


1. Estrovis
2. Ethinyl Estradiol 3 Cyclopentyl Ether
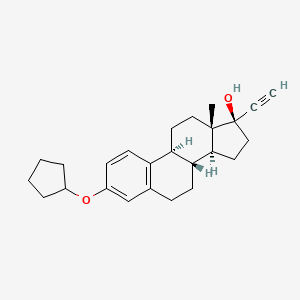
3. Ethinyl Estradiol 3-cyclopentyl Ether
1. 152-43-2
2. Estrovis
3. Estradiol-17-beta 3-cyclopentyl Ether
4. Quinestrolo [dcit]
5. Quinestrolum
6. Quinestrolum [inn-latin]
7. Estrovister
8. Plestrovis
9. Eston
10. 17-alpha-ethinylestradiol 3-cyclopentyl Ether
11. 17alpha-ethynylestradiol 3-cyclopentyl Ether
12. Qui-lea
13. Eecpe
14. Estrovis 4000
15. W 3566
16. W-3566
17. (8r,9s,13s,14s,17r)-3-cyclopentyloxy-17-ethynyl-13-methyl-7,8,9,11,12,14,15,16-octahydro-6h-cyclopenta[a]phenanthren-17-ol
18. Jr0n7xd5gz
19. Mls000069756
20. Chebi:8716
21. Nsc-759637
22. Ncgc00166146-01
23. Quinestrolo
24. Smr000058815
25. Dsstox_cid_26553
26. Dsstox_rid_81714
27. Dsstox_gsid_46553
28. Quilea
29. 3-o-cyclopentyl-17alpha-ethinyl-estra-1,3,5(10)-triene-3,17beta-diol
30. 17alpha-ethylnyl-1,3,5[10]estratriene-3,17beta-diol 3-cyclopentyl Ether
31. Estrovis (tn)
32. Cas-152-43-2
33. Quinestrol (usan/inn)
34. Einecs 205-803-1
35. Unii-jr0n7xd5gz
36. Quinestriol
37. 3-cyclopentyloxy-17alpha-ethynylestra-1,3,5(10)-trien-17beta-ol
38. Quinestrol [usan:usp:inn:ban]
39. 3-(cyclopentyloxy)-19-nor-17alpha-pregna-1,3,5(10)-trien-20-yn-17-ol
40. Ee2cpe
41. Opera_id_502
42. Quinestrol [mi]
43. Quinestrol [inn]
44. Quinestrol [usan]
45. Quinestrol [vandf]
46. Quinestrol [mart.]
47. Quinestrol [who-dd]
48. Mls001077287
49. Schembl221134
50. Gtpl7097
51. Chembl1201165
52. Dtxsid6046553
53. Quinestrol [orange Book]
54. Hms2235a05
55. 3-(cyclopentyloxy)-17beta-ethynylestra-1,3,5(10)-trien-17-ol
56. Hy-b1012
57. Zinc3875993
58. Ethinylestradiol 3-cyclopentyl Ether
59. Tox21_112340
60. Lmst02010037
61. Mfcd00079189
62. S3671
63. Ethynyl Estradiol-3-cyclopentyl Ether
64. 19-nor-17-alpha-pregna-1,3,5(10)-trien-20-yn-17-ol, 3-(cyclopentyloxy)-
65. Akos025310158
66. Tox21_112340_1
67. Ccg-268221
68. Cs-4525
69. Db04575
70. Nsc 759637
71. 19-norpregna-1,3,5(10)-trien-20-yn-17-ol, 3-(cyclopentyloxy)-, (17alpha)-
72. Ncgc00166146-02
73. 17?-ethynylestradiol 3-cyclopentyl Ether
74. As-13038
75. Q0091
76. C07619
77. C72888
78. D00576
79. 152q432
80. A809306
81. Sr-01000759180
82. Q3927871
83. Sr-01000759180-3
84. W-108053
85. 17a-ethynyl-1,3,5(10)-estratriene-3,17b-diol 3-cyclopentyl Ether
86. 3-(cyclopentyloxy)-19-norpregna-1,3,5(10)-trien-20-yn-17.alpha.-ol
87. Estra-1(10),2,4-trien-17-ol, 3-(cyclopentyloxy)-17-ethynyl-, (17)-
88. 19-norpregna-1,3,5(10)-trien-20-yn-17-ol, 3-(cyclopentyloxy)-, 17.alpha.
89. 3-(cyclopentyloxy)-19-nor-17.alpha.-pregna-1,3,5(10)-trien-20-yn-17-ol
90. (1s,10r,11s,14r,15s)-5-(cyclopentyloxy)-14-ethynyl-15-methyltetracyclo[8.7.0.0?,?.0??,??]heptadeca-2,4,6-trien-14-ol
| Molecular Weight | 364.5 g/mol |
|---|---|
| Molecular Formula | C25H32O2 |
| XLogP3 | 5.3 |
| Hydrogen Bond Donor Count | 1 |
| Hydrogen Bond Acceptor Count | 2 |
| Rotatable Bond Count | 3 |
| Exact Mass | 364.240230259 g/mol |
| Monoisotopic Mass | 364.240230259 g/mol |
| Topological Polar Surface Area | 29.5 Ų |
| Heavy Atom Count | 27 |
| Formal Charge | 0 |
| Complexity | 613 |
| Isotope Atom Count | 0 |
| Defined Atom Stereocenter Count | 5 |
| Undefined Atom Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Defined Bond Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Undefined Bond Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Covalently Bonded Unit Count | 1 |
Used in hormone replacement therapy, treating symptoms of menopause such as hot flashes. Also used to treat breast and prostate cancer.
Quinestrol is the 3-cyclopentyl ether of ethinyl estradiol (the active metabolite). After gastrointestinal absorption, it is stored in adipose tissue where it is slowly released and metabolized principally to the parent compound, ethinyl estradiol. Ethinyl estradiol is a synthetic derivative of the natural estrogen estradiol.
Estrogens
Compounds that interact with ESTROGEN RECEPTORS in target tissues to bring about the effects similar to those of ESTRADIOL. Estrogens stimulate the female reproductive organs, and the development of secondary female SEX CHARACTERISTICS. Estrogenic chemicals include natural, synthetic, steroidal, or non-steroidal compounds. (See all compounds classified as Estrogens.)
Absorption
Absorbed following oral administration.
Metabolized principally to the parent compound, ethinyl estradiol. Ethinyl estradiol is metabolized in the liver. Quantitatively, the major metabolic pathway for ethinyl estradiol, both in rats and in humans, is aromatic hydroxylation, as it is for the natural estrogens.
Estrogens diffuse into their target cells and interact with a protein receptor (the estrogen receptor). Estrogen interacts with a target cell receptor. When the estrogen receptor has bound its ligand it can enter the nucleus of the target cell, and regulate gene transcription which leads to formation of messenger RNA. The mRNA interacts with ribosomes to produce specific proteins that express the effect of estradiol upon the target cell. Estrogens increase the hepatic synthesis of sex hormone binding globulin (SHBG), thyroid-binding globulin (TBG), and other serum proteins and suppress follicle-stimulating hormone (FSH) from the anterior pituitary. Target cells include the female reproductive tract, the mammary gland, the hypothalamus, and the pituitary. Estrogens increase the hepatic synthesis of sex hormone binding globulin (SHBG), thyroid-binding globulin (TBG), and other serum proteins and suppress follicle-stimulating hormone (FSH) from the anterior pituitary. The combination of an estrogen with a progestin suppresses the hypothalamic-pituitary system, decreasing the secretion of gonadotropin-releasing hormone (GnRH).
