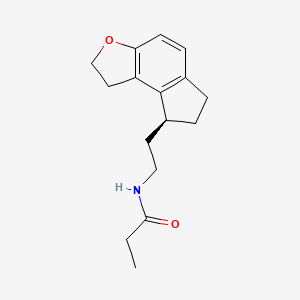

1. (s)-n-(2-(1,6,7,8-tetrahydro-2h-indeno-(5,4)furan-8-yl)ethyl)propionamide
2. Rozerem
3. Tak-375
1. 196597-26-9
2. Rozerem
3. Tak-375
4. (s)-n-[2-(1,6,7,8-tetrahydro-2h-indeno-[5,4-b]furan-8-yl)ethyl]propionamide
5. (s)-n-(2-(1,6,7,8-tetrahydro-2h-indeno[5,4-b]furan-8-yl)ethyl)propionamide
6. Tak375
7. Chembl1218
8. 901as54i69
9. Ramelteon [usan]
10. N-[2-[(8s)-2,6,7,8-tetrahydro-1h-cyclopenta[e][1]benzofuran-8-yl]ethyl]propanamide
11. N-[2-[(8s)-1,6,7,8-tetrahydro-2h-indeno[5,4-b]furan-8-yl]ethyl]propanamide
12. N-{2-[(8s)-1,6,7,8-tetrahydro-2h-indeno[5,4-b]furan-8-yl]ethyl}propanamide
13. N-{2-[(8s)-1h,2h,6h,7h,8h-indeno[5,4-b]furan-8-yl]ethyl}propanamide
14. Smr002544684
15. Rozerem (tn)
16. Sr-05000001957
17. Ramelteon (jan/usan/inn)
18. (s)-n-(2-(1,6,7,8-tetrahydro-2h-indeno-(5,4)furan-8-yl)ethyl)propionamide
19. Unii-901as54i69
20. Hsdb 7787
21. Ramelteon Solution
22. (s)-n-(2-[1,6,7,8-tetrahydro-2h-indeno[5,4-b]furan-8-yl]ethyl)propionamide
23. (s)-n-[2-(1,6,7,8-tetrahydro-2h-indeno[5,4-b]furan-8-yl)ethyl]propionamide
24. Ramelteon [usan:inn:ban:jan]
25. Jev
26. Ramelteon [inn]
27. Ramelteon [jan]
28. Ramelteon [hsdb]
29. Ramelteon [vandf]
30. Ramelteon (tak-375)
31. Ramelteon [mart.]
32. Ramelteon [who-dd]
33. (-)-n-(2-(((8s)-1,6,7,8-tetrahydro-2h-indeno(5,4-b)furan-8-yl)ethyl)propanamide
34. Schembl29237
35. Bspbio_002318
36. Mls003915619
37. Mls006010029
38. Tak-375sl
39. Spectrum1505817
40. Gtpl1356
41. Ramelteon [orange Book]
42. Dtxsid6045951
43. Tak 375
44. Chebi:109549
45. Hms1922h18
46. Hms2093f12
47. Hms3884k07
48. Act06830
49. Hy-a0014
50. Zinc3960338
51. Bdbm50118470
52. Mfcd08067736
53. S1259
54. Ramelteon 1.0 Mg/ml In Acetonitrile
55. Akos015895741
56. Ac-5275
57. Am84670
58. Ccg-213557
59. Cs-0382
60. Db00980
61. N-[2-[(8s)-2,6,7,8-tetrahydro-1h-cyclopenta[e]benzofuran-8-yl]ethyl]propanamide
62. Propanamide, N-(2-((8s)-1,6,7,8-tetrahydro-2h-indeno(5,4-b)furan-8-yl)ethyl)-
63. Ncgc00178707-03
64. Ncgc00178707-05
65. As-15740
66. Sbi-0206874.p001
67. R0216
68. Sw219712-1
69. D02689
70. Ab01274760-01
71. Ab01274760_02
72. Ab01274760_03
73. 597r269
74. Q417689
75. J-502508
76. Sr-05000001957-1
77. Sr-05000001957-3
78. Brd-k28761891-001-01-0
79. Brd-k28761891-001-04-4
80. Z2037281108
81. 1-boc-2-[(4-fluoro-phenylamino)-methyl]-piperidine
82. (s)-n-(2-(2,6,7,8-tetrahydro-1h-indeno[5,4-b]furan-8-yl)ethyl)propionamide
83. N-[2-(1,6,7,8-tetrahydro-2h-3-oxa-as-indacen-8-yl)-ethyl]-propionamide(s)-(-)-22b
84. N-[2-[(8s)-2,6,7,8-tetrahydro-1h-cyclopenta[e][1]benzoxol-8-yl]ethyl]propanamide
85. Ramelteon Solution, 1.0 Mg/ml In Acetonitrile, Ampule Of 1 Ml, Certified Reference Material
86. (-)-n-(2-(((8s)-1,6,7,8-tetrahydro-2h-indeno(5,4-.beta.)furan-8-yl)ethyl)propanamide
87. Propanamide, N-(2-((8s)-1,6,7,8-tetrahydro-2h-indeno(5,4-.beta.)furan-8-yl)ethyl)-
| Molecular Weight | 259.34 g/mol |
|---|---|
| Molecular Formula | C16H21NO2 |
| XLogP3 | 2.7 |
| Hydrogen Bond Donor Count | 1 |
| Hydrogen Bond Acceptor Count | 2 |
| Rotatable Bond Count | 4 |
| Exact Mass | 259.157228913 g/mol |
| Monoisotopic Mass | 259.157228913 g/mol |
| Topological Polar Surface Area | 38.3 Ų |
| Heavy Atom Count | 19 |
| Formal Charge | 0 |
| Complexity | 331 |
| Isotope Atom Count | 0 |
| Defined Atom Stereocenter Count | 1 |
| Undefined Atom Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Defined Bond Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Undefined Bond Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Covalently Bonded Unit Count | 1 |
| 1 of 4 | |
|---|---|
| Drug Name | Ramelteon |
| PubMed Health | Ramelteon (By mouth) |
| Drug Classes | Nonbarbiturate Hypnotic |
| Drug Label | ROZEREM (ramelteon) is an orally active hypnotic chemically designated as (S)-N-[2-(1,6,7,8-tetrahydro-2H-indeno-[5,4-b]furan-8-yl)ethyl]propionamide and containing one chiral center. The compound is produced as the (S)-enantiomer, with an empirical... |
| Active Ingredient | Ramelteon |
| Dosage Form | Tablet |
| Route | Oral |
| Strength | 8mg |
| Market Status | Prescription |
| Company | Teva Pharms Usa |
| 2 of 4 | |
|---|---|
| Drug Name | Rozerem |
| PubMed Health | Ramelteon (By mouth) |
| Drug Classes | Nonbarbiturate Hypnotic |
| Drug Label | ROZEREM (ramelteon) is an orally active hypnotic chemically designated as (S)-N-[2-(1,6,7,8-tetrahydro-2H-indeno-[5,4-b]furan-8-yl)ethyl]propionamide and containing one chiral center. The compound is produced as the (S)-enantiomer, with an empirical... |
| Active Ingredient | Ramelteon |
| Dosage Form | Tablet |
| Route | Oral |
| Strength | 8mg |
| Market Status | Prescription |
| Company | Takeda Pharms Usa |
| 3 of 4 | |
|---|---|
| Drug Name | Ramelteon |
| PubMed Health | Ramelteon (By mouth) |
| Drug Classes | Nonbarbiturate Hypnotic |
| Drug Label | ROZEREM (ramelteon) is an orally active hypnotic chemically designated as (S)-N-[2-(1,6,7,8-tetrahydro-2H-indeno-[5,4-b]furan-8-yl)ethyl]propionamide and containing one chiral center. The compound is produced as the (S)-enantiomer, with an empirical... |
| Active Ingredient | Ramelteon |
| Dosage Form | Tablet |
| Route | Oral |
| Strength | 8mg |
| Market Status | Prescription |
| Company | Teva Pharms Usa |
| 4 of 4 | |
|---|---|
| Drug Name | Rozerem |
| PubMed Health | Ramelteon (By mouth) |
| Drug Classes | Nonbarbiturate Hypnotic |
| Drug Label | ROZEREM (ramelteon) is an orally active hypnotic chemically designated as (S)-N-[2-(1,6,7,8-tetrahydro-2H-indeno-[5,4-b]furan-8-yl)ethyl]propionamide and containing one chiral center. The compound is produced as the (S)-enantiomer, with an empirical... |
| Active Ingredient | Ramelteon |
| Dosage Form | Tablet |
| Route | Oral |
| Strength | 8mg |
| Market Status | Prescription |
| Company | Takeda Pharms Usa |
Ramelteon is used in the management of insomnia characterized by difficulty with sleep onset. /Use Included in US product label/
American Society of Health System Pharmacists; AHFS Drug Information 2009. Bethesda, MD. (2009), p. 2634
THERAPEUTIC CATEGORY: Sedative, hypnotic
O'Neil, M.J. (ed.). The Merck Index - An Encyclopedia of Chemicals, Drugs, and Biologicals. Whitehouse Station, NJ: Merck and Co., Inc., 2006., p. 1395
Ramelteon did not demonstrate a respiratory depressant effect in patients with mild to moderate chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. The effect of ramelteon in patients with severe chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (e.g., those with elevated PCO2, those requiring nocturnal oxygen therapy) has not been studied, and use in these patients is not recommended. In studies in patients with mild to moderate obstructive sleep apnea, ramelteon did not produce differences in measures of apnea indices.1 However, the effect of ramelteon on severe obstructive sleep apnea has not been studied, and use in these patients is not recommended.
American Society of Health System Pharmacists; AHFS Drug Information 2009. Bethesda, MD. (2009), p. 2634
In a 35-night randomized study evaluating next-day residual effects of ramelteon, adult patients receiving 8 mg of the drug every night experienced reduced immediate/delayed memory recall and increased sluggishness, fatigue, and irritation at weeks 1 and 3 of treatment compared with those receiving placebo. However, next-day residual effects were not substantially different between ramelteon- and placebo-treated patients at week 5.1 2 A similar study in geriatric patients receiving 4 or 8 mg of ramelteon every night did not produce any substantial differences in measures of residual effects.
American Society of Health System Pharmacists; AHFS Drug Information 2009. Bethesda, MD. (2009), p. 2634
Studies employing subjective measures (e.g., questionnaires) did not reveal evidence of a withdrawal syndrome (including rebound insomnia) following discontinuance of long-term ramelteon therapy (4, 8, or 16 mg daily for up to 35 days).
American Society of Health System Pharmacists; AHFS Drug Information 2009. Bethesda, MD. (2009), p. 2634
No evidence of abuse potential was detected following administration of relatively high ramelteon doses (up to 20 times the recommended hypnotic dose) in patients with a history of drug (e.g., sedative-hypnotic, anxiolytic) abuse or dependence. Ramelteon does not appear to produce physical dependence.
American Society of Health System Pharmacists; AHFS Drug Information 2009. Bethesda, MD. (2009), p. 2633
For more Drug Warnings (Complete) data for Ramelteon (18 total), please visit the HSDB record page.
For the treatment of insomnia characterized by difficulty with sleep onset.
FDA Label
Ramelteon is the first selective melatonin agonist. It works by mimicking melatonin (MT), a naturally occuring hormone that is produced during the sleep period and thought to be responsible for the regulation of circadian rhythm underlying the normal sleep-wake cycle. Ramelteon has a high affinity for the MT1 and MT2 receptors. The MT1 and MT2 receptors are located in the brain's suprachiasmatic nuclei (SCN),which is known as the body's "master clock" because it regulates the 24-hour sleep-wake cycle. Ramelteon has an active metabolite that is less potent but circulates in higher concentrations than the parent compound. The metabolite also has weak affinity for the 5HT2b receptor.
N - Nervous system
N05 - Psycholeptics
N05C - Hypnotics and sedatives
N05CH - Melatonin receptor agonists
N05CH02 - Ramelteon
Absorption
Rapid, total absorption is at least 84%.
Route of Elimination
Following oral administration of radiolabeled ramelteon, 84% of total radioactivity was excreted in urine and approximately 4% in feces, resulting in a mean recovery of 88%. Less than 0.1% of the dose was excreted in urine and feces as the parent compound.
Volume of Distribution
73.6 L
In vitro protein binding of ramelteon is approximately 82% in human serum, independent of concentration. Binding to albumin accounts for most of that binding, since 70% of the drug is bound in human serum albumin. Ramelteon is not distributed selectively to red blood cells. Ramelteon has a mean volume of distribution after intravenous administration of 73.6 L, suggesting substantial tissue distribution.
US Natl Inst Health; DailyMed. Current Medication Information for ROZEREM (ramelteon) tablet, film-coated (October 2008). Available from, as of February 16, 2010: https://dailymed.nlm.nih.gov/dailymed/drugInfo.cfm?id=13323
Ramelteon is absorbed rapidly, with median peak concentrations occurring at approximately 0.75 hour (range, 0.5 to 1.5 hours) after fasted oral administration. Although the total absorption of ramelteon is at least 84%, the absolute oral bioavailability is only 1.8% due to extensive first-pass metabolism
US Natl Inst Health; DailyMed. Current Medication Information for ROZEREM (ramelteon) tablet, film-coated (October 2008). Available from, as of February 16, 2010: https://dailymed.nlm.nih.gov/dailymed/drugInfo.cfm?id=13323
Distributed into milk in rats; not known whether ramelteon is distributed into human milk.
American Society of Health System Pharmacists; AHFS Drug Information 2009. Bethesda, MD. (2009), p. 2634
Following oral administration of radiolabeled ramelteon, 84% of total radioactivity was excreted in urine and approximately 4% in feces, resulting in a mean recovery of 88%. Less than 0.1% of the dose was excreted in urine and feces as the parent compound. Elimination was essentially complete by 96 hours post-dose. Repeated once daily dosing with Rozerem does not result in significant accumulation owing to the short elimination half-life of ramelteon (on average, approximately 1- 2.6 hours). The half-life of M-II is 2 to 5 hours and independent of dose. Serum concentrations of the parent drug and its metabolites in humans are at or below the lower limits of quantitation within 24 hours
US Natl Inst Health; DailyMed. Current Medication Information for ROZEREM (ramelteon) tablet, film-coated (October 2008). Available from, as of February 16, 2010: https://dailymed.nlm.nih.gov/dailymed/drugInfo.cfm?id=13323
Hepatic
Metabolism of ramelteon consists primarily of oxidation to hydroxyl and carbonyl derivatives, with secondary metabolism producing glucuronide conjugates. CYP1A2 is the major isozyme involved in the hepatic metabolism of ramelteon; the CYP2C subfamily and CYP3A4 isozymes are also involved to a minor degree. The rank order of the principal metabolites by prevalence in human serum is M-II, M-IV, M-I, and M-III. These metabolites are formed rapidly and exhibit a monophasic decline and rapid elimination. The overall mean systemic exposure of M-II is approximately 20- to 100-fold higher than parent drug.
US Natl Inst Health; DailyMed. Current Medication Information for ROZEREM (ramelteon) tablet, film-coated (October 2008). Available from, as of February 16, 2010: https://dailymed.nlm.nih.gov/dailymed/drugInfo.cfm?id=13323
~1-2.6 hours
Ramelteon is a melatonin receptor agonist with both high affinity for melatonin MT1 and MT2 receptors, and lower selectivity for the MT3 receptor. Melatonin production is concurrent with nocturnal sleep, meaning that an increase in melatonin levels is related to the onset of self-reported sleepiness and an increase in sleep propensity. MT1 receptors are believed to be responsible for regulation of sleepiness and facilitation of sleep onset, and MT2 receptors are believed to mediate phase-shifting effects of melatonin on the circadian rhythm. While MT1 and MT2 receptors are associated with the sleep-wake cycle, MT3 has a completely different profile, and therefore is not likely to be involved in the sleep-wake cycle. Remelteon has no appreciable affinity for the gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA) receptor complex or receptors that bind neuropeptides, cytokines, serotonin, dopamine, norepinephrine, acetylcholine, or opiates.
Ramelteon is a melatonin receptor agonist with both high affinity for melatonin MT1 and MT2 receptors and selectivity over the MT3 receptor. Ramelteon demonstrates full agonist activity in vitro in cells expressing human MT1 or MT2 receptors. The activity of ramelteon at the MT1 and MT2 receptors is believed to contribute to its sleep-promoting properties, as these receptors, acted upon by endogenous melatonin, are thought to be involved in the maintenance of the circadian rhythm underlying the normal sleep-wake cycle. Ramelteon has no appreciable affinity for the GABA receptor complex or for receptors that bind neuropeptides, cytokines, serotonin, dopamine, noradrenaline, acetylcholine, and opiates. Ramelteon also does not interfere with the activity of a number of selected enzymes in a standard panel. The major metabolite of ramelteon, M-II, is active and has approximately one tenth and one fifth the binding affinity of the parent molecule for the human MT1 and MT2 receptors, respectively, and is 17- to 25-fold less potent than ramelteon in in vitro functional assays. Although the potency of M-II at MT1 and MT2 receptors is lower than the parent drug, M-II circulates at higher concentrations than the parent producing 20- to 100-fold greater mean systemic exposure when compared to ramelteon. M-II has weak affinity for the serotonin 5-HT2B receptor, but no appreciable affinity for other receptors or enzymes. Similar to ramelteon, M-II does not interfere with the activity of a number of endogenous enzymes. All other known metabolites of ramelteon are inactive
US Natl Inst Health; DailyMed. Current Medication Information for ROZEREM (ramelteon) tablet, film-coated (October 2008). Available from, as of February 16, 2010: https://dailymed.nlm.nih.gov/dailymed/drugInfo.cfm?id=13323