

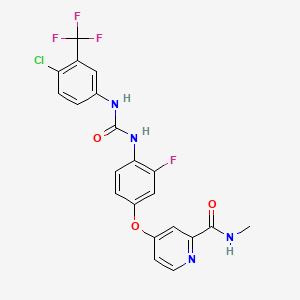

1. 4-(4-(((4-chloro-3-(trifluoromethyl)phenyl)carbamoyl)amino)-3-fluorophenoxy)-n-methylpyridine-2-carboxamide
2. Bay 73-4506
3. Bay-73-4506
4. Bay73-4506
5. Stivarga
1. 755037-03-7
2. Bay 73-4506
3. Stivarga
4. 4-(4-(3-(4-chloro-3-(trifluoromethyl)phenyl)ureido)-3-fluorophenoxy)-n-methylpicolinamide
5. Regorafenibum
6. Regorafenib (bay 73-4506)
7. Bay73-4506
8. Bay-73-4506
9. 4-[4-({[4-chloro-3-(trifluoromethyl)phenyl]carbamoyl}amino)-3-fluorophenoxy]-n-methylpyridine-2-carboxamide
10. Regorafenib-13c-d3
11. 4-[4-[[4-chloro-3-(trifluoromethyl)phenyl]carbamoylamino]-3-fluorophenoxy]-n-methylpyridine-2-carboxamide
12. 24t2a1doyb
13. Chembl1946170
14. Chebi:68647
15. Bay-734506
16. Stivarga (tn)
17. 4-(4-(((4-chloro-3-(trifluoromethyl)phenyl)carbamoyl)amino)-3-fluorophenoxy)-n-methylpyridine-2-carboxamide
18. Regorafenib [inn]
19. Regorafenib [usan:inn]
20. Unii-24t2a1doyb
21. Fluoro-sorafenib
22. 4-(4-(((4-chloro-3-(trifluoromethyl)phenyl)carbamoyl}amino)-3-fluorophenoxy)-n-methylpyridine-2-carboxamide
23. Regorafenib [mi]
24. Regorafenib (usan/inn)
25. Regorafenib [vandf]
26. Regorafenib Anhydrous
27. Regorafenib [who-dd]
28. Mls006010303
29. Regorafenib Crystalline Form I
30. Schembl432230
31. Regorafenib,bay 73-4506
32. Gtpl5891
33. Dtxsid60226441
34. Ex-a058
35. Regorafenib - Bay 73-4506
36. Bcpp000352
37. Hms3654k16
38. Hms3672e15
39. Bcp02105
40. Bkd17855
41. Zinc6745272
42. Bdbm50363397
43. Mfcd16038047
44. Nsc763932
45. Nsc800865
46. S1178
47. Akos015951107
48. Am81251
49. Bay 734506
50. Bcp9000384
51. Ccg-269571
52. Cs-0170
53. Db08896
54. Nsc-763932
55. Nsc-800865
56. Sb16819
57. Ncgc00263138-01
58. Ncgc00263138-13
59. Ncgc00263138-19
60. 2-pyridinecarboxamide,4-[4-[[[[4-chloro-3-(trifluoromethyl)phenyl]amino]carbonyl]amino]-3-fluorophenoxy]-n-methyl-
61. 835621-08-4
62. Ac-25075
63. Ac-31116
64. As-16304
65. Hy-10331
66. Smr004701370
67. Ft-0674338
68. R0142
69. Sw218097-2
70. Cas:835621-07-3;regorafenib Hydrochloride
71. Regorafenib (bay73-4506,fluoro-sorafenib)
72. A25020
73. D10138
74. Ab01565826_02
75. Sr-01000941571
76. Q3891664
77. Sr-01000941571-1
78. Brd-k16730910-001-02-4
79. 2-pyridinecarboxamide, 4-[4-[[[[4-chloro-3-(trifluoromethyl)phenyl]amino]carbonyl]amino]-3-fluorophenoxy]-n-methyl-
80. 4-[4-({[4-chloro-3-(trifluoromethy)phenyl]carbamoyl}amino)-3-fluorophenoxy]-1-methylpyridine-2-carboxamide
81. 4{4-[3-(4-chloro-3-trifluoromethylphenyl)-ureido]-3-fluorophenoxy}-pyridine-2-carboxylic Acid Methylamide
82. Regorafenib;1-(4-chloro-3-(trifluoromethyl)phenyl)-3-(2-fluoro-4-(2-(methylcarbamoyl)pyridin-4-yloxy)phenyl)urea
| Molecular Weight | 482.8 g/mol |
|---|---|
| Molecular Formula | C21H15ClF4N4O3 |
| XLogP3 | 4.2 |
| Hydrogen Bond Donor Count | 3 |
| Hydrogen Bond Acceptor Count | 8 |
| Rotatable Bond Count | 5 |
| Exact Mass | 482.0768807 g/mol |
| Monoisotopic Mass | 482.0768807 g/mol |
| Topological Polar Surface Area | 92.4 Ų |
| Heavy Atom Count | 33 |
| Formal Charge | 0 |
| Complexity | 686 |
| Isotope Atom Count | 0 |
| Defined Atom Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Undefined Atom Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Defined Bond Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Undefined Bond Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Covalently Bonded Unit Count | 1 |
| 1 of 2 | |
|---|---|
| Drug Name | Stivarga |
| PubMed Health | Regorafenib (By mouth) |
| Drug Classes | Antineoplastic Agent |
| Drug Label | Stivarga (regorafenib) has the chemical name 4-[4-({[4-chloro-3-(trifluoromethyl) phenyl] carbamoyl} amino)-3-fluorophenoxy]-N-methylpyridine-2-carboxamide monohydrate. Regorafenib has the following structural formula:Regorafenib is a monohydrate and... |
| Active Ingredient | Regorafenib |
| Dosage Form | Tablet |
| Route | oral; Oral |
| Strength | 40mg |
| Market Status | Prescription |
| Company | Bayer Healthcare Pharms; Bayer Hlthcare |
| 2 of 2 | |
|---|---|
| Drug Name | Stivarga |
| PubMed Health | Regorafenib (By mouth) |
| Drug Classes | Antineoplastic Agent |
| Drug Label | Stivarga (regorafenib) has the chemical name 4-[4-({[4-chloro-3-(trifluoromethyl) phenyl] carbamoyl} amino)-3-fluorophenoxy]-N-methylpyridine-2-carboxamide monohydrate. Regorafenib has the following structural formula:Regorafenib is a monohydrate and... |
| Active Ingredient | Regorafenib |
| Dosage Form | Tablet |
| Route | oral; Oral |
| Strength | 40mg |
| Market Status | Prescription |
| Company | Bayer Healthcare Pharms; Bayer Hlthcare |
Regorafenib is indicated for the treatment of patients with metastatic colorectal cancer (CRC) who have been previously treated with fluoropyrimidine-, oxaliplatin- and irinotecan-based chemotherapy, an anti-VEGF therapy, and, if KRAS wild type, an anti-EGFR therapy. Regorafenib is also indicated for the treatment of patients with locally advanced, unresectable or metastatic gastrointestinal stromal tumour (GIST) who have been previously treated with imatinib mesylate and sunitinib malate. Regorafenib is also indicated for the treatment of patients with hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) previously treated with sorafenib.
FDA Label
Stivarga is indicated as monotherapy for the treatment of adult patients with:
- metastatic colorectal cancer (CRC) who have been previously treated with, or are not considered candidates for, available therapies - these include fluoropyrimidine-based chemotherapy, an anti-VEGF therapy and an anti-EGFR therapy;
- unresectable or metastatic gastrointestinal stromal tumors (GIST) who progressed on or are intolerant to prior treatment with imatinib and sunitinib;
- hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) who have been previously treated with sorafenib.
L01EX05
L01XE21
S76 | LUXPHARMA | Pharmaceuticals Marketed in Luxembourg | Pharmaceuticals marketed in Luxembourg, as published by d'Gesondheetskeess (CNS, la caisse nationale de sante, www.cns.lu), mapped by name to structures using CompTox by R. Singh et al. (in prep.). List downloaded from https://cns.public.lu/en/legislations/textes-coordonnes/liste-med-comm.html. Dataset DOI:10.5281/zenodo.4587355
L - Antineoplastic and immunomodulating agents
L01 - Antineoplastic agents
L01E - Protein kinase inhibitors
L01EX - Other protein kinase inhibitors
L01EX05 - Regorafenib
Absorption
Cmax = 2.5 g/mL; Tmax = 4 hours; AUC = 70.4 g*h/mL; Cmax, steady-state = 3.9 g/mL; AUC, steady-state = 58.3 g*h/mL; The mean relative bioavailability of tablets compared to an oral solution is 69% to 83%.
Route of Elimination
Approximately 71% of a radiolabeled dose was excreted in feces (47% as parent compound, 24% as metabolites) and 19% of the dose was excreted in urine (17% as glucuronides) within 12 days after administration of a radiolabeled oral solution at a dose of 120 mg.
Volume of Distribution
Regorafenib undergoes enterohepatic circulation with multiple plasma concentration peaks observed across the 24-hour dosing interval.
Regorafenib is metabolized by CYP3A4 and UGT1A9. The main circulating metabolites of regorafenib measured at steady-state in human plasma are M-2 (N-oxide) and M-5 (N-oxide and N-desmethyl), both of them having similar in vitro pharmacological activity and steady-state concentrations as regorafenib. M-2 and M-5 are highly protein bound (99.8% and 99.95%, respectively). Regorafenib is an inhibitor of P-glycoprotein, while its active metabolites M-2 (N-oxide) and M-5 (N-oxide and N-desmethyl) are substrates of P-glycoprotein.
Regorafenib, 160 mg oral dose = 28 hours (14 - 58 hours); M2 metabolite, 160 mg oral dose = 25 hours (14-32 hours); M5 metabolite, 160 mg oral dose = 51 hours (32-72 hours);
Regorafenib is a small molecule inhibitor of multiple membrane-bound and intracellular kinases involved in normal cellular functions and in pathologic processes such as oncogenesis, tumor angiogenesis, and maintenance of the tumor microenvironment. In in vitro biochemical or cellular assays, regorafenib or its major human active metabolites M-2 and M-5 inhibited the activity of RET, VEGFR1, VEGFR2, VEGFR3, KIT, PDGFR-alpha, PDGFR-beta, FGFR1, FGFR2, TIE2, DDR2, TrkA, Eph2A, RAF-1, BRAF, BRAFV600E , SAPK2, PTK5, and Abl at concentrations of regorafenib that have been achieved clinically. In in vivo models, regorafenib demonstrated anti-angiogenic activity in a rat tumor model, and inhibition of tumor growth as well as anti-metastatic activity in several mouse xenograft models including some for human colorectal carcinoma.