
1. 278, Tmc
2. Hcl, Rilpivirine
3. Hydrochloride, Rilpivirine
4. R278474
5. Rilpivirine Hcl
6. Rilpivirine Hydrochloride
7. Tmc 278
8. Tmc-278
9. Tmc278
1. 500287-72-9
2. Tmc278
3. Edurant
4. Rilpivirine Free Base
5. R278474
6. Tmc 278
7. Tmc-278
8. R 278474
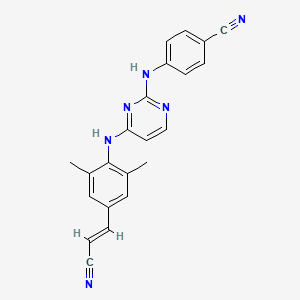
9. (e)-4-((4-((4-(2-cyanovinyl)-2,6-dimethylphenyl)amino)pyrimidin-2-yl)amino)benzonitrile
10. (e)-4-(4-(4-(2-cyanovinyl)-2,6-dimethylphenylamino)pyrimidin-2-ylamino)benzonitrile
11. 4-{[4-({4-[(e)-2-cyanoethenyl]-2,6-dimethylphenyl}amino)pyrimidin-2-yl]amino}benzonitrile
12. 4-{[4-({4-[(e)-2-cyanovinyl]-2,6-dimethylphenyl}amino)pyrimidin-2-yl]amino}benzonitrile
13. Chebi:68606
14. Fi96a8x663
15. 500287-72-9 (free Base)
16. 4-[[4-[[4-[(e)-2-cyanoethenyl]-2,6-dimethyl-phenyl]amino]pyrimidin-2-yl]amino]benzonitrile
17. Db08864
18. R-278474
19. Rilpivirine [inn]
20. Rilpivirine [usan:inn]
21. Rilpivirina
22. Unii-fi96a8x663
23. Hsdb 8153
24. Edurant(tm)
25. 4-((4-((4-((1e)-2-cyanoethenyl)-2,6-dimethylphenyl)amino)-2-pyrimidinyl)amino)benzonitrile
26. 4-[[4-[[4-[(1e)-2-cyanoethenyl]-2,6-dimethylphenyl]amino]-2-pyrimidinyl]amino]benzonitrile
27. T27
28. Rilpivirine [mi]
29. Rilpivirine [jan]
30. Rilpivirine [usan]
31. Rilpivirine [vandf]
32. Rilpivirine [mart.]
33. Rilpivirine [who-dd]
34. Schembl384696
35. Schembl385113
36. Rilpivirine (jan/usan/inn)
37. Chembl175691
38. Gtpl11387
39. Dtxsid10198189
40. Ex-a245
41. Rilpivirine [orange Book]
42. Bdbm222178
43. Bcp03563
44. Zinc1554274
45. Cabenuva Component Rilpivirine
46. Mfcd11046372
47. S7303
48. Stl484047
49. Akos015901680
50. Bcp9000016
51. Ccg-268241
52. Cs-0440
53. Ke-0036
54. R278474;tmc278
55. 4-[[4-[4-[(e)-2-cyanovinyl]-2,6-dimethyl-anilino]pyrimidin-2-yl]amino]benzonitrile
56. Rilpivirine Component Of Cabenuva
57. Ncgc00319175-03
58. Ncgc00319175-08
59. Rilpivirine(r 278474, Tmc 278)
60. Ac-30619
61. Hy-10574
62. Bcp0726000192
63. Sw220232-1
64. D09720
65. A827939
66. Q421547
67. W-202888
68. 4-[[4-[[4-(2-cyanoethenyl)-2,6-dimethylphenyl]amino]pyrimidine-2-yl]amino]benzonitrile
69. 4-[[4-[4-[(e)-2-cyanoethenyl]-2,6-dimethylanilino]-2-pyrimidinyl]amino]benzonitrile
70. 4-{4-[4-((e)-2-cyano-vinyl)-2,6-dimethyl-phenylamino]-pyrimidin-2-ylamino}-benzonitrile
71. (e)-3-{4-[2-(p-cyanophenylamino)-4-pyrimidinylamino]-3,5-xylyl}acrylonitrile; 4-[[4-[[4-[(1e)-2-cyanoethenyl]-2,6-dimethylphenyl]amino]-2-pyrimidinyl]amino]benzonitrile
72. 4-((4-((4-((1e)-2-cyanoethenyl)-2,6-dimethylphenyl)amino)pyrimidin-2-yl)amino)benzonitrile
73. 4-[[4-[[4-[(e)-2-cyanoethenyl]-2,6-dimethyl-phenyl]amino]pyrimidin-2-yl]amino]benzenecarbonitrile
74. Benzonitrile, 4-((4-((4-((1e)-2-cyanoethenyl)-2,6-dimethylphenyl)amino)-2- Pyrimidinyl)amino)-
75. Benzonitrile, 4-((4-((4-((1e)-2-cyanoethenyl)-2,6-dimethylphenyl)amino)-2-pyrimidinyl)amino)-
| Molecular Weight | 366.4 g/mol |
|---|---|
| Molecular Formula | C22H18N6 |
| XLogP3 | 4.5 |
| Hydrogen Bond Donor Count | 2 |
| Hydrogen Bond Acceptor Count | 6 |
| Rotatable Bond Count | 5 |
| Exact Mass | 366.15929460 g/mol |
| Monoisotopic Mass | 366.15929460 g/mol |
| Topological Polar Surface Area | 97.4 Ų |
| Heavy Atom Count | 28 |
| Formal Charge | 0 |
| Complexity | 607 |
| Isotope Atom Count | 0 |
| Defined Atom Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Undefined Atom Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Defined Bond Stereocenter Count | 1 |
| Undefined Bond Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Covalently Bonded Unit Count | 1 |
| 1 of 2 | |
|---|---|
| Drug Name | Edurant |
| PubMed Health | Rilpivirine (By mouth) |
| Drug Classes | Antiretroviral Agent |
| Active Ingredient | Rilpivirine hydrochloride |
| Dosage Form | Tablet |
| Route | Oral |
| Strength | eq 25mg base |
| Market Status | Prescription |
| Company | Janssen Prods |
| 2 of 2 | |
|---|---|
| Drug Name | Edurant |
| PubMed Health | Rilpivirine (By mouth) |
| Drug Classes | Antiretroviral Agent |
| Active Ingredient | Rilpivirine hydrochloride |
| Dosage Form | Tablet |
| Route | Oral |
| Strength | eq 25mg base |
| Market Status | Prescription |
| Company | Janssen Prods |
HIV Reverse Transcriptase/antagonists & inhibitors
National Library of Medicine's Medical Subject Headings. Rilpivirine. Online file (MeSH, 2014). Available from, as of November 19, 2013: https://www.nlm.nih.gov/mesh/2014/mesh_browser/MBrowser.html
Due to ongoing neuropsychiatric adverse events in some efavirenz (EFV)-treated patients, a switch to an alternative non-nucleoside reverse transcriptase inhibitor may be considered. Rilpivirine (RPV) has been coformulated as a single-tablet regimen (STR) with emtricitabine/tenofovir disoproxil fumarate (FTC/TDF), and the components have demonstrated noninferior efficacy to EFV+FTC/TDF, good tolerability profile, and high adherence. After discontinuation, EFV has an extended inductive effect on cytochrome P450 (CYP) 3A4 that, after switching, may reduce RPV exposures and adversely impact clinical outcomes. This study examines the clinical implications of reduced RPV exposures with concomitant FTC/TDF and declining EFV exposures when patients, intolerant to EFV, switch from EFV/FTC/TDF to RPV/FTC/TDF. This 48-week, phase 2b, open-label, multicenter study evaluated the efficacy and safety of switching from EFV/FTC/TDF (>/= 3 months duration) to RPV/FTC/TDF. Virologic suppression (HIV-1 RNA <50 copies/mL), safety, and EFV and RPV pharmacokinetics were assessed. At weeks 12 and 24, all 49 dosed subjects remained suppressed on RPV/FTC/TDF. At week 48, 46 (93.9%) subjects remained suppressed and virologic failure occurred in 2/49 (4.1%) subjects with no emergence of resistance. EFV concentrations were above the 90th percentile for inhibitory concentration (IC90) for several weeks after EFV discontinuation, and RPV exposures were in the range observed in phase 3 studies by approximately 2 weeks post switch. No subjects discontinued the study due to an adverse event. Switching from EFV/FTC/TDF to RPV/FTC/ TDF was a safe, efficacious option for virologically suppressed HIV-infected patients with EFV intolerance wishing to remain on an STR.
PMID:24144898 Mills AM et al; HIV Clin Trials 14 (5): 216-23 (2013)
Adverse effects of moderate or severe intensity and reported in 2% or more of patients receiving rilpivirine include depressive disorders, insomnia, headache, and rash. Increased serum AST and/or ALT concentrations (more than 2.5 times the upper limit of normal (ULN) were reported in 3-4% of patients receiving rilpivirine.
American Society of Health-System Pharmacists 2013; Drug Information 2013. Bethesda, MD. 2013, p. 680
Rilpivirine should be used with caution and with increased monitoring for adverse effects in patients with severe renal impairment or end-stage renal disease since concentrations of the drug may be increased due to alterations in absorption, distribution, or metabolism.
American Society of Health-System Pharmacists 2013; Drug Information 2013. Bethesda, MD. 2013, p. 680
Rilpivirine and the fixed combination containing rilpivirine, emtricitabine, and tenofovir (Complera) have not been studied in patients with severe hepatic impairment (Child-Pugh class C).
American Society of Health-System Pharmacists 2013; Drug Information 2013. Bethesda, MD. 2013, p. 680
Experience in those 65 years of age and older is insufficient to determine whether they respond differently than younger adults. Dosage should be selected with caution because of age-related decreases in hepatic and/or renal function and potential for concomitant disease and drug therapy.
American Society of Health-System Pharmacists 2013; Drug Information 2013. Bethesda, MD. 2013, p. 680
For more Drug Warnings (Complete) data for Rilpivirine (13 total), please visit the HSDB record page.
Rilpivirine, in combination with other agents, is indicated for the treatment of HIV-1 infections in antiretroviral treatment-naive patients with HIV-1 RNA 100,000 copies/mL and CD4+ cell count >200 cells/mm3. The FDA combination therapy approval of rilpivirine and dolutegravir is indicated for adults with HIV-1 infections whose virus is currently suppressed (< 50 copies/ml) on a stable regimen for at least six months, without history of treatment failure and no known substitutions associated to resistance to any of the two components of the therapy.
FDA Label
Edurant, in combination with other antiretroviral medicinal products, is indicated for the treatment of human immunodeficiency virus type 1 (HIV1) infection in antiretroviral treatmentnave patients 12 years of age and older with a viral load 100,000 HIV1 RNA copies/ml.
As with other antiretroviral medicinal products, genotypic resistance testing should guide the use of Edurant.
Treatment of human immunodeficiency virus (HIV-1) infection
Rekambys is indicated, in combination with cabotegravir injection, for the treatment of human immunodeficiency virus type 1 (HIV 1) infection in adults who are virologically suppressed (HIV-1 RNA < 50 copies/mL) on a stable antiretroviral regimen without present or past evidence of viral resistance to, and no prior virological failure with, agents of the NNRTI and INI class.
Rilpivirine is a non-nucleoside reverse transcriptase inhibitor that inhibits the replication of HIV-1. It has a long duration of action as the oral tablet is given daily and the intramuscular suspension is given monthly. Patients should be counselled regarding the risk of hypersensitivity reactions, hepatotoxicity, depressive disorders, and the redistribution or accumulation of body fat.
Anti-HIV Agents
Agents used to treat AIDS and/or stop the spread of the HIV infection. These do not include drugs used to treat symptoms or opportunistic infections associated with AIDS. (See all compounds classified as Anti-HIV Agents.)
Reverse Transcriptase Inhibitors
Inhibitors of reverse transcriptase (RNA-DIRECTED DNA POLYMERASE), an enzyme that synthesizes DNA on an RNA template. (See all compounds classified as Reverse Transcriptase Inhibitors.)
J05AG05
J05AG05
J05AG05
S76 | LUXPHARMA | Pharmaceuticals Marketed in Luxembourg | Pharmaceuticals marketed in Luxembourg, as published by d'Gesondheetskeess (CNS, la caisse nationale de sante, www.cns.lu), mapped by name to structures using CompTox by R. Singh et al. (in prep.). List downloaded from https://cns.public.lu/en/legislations/textes-coordonnes/liste-med-comm.html. Dataset DOI:10.5281/zenodo.4587355
J - Antiinfectives for systemic use
J05 - Antivirals for systemic use
J05A - Direct acting antivirals
J05AG - Non-nucleoside reverse transcriptase inhibitors
J05AG05 - Rilpivirine
Absorption
Rilpivirine has a Tmax of 3-4 hours and has a mean AUC of 2235 851 ng\*h/mL. A 25mg dose reaches a Cmax of 247 ng/mL in healthy subjects and 138.6 ng/mL in patients with HIV-1.
Route of Elimination
Rilpivirine is 85% eliminated in the feces and 6.1% eliminated in the urine. 25% of a dose is recovered in the feces as the unchanged parent drug, while <1% of a dose is recovered in the urine as the unchanged parent drug.
Volume of Distribution
In HIV-1 patients, the apparent volume of distribution in the central compartment was 152-173 L.
Clearance
In HIV-1 patients, the apparent total clearance is estimated to be 6.89-8.66 L/h.
After a single oral dose, an average of 85% of the dose is eliminated in feces (75% as metabolites) and 6% is eliminated in urine (only trace amounts as unchanged rilpivirine).
American Society of Health-System Pharmacists 2013; Drug Information 2013. Bethesda, MD. 2013, p. 681
It is not known whether rilpivirine is distributed into human milk; however, the drug is distributed into milk in rats.
American Society of Health-System Pharmacists 2013; Drug Information 2013. Bethesda, MD. 2013, p. 680
Rilpivirine is predominantly metabolized by CYP3A4 and CYP3A5 to the hydroxylated metabolites M1, M2, M3, and M4. UGT1A1 glucuronidates the M2 metabolite to form M6, UGT1A4 glucuronidates rilpivirine to form M5, and an unknown UGT glucuronidates the M4 metabolite to form M7.
Rilpivirine is metabolized by the cytochrome P-450 (CYP) isoenzyme 3A.
American Society of Health-System Pharmacists 2013; Drug Information 2013. Bethesda, MD. 2013, p. 680
Rilpivirine has a terminal half-life of 34-55 hours.
The terminal elimination half-life of rilpivirine is approximately 50 hours.
American Society of Health-System Pharmacists 2013; Drug Information 2013. Bethesda, MD. 2013, p. 681
Rilpivirine is a non-competitive NNRTI that binds to reverse transcriptase. Its binding results in the blockage of RNA and DNA- dependent DNA polymerase activities, like HIV-1 replication. It does not present activity against human DNA polymerases , and . Rilpivirine's flexible structure around the aromatic rings allows the adaptation to changes in the non-nucleoside RT binding pocket, reducing the likelihood of viral mutations conferring resistance.
Rilpivirine, a diarylpyrimidine nonnucleoside reverse transcriptase inhibitor (NNRTI), inhibits replication of human immunodeficiency virus type 1 (HIV-1) by interfering with viral RNA- and DNA-directed polymerase activities of reverse transcriptase. Diarylpyrimidine NNRTIs (e.g., rilpivirine, etravirine) are capable of adapting to mutations in HIV-1 reverse transcriptase because of structural flexibility that allows for binding to the allosteric NNRTI binding pocket in a variety of conformations. Unlike other currently available NNRTIs, rilpivirine contains a cyanovinyl group that contributes to potency and maintains the drug's binding ability, despite the emergence of some resistance mutations.
American Society of Health-System Pharmacists 2013; Drug Information 2013. Bethesda, MD. 2013, p. 681