

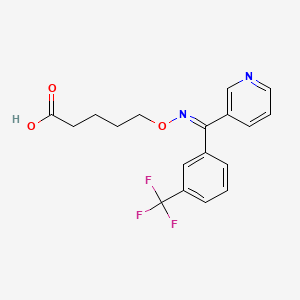

1. 5-((((3-pyridinyl)(3-(trifluoromethyl)phenyl)methylene)amino)oxy)pentanoic Acid
2. R 68,070
3. R 68070
4. R 70416
5. R-68070
6. R-70416
1. 110140-89-1
2. Ridogrelum [inn-latin]
3. R-68070
4. R 68070
5. Qts5qoo42o
6. 5-[(e)-[pyridin-3-yl-[3-(trifluoromethyl)phenyl]methylidene]amino]oxypentanoic Acid
7. Chembl280728
8. Ridogrelum
9. Pentanoic Acid, 5-(((3-pyridinyl(3-(trifluoromethyl)phenyl)methylene)amino)oxy)-, (e)-
10. Ibidel
11. 5-[[pyridin-3-yl-[3-(trifluoromethyl)phenyl]methylidene]amino]oxypenta Noic Acid
12. Ridogrel (usan/inn)
13. Unii-qts5qoo42o
14. Ridogrel [usan:inn:ban]
15. Ridogrel [usan]
16. Ridogrel [inn]
17. Ridogrel [mi]
18. Schembl11709
19. Dtxsid90872935
20. Chebi:135542
21. Hy-a0221
22. Bdbm50003795
23. Akos015951347
24. Db01207
25. (e)-5-(((alpha-3-pyridyl-m-(trifluoromethyl)benzylidene)amino)oxy)valeric Acid
26. Cs-0017567
27. Ec-000.2105
28. D05727
29. L001350
30. (e)-5-(((.alpha.-3-pyridyl-m-(trifluoromethyl)benzylidene)amino)oxy)valeric Acid
31. (e)-5-(pyridin-3-yl(3-(trifluoromethyl)phenyl)methyleneaminooxy)pentanoic Acid
32. 5-[1-pyridin-3-yl-1-(3-trifluoromethyl-phenyl)-meth-(e)-ylideneaminooxy]-pentanoic Acid
33. 5-[pyridin-3-yl-(3-trifluoromethyl-phenyl)-methyleneaminooxy]-pentanoic Acid
34. 5-{[(e)-{pyridin-3-yl[3-(trifluoromethyl)phenyl]methylidene}amino]oxy}pentanoic Acid
| Molecular Weight | 366.3 g/mol |
|---|---|
| Molecular Formula | C18H17F3N2O3 |
| XLogP3 | 3.9 |
| Hydrogen Bond Donor Count | 1 |
| Hydrogen Bond Acceptor Count | 8 |
| Rotatable Bond Count | 8 |
| Exact Mass | 366.11912689 g/mol |
| Monoisotopic Mass | 366.11912689 g/mol |
| Topological Polar Surface Area | 71.8 Ų |
| Heavy Atom Count | 26 |
| Formal Charge | 0 |
| Complexity | 483 |
| Isotope Atom Count | 0 |
| Defined Atom Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Undefined Atom Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Defined Bond Stereocenter Count | 1 |
| Undefined Bond Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Covalently Bonded Unit Count | 1 |
Used as an adjunctive therapy to induce thrombolysis in patients suffering acute myocardial infarction.
Ridogrel, a combined thromboxane synthase inhibitor and receptor antagonist, is used with streptokinase as an adjunctive therapy to reduce the formation and size of blood clots. Blood clots can cause ischemic cardiac events (heart attacks). Ridogrel has the dual property of inhibiting the synthesis of thromboxane and blocking the receptors of thromboxane/prostaglandin/endoperoxides. It has been shown to accelerate the speed of recanalization and to delay or prevent reocclusion during systemic thrombolysis with tissue plasminogen activator (streptokinase). Ridogrel is a more potent antiplatelet agent than aspirin and might offer an advantage over aspirin as an adjunct to thrombolysis in patients suffering from acute myocardial infarction. While aspirin inhibits cyclooxygenase, the enzyme responsible for producing thromboxane, ridogrel inhibits thromboxane synthesis directly. A recent comparison between aspirin and ridogrel in as adjunct to thrombolysis in patients with acute myocardial infarction demonstrated that ridogrel is not superior to aspirin in enhancing the fibrinolytic efficacy of streptokinase but might be more effective in preventing new ischemic events. Clinical experience with this drug is still relatively limited.
Enzyme Inhibitors
Compounds or agents that combine with an enzyme in such a manner as to prevent the normal substrate-enzyme combination and the catalytic reaction. (See all compounds classified as Enzyme Inhibitors.)
Platelet Aggregation Inhibitors
Drugs or agents which antagonize or impair any mechanism leading to blood platelet aggregation, whether during the phases of activation and shape change or following the dense-granule release reaction and stimulation of the prostaglandin-thromboxane system. (See all compounds classified as Platelet Aggregation Inhibitors.)
Gastrointestinal Agents
Drugs used for their effects on the gastrointestinal system, as to control gastric acidity, regulate gastrointestinal motility and water flow, and improve digestion. (See all compounds classified as Gastrointestinal Agents.)
Absorption
Rapidly absorbed after oral administration (30-60 min)
Ridogrel inhibits thromboxane A2 synthase and also blocks the thromboxane A2/prostaglandin endoperoxide receptors. Thromboxane synthetase produces thromboxane in platelets. Thromboxane is a vasoconstrictor and facilitates the clumping of platelets. Therefore by inhibiting the production and promotion of thromboxane, thrombolysis is enhanced.
