

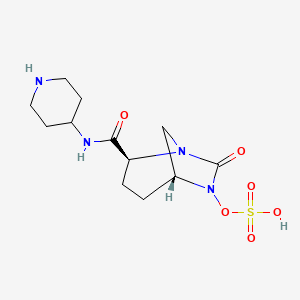

1. (2s,5r)-7-oxo-n-(4-piperidinyl)-6-(sulfooxy)-1,6-diazabicyclo(3.2.1)octane-2-carboxamide
2. Mk-7655
3. Mk7655
4. Relebactam Anhydrous
1. 1174018-99-5
2. Mk-7655
3. Relebactam Anhydrous
4. Relebactam [inn]
5. (-)-relebactam Anhydrous
6. 1oqf7tt3pf
7. Chembl3112741
8. Mk-7655a
9. Mk7655
10. Sulfuric Acid Mono-((2s,5r)-7-oxo-2-(piperidin-4-ylcarbamoyl)-1,6-diaza-bicyclo(3.2.1)oct-6-yl) Ester
11. (1r,2s,5r)-7-oxo-2-(piperidin-4-ylcarbamoyl)-1,6-diazabicyclo[3.2.1]octan-6-yl Hydrogen Sulfate
12. [(2s,5r)-7-oxo-2-(piperidin-4-ylcarbamoyl)-1,6-diazabicyclo[3.2.1]octan-6-yl] Hydrogen Sulfate
13. Unii-1oqf7tt3pf
14. Relebactam [mi]
15. Relebactam [who-dd]
16. Bdbm1858
17. Schembl3721178
18. Gtpl10852
19. Ex-a864
20. Sulfuric Acid Mono-[7-oxo-2-(piperidin-4-ylcarbamoyl)-1,6-diaza-bicyclo[3.2.1]oct-6-yl] Ester
21. Bdbm50447651
22. Mfcd28502833
23. Zinc43206319
24. Cs-5391
25. Db12377
26. Ac-36163
27. As-35205
28. Br163749
29. Hy-16752
30. Us8487073, 1a
31. S0074
32. J3.628.086g
33. Mk-7655;mk7655;mk 7655
34. J-690043
35. Q27252695
36. (2s,5r)-7-oxo-n-piperidin-4-yl-6-(sulfooxy)-1,6-diazabicyclo[3.2.1]octane-2-carboxamide
| Molecular Weight | 348.38 g/mol |
|---|---|
| Molecular Formula | C12H20N4O6S |
| XLogP3 | -3.6 |
| Hydrogen Bond Donor Count | 3 |
| Hydrogen Bond Acceptor Count | 7 |
| Rotatable Bond Count | 4 |
| Exact Mass | 348.11035554 g/mol |
| Monoisotopic Mass | 348.11035554 g/mol |
| Topological Polar Surface Area | 137 Ų |
| Heavy Atom Count | 23 |
| Formal Charge | 0 |
| Complexity | 585 |
| Isotope Atom Count | 0 |
| Defined Atom Stereocenter Count | 2 |
| Undefined Atom Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Defined Bond Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Undefined Bond Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Covalently Bonded Unit Count | 1 |
Relebactam is indicated in combination with [imipenem] and [cilastatin] for the treatment of complicated urinary tract infections (including pyelonephritis), and complicated intra-abdominal infections caused by susceptible organisms in adults.
Relebactam prevents the hydrolysis of [imipenem], allowing it to exert its bactericidal effect.
beta-Lactamase Inhibitors
Endogenous substances and drugs that inhibit or block the activity of BETA-LACTAMASES. (See all compounds classified as beta-Lactamase Inhibitors.)
Absorption
Currently, relebactam is only available as an intravenous product; therefore, there is no relevant absorption data in the literature.
Route of Elimination
Approximately 90-100% of relebactam is renally eliminated.
Volume of Distribution
Relebactam has a volume of distribution of approximately 19 L with both single and steady state dosing.
Clearance
Relebactam has a reported total clearance of approximately 130-150 mL/min (8 L/h). About 30% of the total drug clearance can be attributed to active tubular secretion.
Relebactam does not undergo significant metabolism and can be found mostly unchanged in human plasma.
Relebactam has a half-life of 1.2 hours as per official FDA labeling. Values reported in pharmacokinetic studies vary from 1.35-1.8 hours.
Relebactam is a beta-lactamase inhibitor known to inhibit many types of beta-lactamases including Ambler class A and Ambler class C enzymes, helping to prevent [imipenem] from degrading in the body. Similar to the structurally-related [avibactam], first, relebactam binds non-covalently to a beta-lactamase binding site, then, it covalently acylates the serine residue in the active site of the enzyme. In contrast to some other beta-lactamase inhibitors, once relebactam de-acylates from the active site, it can reform it's 5 membered ring and is capable of rebinding to target enzymes.