

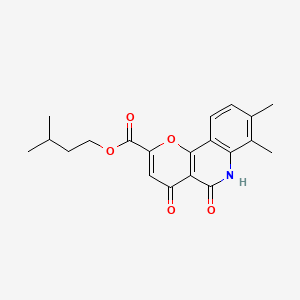

1. Isoamyl 5,6-dihydro-7,8-dimethyl-4,5-dioxo-4h-pyrano(3,2-c)quinoline -2-carboxylate
2. My 5116
3. My-5116
1. 73080-51-0
2. Romet
3. My-5116
4. Isopentyl 7,8-dimethyl-4,5-dioxo-5,6-dihydro-4h-pyrano[3,2-c]quinoline-2-carboxylate
5. 3-methylbutyl 7,8-dimethyl-4,5-dioxo-6h-pyrano[3,2-c]quinoline-2-carboxylate
6. 4k8ka8b61g
7. Repirinastum
8. Repirinastum [inn-latin]
9. 3-methylbutyl 5-hydroxy-7,8-dimethyl-4-oxopyrano[3,2-c]quinoline-2-carboxylate
10. Repirinast [usan:inn:jan]
11. Brn 4267921
12. Unii-4k8ka8b61g
13. Repirinast-[d4]
14. Isoamyl 5,6-dihydro-7,8-dimethyl-4,5-dioxo-4h-pyrano(3,2-c)quinoline-2-carboxylate
15. Romet (tn)
16. Repirinast [mi]
17. Repirinast [inn]
18. Repirinast [jan]
19. Repirinast [usan]
20. Repirinast [mart.]
21. Isopentyl 5,6-dihydro-7,8-dimethyl-4,5-dioxo-4h-pyrano(3,2-c)quinoline-2-carboxylate
22. Repirinast [who-dd]
23. Schembl29997
24. Repirinast (jan/usan/inn)
25. Chembl2105300
26. Chebi:32092
27. Dtxsid10223349
28. Zinc538285
29. Bcp16315
30. Ex-a3508
31. My5116
32. Akos016014130
33. Ac-5020
34. 4h-pyrano(3,2-c)quinoline-2-carboxylic Acid, 5,6-dihydro-7,8-dimethyl-4,5-dioxo-, 3-methylbutyl Ester
35. 4h-pyrano(3,2-c)quinoline-2-carboxylic Acid, 5,6-dihydro-7,8-dimethyl-4,5-dioxo-, Isopentyl Ester
36. Db-055720
37. Hy-109544
38. Cs-0031286
39. Ft-0630818
40. D01890
41. 080r510
42. A837709
43. Q7314016
| Molecular Weight | 355.4 g/mol |
|---|---|
| Molecular Formula | C20H21NO5 |
| XLogP3 | 3.4 |
| Hydrogen Bond Donor Count | 1 |
| Hydrogen Bond Acceptor Count | 5 |
| Rotatable Bond Count | 5 |
| Exact Mass | 355.14197277 g/mol |
| Monoisotopic Mass | 355.14197277 g/mol |
| Topological Polar Surface Area | 81.7 Ų |
| Heavy Atom Count | 26 |
| Formal Charge | 0 |
| Complexity | 690 |
| Isotope Atom Count | 0 |
| Defined Atom Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Undefined Atom Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Defined Bond Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Undefined Bond Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Covalently Bonded Unit Count | 1 |
Immunosuppressive Agents
Agents that suppress immune function by one of several mechanisms of action. Classical cytotoxic immunosuppressants act by inhibiting DNA synthesis. Others may act through activation of T-CELLS or by inhibiting the activation of HELPER CELLS. While immunosuppression has been brought about in the past primarily to prevent rejection of transplanted organs, new applications involving mediation of the effects of INTERLEUKINS and other CYTOKINES are emerging. (See all compounds classified as Immunosuppressive Agents.)
Histamine Antagonists
Drugs that bind to but do not activate histamine receptors, thereby blocking the actions of histamine or histamine agonists. Classical antihistaminics block the histamine H1 receptors only. (See all compounds classified as Histamine Antagonists.)
