


1. Cns 7056
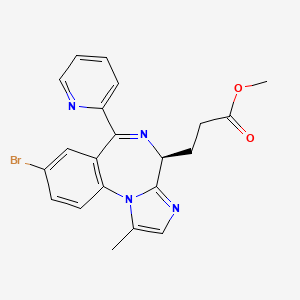
2. Methyl 3-(8-bromo-1-methyl-6-(2-pyridinyl)-4h-imidazo(1,2-a)(1,4)benzodiazepin-4-yl)propanoate
3. Ono 2745
4. Ono-2745
5. Ono2745
1. 308242-62-8
2. Cns 7056
3. Cns-7056
4. Ono-2745
5. 7v4a8u16mb
6. 308242-62-8 (freee Base)
7. 4h-imidazo(1,2-a)(1,4)benzodiazepine-4-propanoic Acid, 8-bromo-1-methyl-6-(2-pyridinyl)-, Methyl Ester, (4s)-
8. Methyl (s)-3-(8-bromo-1-methyl-6-(pyridin-2-yl)-4h-benzo[f]imidazo[1,2-a][1,4]diazepin-4-yl)propanoate
9. Remimazolam [inn]
10. Unii-7v4a8u16mb
11. Remimazolam [mi]
12. Remimazolam (usan/inn)
13. Remimazolam [usan:inn]
14. Remimazolam [usan]
15. Remimazolam [who-dd]
16. Schembl846435
17. Chembl4297526
18. Dtxsid20953024
19. Ono2745
20. Amy15524
21. Ex-a5536
22. Ono 2745
23. Who 9232
24. Zinc3927450
25. Akos025213215
26. Db12404
27. Hy-14867
28. 4523b
29. Cs-0003605
30. D11788
31. 4h-imidazol(1,2-a)(1,4)benzodiazepine-4-propionic Acid, (s)-
32. (s)-methyl 3-(8-bromo-1-methyl-6-(pyridin-2-yl)-4h-benzo[f]imidazo[1,2-a][1,4]diazepin-4-yl)propanoate
33. Methyl 3-((4s)-8-bromo-1-methyl-6-(pyridin-2-yl)-4h-imidazo(1,2-a)(1,4)benzodiazepin-4-yl)propanoate
34. Methyl 3-[(4s)-8-bromo-1-methyl-6-(2-pyridyl)-4h-imidazo[1,2-a][1,4]benzodiazepin-4-yl]propanoate
35. Methyl 3-[(4s)-8-bromo-1-methyl-6-pyridin-2-yl-4h-imidazo[1,2-a][1,4]benzodiazepin-4-yl]propanoate
36. Methyl 3-[8-bromo-1-methyl-6-(pyridin-2-yl)-4h-imidazo[1,2-a][1,4]benzodiazepin-4-yl]propanoate
| Molecular Weight | 439.3 g/mol |
|---|---|
| Molecular Formula | C21H19BrN4O2 |
| XLogP3 | 3.4 |
| Hydrogen Bond Donor Count | 0 |
| Hydrogen Bond Acceptor Count | 5 |
| Rotatable Bond Count | 5 |
| Exact Mass | 438.06914 g/mol |
| Monoisotopic Mass | 438.06914 g/mol |
| Topological Polar Surface Area | 69.4 Ų |
| Heavy Atom Count | 28 |
| Formal Charge | 0 |
| Complexity | 601 |
| Isotope Atom Count | 0 |
| Defined Atom Stereocenter Count | 1 |
| Undefined Atom Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Defined Bond Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Undefined Bond Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Covalently Bonded Unit Count | 1 |
Remimazolam is indicated for the induction and maintenance of procedural sedation in adults undergoing procedures lasting 30 minutes or less.
FDA Label
Remimazolam is indicated in adults for procedural sedation.
Remimazolam modulates the effects of GABA(A) receptors in order to enhance the effects of GABA. It is considered an "ultra short-acting" benzodiazepine that achieves peak sedation within 3 to 3.5 minutes following intravenous administration, a property that makes it desirable for use during short procedures. Hepatic impairment can result in elevated serum levels of remimazolam - patients with severe hepatic impairment should be carefully titrated to effect. As of its approval date, remimazolam has not received a scheduling action by the DEA under the Controlled Substances Act. As benzodiazepines as a class have been implicated in the development of drug dependence and have a known potential for abuse, remimazolam should be used with caution in patients with a history of drug dependence or abuse.
N05CD
N - Nervous system
N05 - Psycholeptics
N05C - Hypnotics and sedatives
N05CD - Benzodiazepine derivatives
N05CD14 - Remimazolam
Absorption
The Cmax and AUC0-inf following intravenous administration of 0.01 to 0.5 mg/kg were 189 to 6,960 ng/mL and 12.1 to 452 ngh/mL, respectively, and appear to be relatively dose proportional. The Tmax of the inactive CNS7054 metabolite is approximately 20-30 minutes and its AUC0-inf ranges from 231 to 7,090 ngh/mL.
Route of Elimination
In patients undergoing colonoscopy, approximately 0.003% of the administered dose is excreted in the urine as unchanged parent drug and 50-60% is excreted in the urine as CNS7054. In healthy subjects, >80% of the administered dose is excreted in the urine as CNS7054.
Volume of Distribution
The volume of distribution is approximately 0.76 - 0.98 L/kg.
Clearance
The clearance of remimazolam is approximately 24 - 75 L/h and is independent of body weight.
Remimazolam does not appear to undergo biotransformation via hepatic cytochrome P450 enzymes, nor does it induce or inhibit these enzymes. Its primary route of metabolism is hydrolysis via hepatic carboxylesterase-1 (CES1) to yield the inactive CNS7054 metabolite, which then undergoes glucuronidation and hydroxylation prior to elimination. CNS7054 possesses a 300-fold lesser affinity for GABA(A) receptors as compared to the parent drug.
Following intravenous administration, the distribution half-life is of remimazolam is 0.5 - 2 minutes and the terminal elimination half-life is 37 - 53 minutes. Half-life is increased in patients with hepatic impairment necessitating careful dose titration in this population. The half-life of remimazolam's major inactive metabolite, CNS7054, is 2.4 - 3.8 hours.
Like other benzodiazepines, remimazolam exerts its therapeutic effects by potentiating the effect of gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA) on GABA(A) receptors, the main inhibitory neurotransmitter receptors in the mammalian brain. GABA(A) receptors are a component of GABA-gated ionotropic chloride channels that produce inhibitory postsynaptic potentials - following activation by GABA, the channel undergoes a conformational change that allows the passage of chloride ions through the channel. The inhibitory potentials produced by GABA neurotransmission play an integral role in the suppression and control of epileptiform nerve firing such as that seen in epilepsy, which makes the GABA system a desirable target in the treatment of epilepsy. Benzodiazepines are positive allosteric modulators of GABA(A) function. They bind to the interface between alpha () and gamma () subunits on the receptor, commonly referred to as the benzodiazepine binding site, and modulate the receptor such that its inhibitory response to GABA binding is dramatically increased.
