

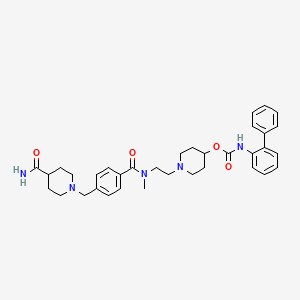

1. Biphenyl-2-ylcarbamic Acid 1-(2-((4-(4-carbamoylpiperidin-1-ylmethyl)benzoyl)methylamino)ethyl)piperidin-4-yl Ester
2. Td-4208
3. Yupelri
1. 864750-70-9
2. Td-4208
3. Yupelri
4. Gsk-1160724
5. Gsk1160724
6. Revefenacin [inn]
7. Revefenacin [who-dd]
8. G2ae2ve07o
9. 864750-70-9 (free Base)
10. [1-[2-[[4-[(4-carbamoylpiperidin-1-yl)methyl]benzoyl]-methylamino]ethyl]piperidin-4-yl] N-(2-phenylphenyl)carbamate
11. 1-(2-(4-((4-carbamoylpiperidin-1-yl)methyl)-n-methylbenzamido)ethyl)piperidin-4-yl N-((1,1'-biphenyl)-2-yl)carbamate
12. 1-(2-(3-((4-carbamoylpiperidin-1-yl)methyl)-n-methylbenzamido)ethyl)piperidin-4-yl [1,1'-biphenyl]-2-ylcarbamate
13. Biphenyl-2-ylcarbamic Acid, 1-(2-((4-(4-carbamoylpiperidin-1-ylmethyl)benzoyl)methylamino)ethyl)piperidin-4-yl Ester
14. Carbamic Acid, N-(1,1'-biphenyl)-2-yl-, 1-(2-((4-((4-(aminocarbonyl)-1-piperidinyl)methyl)benzoyl)methylamino)ethyl)-4-piperidinyl Ester
15. Td-4208; Gsk-1160724;[1-[2-[[4-[(4-carbamoylpiperidin-1-yl)methyl]benzoyl]-methylamino]ethyl]piperidin-4-yl] N-(2-phenylphenyl)carbamate
16. Revefenacin [mi]
17. Revefenacin (usan/inn)
18. Revefenacin [usan:inn]
19. Revefenacin [usan]
20. Unii-g2ae2ve07o
21. Revefenacin;gsk1160724
22. Schembl356480
23. Chembl3833319
24. Gtpl10129
25. Revefenacin [orange Book]
26. Dtxsid701027775
27. Hms3886k17
28. Amy16789
29. Bcp15793
30. Ex-a1722
31. S5258
32. Td4208
33. Akos037649398
34. Ccg-270187
35. Cs-7743
36. Db11855
37. Sb17262
38. Bs-18189
39. Hy-15851
40. Revefenacin; Td-4208; Gsk-1160724
41. D10978
42. A903445
43. Q27278649
44. Revefenacin; Td 4208; Td4208; Gsk-1160724; Gsk1160724; Gsk 1160724
45. 1-(2-(4-((4-carbamoylpiperidin-1-yl)methyl)-n-methylbenzamido)ethyl)piperidin-4-yl [1,1'-biphenyl]-2-ylcarbamate
46. 1211931-83-7
47. Td-4208; Td 4208; Td4208; Gsk-1160724; Gsk1160724;1-(2-(4-((4-carbamoylpiperidin-1-yl)methyl)-n-methylbenzamido)ethyl)piperidin-4-yl N-((1,1'-biphenyl)-2-yl)carbamate
| Molecular Weight | 597.7 g/mol |
|---|---|
| Molecular Formula | C35H43N5O4 |
| XLogP3 | 4.1 |
| Hydrogen Bond Donor Count | 2 |
| Hydrogen Bond Acceptor Count | 6 |
| Rotatable Bond Count | 11 |
| Exact Mass | 597.33150487 g/mol |
| Monoisotopic Mass | 597.33150487 g/mol |
| Topological Polar Surface Area | 108 Ų |
| Heavy Atom Count | 44 |
| Formal Charge | 0 |
| Complexity | 918 |
| Isotope Atom Count | 0 |
| Defined Atom Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Undefined Atom Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Defined Bond Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Undefined Bond Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Covalently Bonded Unit Count | 1 |
Revefenacin is indicated as an inhalation solution for the maintenance treatment of patients with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD). COPD is a growing disease being the third leading cause of death in the US. This disease is characterized by not fully reversible airflow limitation.
FDA Label
Revefenacin has been reported to produce a sustained, long-acting bronchodilation with lower anti-muscarinic-related side effects. In clinical trials, revefenacin demonstrated to be of a long duration of action and low systemic exposure in patients with COPD. Also, it was reported that a dose of 88 mcg can produce a clinically effective bronchodilation measured by through forced expiratory volume in 1s and serial spirometric assessments. In placebo-controlled trials, revefenacin showed a decrease in the use of albuterol rescue inhalers and sustained increases in the peak expiratory flow rate that reached a steady state at a maximum in day 7. As well, there was a reported superior lung selectivity index when compared with other LABAs such as glycopyrronium and tiotropium which produced a decreased sialagogue effect.
R - Respiratory system
R03 - Drugs for obstructive airway diseases
R03B - Other drugs for obstructive airway diseases, inhalants
R03BB - Anticholinergics
R03BB08 - Revefenacin
Absorption
In pharmacokinetic studies, revefenacin was absorbed very rapidly and presented a linear increase in plasma exposure with Cmax, tmax and AUC that ranged between 0.02-0.15 ng/ml, 0.48-0.51 hours and 0.03-0.36 ng.h/ml, respectively. The bioaccumulation of revefenacin was very limited and the steady-state was achieved by day 7.
Route of Elimination
After reaching maximum concentration, revefenacin concentrations decline in a biphasic manner. This elimination kinetics is observed by a rapid declining plasma concentration followed by a slow apparent bi-exponential elimination. Renal elimination of revefenacin is limited and it presents a mean cumulative amount excreted in urine as the unchanged drug of < 0.2% of the administered dose. Following intravenous revefenacin administration, 54% of the dose is recovered in feces and 27% was recovered in urine which confirms a high hepatobiliary processing.
Volume of Distribution
After intravenous administration of revefenacin, the reported volume of distribution is 218 L which suggests an extensive distribution to the tissues.
Clearance
The renal clearance of revefenacin is negligible and thus, the clearance rate is not a major parameter for this drug.
Revefenacin presents a high metabolic liability producing a rapid metabolic turnover after being distributed from the lung. This metabolic process is done primarily via enzymatic hydrolysis via CYP2D6 to its major hydrolytic metabolite THRX-195518.
The apparent terminal half-life of a dose of 350 mcg of revefenacin was 22.3-70 hours.
Revefenacin is an inhaled bronchodilator muscarinic antagonist with a long-acting bronchodilation activity. It has been shown to present a high affinity and behaved as a competitive antagonist of the five muscarinic cholinergic receptors. Studies have indicated that revefenacin dissociates significantly slower from the muscarinic receptor M3 (hM3) when compared to the receptor M2 (hM2) which indicates a kinetic selectivity for this subtype. This competitive antagonism produces a suppressive action of the acetylcholine-evoked calcium mobilization and contractile responses in the airway tissue. Lastly, due to the duration of the bronchodilation, revefenacin is considered a long-acting muscarinic antagonist which allows it to be dosed once daily. This response is very important for the therapy of COPD as the main goal is the reduce the frequency and severity of exacerbations which are normally driven by the presence of elevated cholinergic bronchoconstrictor tone mediated by muscarinic receptors on parasympathetic ganglia and airway smooth muscle. Hence, the activity of revefenacin produces a potent and long-lasting protection against the bronchoconstrictor response to acetylcholine or methacholine.
