
1. 4-deoxy-4'-methylpyrido(1',2'-1,2)imidazo(5,4c)rifamycin
2. L 105
3. L-105
4. L105
5. Redactiv
6. Xifaxan
1. Rifaxidin
2. Rifacol
3. 80621-81-4
4. Rifamycin L 105
5. Xifaxan
6. Rifamycin L 105sv
7. Fatroximin
8. Rifaximine
9. Normix
10. Rifaximina
11. Xifaxsan
12. L-105
13. Rifamixin
14. Rifaximine [french]
15. Rifaximinum [latin]
16. Rifaximina [spanish]
17. Ritacol
18. Chebi:75246
19. 4-deoxy-4'-methylpyrido(1',2'-1,2)imidazo(5,4-c)rifamycin Sv
20. L36o5t016n
21. Rifaximin (xifaxan)
22. Nsc-758957
23. Rifaximinum
24. Brn 3584528
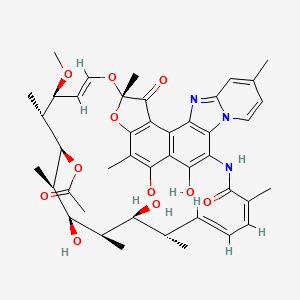
25. (2s,16z,18e,20s,21s,22r,23r,24r,25s,26r,27s,28e)-5,6,21,23-tetrahydroxy-27-methoxy-2,4,11,16,20,22,24,26-octamethyl-1,15-dioxo-1,2-dihydro-2,7-(epoxypentadeca[1,11,13]trienoimino)furo[2'',3'':7',8']naphtho[1',2':4,5]imidazo[1,2-a]pyridin-25-yl Acetate
26. C43h51n3o11
27. Rifaxin
28. Redactiv
29. Ido[1,2-a]benzimidazol-25-yl Acetate
30. (2s,16z,18e,20s,21s,22r,23r,24r,25s,26r,27s,28e)-25-(acetyloxy)-5,6,21,23-tetrahydroxy-27-methoxy-2,4,11,16,20,22,24,26-octamethyl-2,7-(epoxypentadeca[1,11,13]trienimino)benzofuro[4,5-e]pyrido[1,2-a]benzimidazole-1,15(2h)-dione
31. L 105sv
32. L 105 (ansamacrolide Antibiotic)
33. L 105
34. Rifaximinun
35. Flonorm
36. Lumenax
37. Spiraxin
38. Lormyx
39. Rifaximin [usan:inn:ban]
40. Unii-l36o5t016n
41. 5-yl Acetate
42. Ncgc00095842-01
43. (2s,16z,18e,20s,21s,22r,23r,24r,25s,26r,27s,28e)-25-(acetyloxy)-5,6,21,23-tetrahydroxy-27-methoxy-2,4,11,16,20,22,24,26-octamethyl-2,7-(epoxypentadeca(1,11,13)trienimino)benzofuro(4,5-e)pyrido(1,2-a)benzimidazole-1,15(2h)-dione
44. (2s,16z,18e,20s,21s,22r,23r,24r,25s,26r,27s,28e)5,6,21,23-tetrahydroxy-27-methoxy-2,4,11,16,20,22,24,26-octamethyl-1,15-dioxo-1,2-dihydro-2,7-(epoxypentadeca[1,11,13]trienoimino)[1]benzofuro[4,5-e]pyr
45. Xifaxan (tn)
46. Mfcd00864973
47. Rifaximin [inn]
48. Rifaximin [jan]
49. Rifaximin [mi]
50. Rifaximin [usan]
51. Rifaximin [vandf]
52. Rifaximin [mart.]
53. Alpha-0817185
54. Rifaximin [who-dd]
55. Chembl1617
56. Dsstox_cid_25998
57. Dsstox_rid_81280
58. Dsstox_gsid_45998
59. (2s,16z,18e,20s,21s,22r,23r,24r,25s,26s,27s,28e)-5,6,21,23,25 Pentahydroxy-27-methoxy-2,4,11,16,20,22,24,26-octamethyl-2,7-(epoxypentadeca(1,11,13)trienimino)benzofuro(4,5-e)pyrido(1,2-a)benzimidazole-1,15(2h)-dione, 25-acetate
60. Rifaximin (jan/usan/inn)
61. Schembl124066
62. Rifaximin [ep Impurity]
63. Rifaximin [orange Book]
64. Dtxsid7045998
65. Rifaximin [ep Monograph]
66. Gtpl12012
67. Hms3715b19
68. 88747-56-2
69. Tox21_111529
70. Bdbm50347620
71. S1790
72. Akos015963053
73. Zinc169621200
74. Ccg-221129
75. Db01220
76. Nsc 758957
77. Rifaximin 100 Microg/ml In Acetonitrile
78. 2,7-(epoxy(1,11,13)pentadecatrienoimino)furo(2'',3'':7',8')naphth(1',2':4,5)imidazo(1,2-a)pyridine-1,15(2h)-dione, 25-(acetyloxy)-5,6,21,23-tetrahydroxy-27-methoxy-2,4,11,16,20,22,24,26-octamethyl-, ( 2s,16z,18e,20s,21s,22r,23r,24r,25s,26r,27s,28e)-
79. 2,7-(epoxypentadeca(1,11,13)trienimino)benzofuro(4,5-e)pyrido(1,2-a)benzimidazole-1,15(2h)-dione, 25-(acetyloxy)-5,6,21,23-tetrahydroxy-27-methoxy-2,4,11,16,20,22,24,26-octamethyl-, (2s-(2r*,16z,18e,20r*,21r*,22s*,23s*,24s*,25r*,26s*,27r*,28e))-
80. Ac-19112
81. Cas-80621-81-4
82. L/105
83. D02554
84. Ab01209738-01
85. Ab01209738-03
86. Ab01209738_04
87. Rifaximin, Antibiotic For Culture Media Use Only
88. 621r814
89. Q416073
90. Q-201671
91. (2s,16z,18e,20s,21s,22r,23r,24r,25s,26r,27s,28e)-5,6,21,23-tetrahydroxy-27-methoxy-2,4,11,16,20,22,24,26-octamethyl-1,1
92. (7s,11s,12r,13s,14r,15r,16r,17s,18s)-2,15,17,36-tetrahydroxy-11-methoxy-3,7,12,14,16,18,22,30-octamethyl-6,23-dioxo-8,37-dioxa-24,27,33-triazahexacyclo[23.10.1.1^{4,7}.0^{5,35}.0^{26,34}.0^{27,32}]heptatriaconta-1,3,5(35),9,19,21,25(36),26(34),28,30,32-undecaen-13-yl Acetate
93. [(7s,9e,11s,12r,13s,14r,15r,16r,17s,18s,19e,21z)-2,15,17,36-tetrahydroxy-11-methoxy-3,7,12,14,16,18,22,30-octamethyl-6,23-dioxo-8,37-dioxa-24,27,33-triazahexacyclo[23.10.1.14,7.05,35.026,34.027,32]heptatriaconta-1(35),2,4,9,19,21,25(36),26(34),28,30,32-undecaen-13-yl] Acetate
94. 2,7-(epoxypentadeca(1,11,13)trienimino)benzofuro(4,5-e)pyrido(1,2-a)benzimidazole-1,15(2h)-dione, 25-(acetyloxy)-5,6,21,23-tetrahydroxy-27-methoxy-2,4,11,16,20,22,24,26-octamethyl-, (2s,16z,18e,20s,21s,22r,23r,24r,25s,26r,27s,28e)-
95. 5-dioxo-1,2-dihydro-2,7-(epoxypentadeca[1,11,13]trienoimino)furo[2'',3'':7',8']naphtho[1',2':4,5]imidazo[1,2-a]pyridin-2
| Molecular Weight | 785.9 g/mol |
|---|---|
| Molecular Formula | C43H51N3O11 |
| XLogP3 | 6.9 |
| Hydrogen Bond Donor Count | 5 |
| Hydrogen Bond Acceptor Count | 12 |
| Rotatable Bond Count | 3 |
| Exact Mass | 785.35235945 g/mol |
| Monoisotopic Mass | 785.35235945 g/mol |
| Topological Polar Surface Area | 198 Ų |
| Heavy Atom Count | 57 |
| Formal Charge | 0 |
| Complexity | 1590 |
| Isotope Atom Count | 0 |
| Defined Atom Stereocenter Count | 9 |
| Undefined Atom Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Defined Bond Stereocenter Count | 3 |
| Undefined Bond Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Covalently Bonded Unit Count | 1 |
| 1 of 2 | |
|---|---|
| Drug Name | Xifaxan |
| PubMed Health | Rifaximin (By mouth) |
| Drug Classes | Antibiotic |
| Drug Label | XIFAXAN tablets contain rifaximin, a non-aminoglycoside semi-synthetic, nonsystemic antibiotic derived from rifamycin SV. Rifaximin is a structural analog of rifampin. The chemical name for rifaximin is (2 ,16 ,18 ,20 ,21 ,22 ,23 ,24 ,25 ,26 ,27... |
| Active Ingredient | Rifaximin |
| Dosage Form | Tablet |
| Route | Oral |
| Strength | 200mg; 550mg |
| Market Status | Prescription |
| Company | Salix Pharms |
| 2 of 2 | |
|---|---|
| Drug Name | Xifaxan |
| PubMed Health | Rifaximin (By mouth) |
| Drug Classes | Antibiotic |
| Drug Label | XIFAXAN tablets contain rifaximin, a non-aminoglycoside semi-synthetic, nonsystemic antibiotic derived from rifamycin SV. Rifaximin is a structural analog of rifampin. The chemical name for rifaximin is (2 ,16 ,18 ,20 ,21 ,22 ,23 ,24 ,25 ,26 ,27... |
| Active Ingredient | Rifaximin |
| Dosage Form | Tablet |
| Route | Oral |
| Strength | 200mg; 550mg |
| Market Status | Prescription |
| Company | Salix Pharms |
Rifaximin has multiple indications by the FDA: for the treatment of patients (12 years of age) with traveller's diarrhea caused by noninvasive strains of Escherichia coli; for the reduction of overt hepatic encephalopathy recurrence in patients 18 years of age; and in May 2015 it was approved for irritable bowel syndrome with diarrhea (IBS-D) treatment in adult men and women.
FDA Label
Rifaximin is a structural analog of rifampin and a non-systemic, gastrointestinal site-specific antibiotic. This non-systemic property of the drug is due to the addition of a pyridoimidazole ring, which renders it non-absorbable. Rifaximin acts by inhibiting bacterial ribonucleic acid (RNA) synthesis and contributes to restore intestinal microflora imbalance. Other studies have also shown rifaximin to be an pregnane X receptor (PXR) activator. As PXR is responsible for inhibiting the proinflammatory transcription factor NF-kappa B (NF-B) and is inhibited in inflammatory bowel disease (IBD), rifaximin was proven to be effective for the treatment of IBS-D.
Anti-Bacterial Agents
Substances that inhibit the growth or reproduction of BACTERIA. (See all compounds classified as Anti-Bacterial Agents.)
Gastrointestinal Agents
Drugs used for their effects on the gastrointestinal system, as to control gastric acidity, regulate gastrointestinal motility and water flow, and improve digestion. (See all compounds classified as Gastrointestinal Agents.)
A07AA11
S76 | LUXPHARMA | Pharmaceuticals Marketed in Luxembourg | Pharmaceuticals marketed in Luxembourg, as published by d'Gesondheetskeess (CNS, la caisse nationale de sante, www.cns.lu), mapped by name to structures using CompTox by R. Singh et al. (in prep.). List downloaded from https://cns.public.lu/en/legislations/textes-coordonnes/liste-med-comm.html. Dataset DOI:10.5281/zenodo.4587355
A - Alimentary tract and metabolism
A07 - Antidiarrheals, intestinal antiinflammatory/antiinfective agents
A07A - Intestinal antiinfectives
A07AA - Antibiotics
A07AA11 - Rifaximin
D - Dermatologicals
D06 - Antibiotics and chemotherapeutics for dermatological use
D06A - Antibiotics for topical use
D06AX - Other antibiotics for topical use
D06AX11 - Rifaximin
Absorption
Low absorption in both the fasting state and when administered within 30 minutes of a high-fat breakfast.
Route of Elimination
In a mass balance study, after administration of 400 mg 14C-rifaximin orally to healthy volunteers, of the 96.94% total recovery, 96.62% of the administered radioactivity was recovered in feces almost exclusively as the unchanged drug and 0.32% was recovered in urine mostly as metabolites with 0.03% as the unchanged drug.Rifaximin accounted for 18% of radioactivity in plasma. This suggests that the absorbed rifaximin undergoes metabolism with minimal renal excretion of the unchanged drug
In vitro drug interactions studies have shown that rifaximin, at concentrations ranging from 2 to 200 ng/mL, did not inhibit human hepatic cytochrome P450 isoenzymes: 1A2, 2A6, 2B6, 2C9, 2C19, 2D6, 2E1, and 3A4. In an in vitro hepa-tocyte induction model, rifaximin was shown to induce cytochrome P450 3A4 (CYP3A4), an isoenzyme which rifampin is known to induce.
Approximately 6 hours.
Rifaximin acts by inhibiting RNA synthesis in susceptible bacteria by binding to the beta-subunit of bacterial deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA)-dependent ribonucleic acid (RNA) polymerase enzyme. This binding blocks translocation, which stops transcription.