


1. Glanatec
2. K-115
3. K115 Compound
1. 223645-67-8
2. K-115 Free Base
3. K115 Free Base
4. Ripasudil [inn]
5. Ripasudil Free Base
6. K-115 (free Base)
7. Chembl3426621
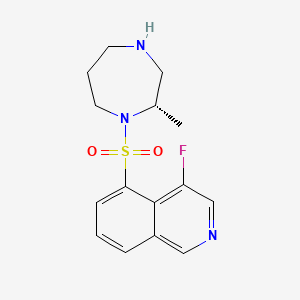
8. 4-fluoro-5-[[(2s)-2-methyl-1,4-diazepan-1-yl]sulfonyl]isoquinoline
9. 11978226xx
10. (s)-4-fluoro-5-((2-methyl-1,4-diazepan-1-yl)sulfonyl)isoquinoline
11. 1h-1,4-diazepine, 1-((4-fluoro-5-isoquinolinyl)sulfonyl)hexahydro-2-methyl-, (2s)-
12. Isoquinoline, 4-fluoro-5-(((2s)-hexahydro-2-methyl-1h-1,4-diazepin-1-yl)sulfonyl)-
13. Unii-11978226xx
14. K 115 Free Base
15. Ripasudil [mi]
16. Ripasudil [who-dd]
17. Schembl31542
18. Gtpl10423
19. Chebi:136046
20. Dtxsid001025609
21. Bcp11083
22. Ex-a3647
23. Zinc3940873
24. Bdbm50087135
25. Hy-15685a
26. Mfcd28291829
27. Nsc800869
28. Cs-3402
29. Db13165
30. Nsc-800869
31. Ncgc00496843-01
32. Ac-36873
33. As-35170
34. K-115 (ripasudil Hydrochloride Dihydrate)
35. Q21098890
36. (s)-(-)-1-(4-fluoro-5-isoquinolinesulfonyl)-2-methyl-1,4-homopiperazine
37. 4-fluoro-5-[[(2s)-2beta-methylhexahydro-1h-1,4-diazepine-1-yl]sulfonyl]isoquinoline
| Molecular Weight | 323.4 g/mol |
|---|---|
| Molecular Formula | C15H18FN3O2S |
| XLogP3 | 1.5 |
| Hydrogen Bond Donor Count | 1 |
| Hydrogen Bond Acceptor Count | 6 |
| Rotatable Bond Count | 2 |
| Exact Mass | 323.11037616 g/mol |
| Monoisotopic Mass | 323.11037616 g/mol |
| Topological Polar Surface Area | 70.7 Ų |
| Heavy Atom Count | 22 |
| Formal Charge | 0 |
| Complexity | 482 |
| Isotope Atom Count | 0 |
| Defined Atom Stereocenter Count | 1 |
| Undefined Atom Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Defined Bond Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Undefined Bond Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Covalently Bonded Unit Count | 1 |
Ripasudil has been proven to be effective in the twice daily treatment of glaucoma and ocular hypertension. It is currently in studies to be approved for both diabetic retinopathy and diabetic macular oedema.
Treatment of corneal dystrophy
Ripasudil has high intraocular permeability and works by decreasing intraocular pressure (IOP) in a dose-dependent manner and increasing flow facility. The maximum reduction of IOP occurs after 1 to 2 hours.
S - Sensory organs
S01 - Ophthalmologicals
S01E - Antiglaucoma preparations and miotics
S01EX - Other antiglaucoma preparations
S01EX07 - Ripasudil
Route of Elimination
Riapsudil is cleared by the kidneys at a rate of 7.112L/h.
Clearance
Ripasudil has a renal clearance of 7.112 L/h.
The half life of Ripasudil is 0.455 hrs.
Ripasudil is a highly selective and potent Rho-associated coiled/coil-containing kinase protein (ROCK) inhibitor. Rho-kinase (ROCK) is an effector protein of Rho which binds with Rho to form a Rho/Rho-kinase complex. This complex then regulates many physiological functions including smooth muscle contractions, chemotaxis, neural growth and gene expression. ROCK comes in 2 isoforms: ROCK-1 and ROCK-2 and these two isoforms are distributed widely in our tissues including ocular tissues such as the iris, retina, trabecular meshwork and ciliary muscles. Atypical regulation of ROCK levels is involved in the pathogenesis of diseases such as glaucoma, ocular hypertension, cataracts and other retinal disorders. Ripasudil acts as very highly selective and potent inhibitor with an IC50 of Ripasudil with ROCK-1 of 0.051 umol/L and with ROCK-2 of 0.019 umol/L. ROCK inhibitors have efficacy in reducing IOP by acting on the trabecular meshwork in the eye directly to increase conventional outflow through the Schlemms canal. Ripasudil will inhibit ROCK and induce cytoskeletal changes including the retraction and rounding of cell bodies and cause disruption of actin bundles in this trabecular meshwork. This can reduce the compaction of trabecular meshwork tissue and eventually result in increased aqueous outflow in the eye and reduced resistance to fluid flow. Thus, Ripasudil is effective by inducing cytoskeletal changes which are depending on ROCK inhibition. Ripasudil decreases IOP by increasing outflow facility along with modulating the behavior of trabecular meshwork cells and Schlemms canal endothelial (SCE) cell permeability along with a disruption of the tight junction. When Ripasudil is used in combination with prostaglandin analogues it results in increased uveoscleral outflow and when used in combination with beta blockers it results in reduced aqueous production.