucosa. /Antihistamines/
USP Convention. USPDI - Drug Information for the Health Care Professional. 15 th ed. Volume 1. Rockville, MD: United States Pharmacopeial Convention, Inc., 1995. (Plus updates.), p. 304
H1 antagonists inhibit most responses of smooth muscle to histamine. Antagonism of the constrictor action of histamine on respiratory smooth muscle is easily shown in vivo and in vitro. /Histamine Antagonists: H1 Antagonists/
Gilman, A.G., T.W. Rall, A.S. Nies and P. Taylor (eds.). Goodman and Gilman's The Pharmacological Basis of Therapeutics. 8th ed. New York, NY. Pergamon Press, 1990., p. 582
H1 antagonists strongly block the action of histamine that results in increased permeability and formation of edema and wheal. /Histamine Antagonists: H1 Antagonists/
Gilman, A.G., T.W. Rall, A.S. Nies and P. Taylor (eds.). Goodman and Gilman's The Pharmacological Basis of Therapeutics. 8th ed. New York, NY. Pergamon Press, 1990., p. 583
Some H1 antagonists possess local anesthetic activity ... . /Histamine Antagonists: H1 Antagonists/
Gilman, A.G., T.W. Rall, A.S. Nies and P. Taylor (eds.). Goodman and Gilman's The Pharmacological Basis of Therapeutics. 8th ed. New York, NY. Pergamon Press, 1990., p. 584
For more Mechanism of Action (Complete) data for PYRILAMINE (6 total), please visit the HSDB record page.