

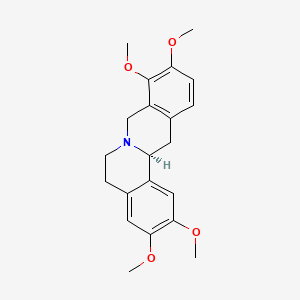

1. (+-)-isomer Of Tetrahydropalmatine
2. (r)-isomer; Corydalis B Of Tetrahydropalmatine
3. (s)-isomer Of Tetrahydropalmatine
4. 5,8,13,13a-tetrahydro-2,3,9,10-tetramethoxy-6h-dibenzo(a,g)quinolizine
5. Corydalis B
6. Gindarin
7. Hcl Of Tetrahydropalmatine
8. Hcl(+-)-isomer Of Tetrahydropalmatine
9. Hcl(r)-isomer Of Tetrahydropalmatine
10. Hcl(s)-isomer Of Tetrahydropalmatine
11. Levo-tetrahydropalmatine
12. Rotundine
13. Rotundium
14. Tetrahydropalmitine
1. Rotundine
2. 483-14-7
3. L-tetrahydropalmatine
4. (-)-tetrahydropalmatine
5. Gindarine
6. Caseanine
7. Hyndarine
8. (s)-tetrahydropalmatine
9. (-)-corydalis B
10. (-)-rotundine
11. (s)-(-)-tetrahydropalmatine
12. (13as)-2,3,9,10-tetramethoxy-6,8,13,13a-tetrahydro-5h-isoquinolino[2,1-b]isoquinoline
13. Tetrahydropalmatine, L-
14. (s)-2,3,9,10-tetramethoxy-6,8,13,13a-tetrahydro-5h-isoquinolino[3,2-a]isoquinoline
15. Tetrahydropalmatine, (-)-
16. Chebi:16563
17. 3x69co5i79
18. 2,3,9,10-tetramethoxy-13aalpha-berbine
19. Hyndarin
20. (-)-corydalis
21. (13as)-2,3,9,10-tetramethoxy-5,8,13,13a-tetrahydro-6h-isoquino[3,2-a]isoquinoline
22. Tetrahydropalmatine, Dl-
23. Nsc36363
24. 5,8,13,13a-tetrahydro-2,3,9,10-tetramethoxy-6h-dibenzo(a,g)quinolizine
25. Berbine, 2,3,9,10-tetramethoxy-
26. (-)-s-tetrahydropalmatine
27. Unii-3x69co5i79
28. 2,3,9,10-tetramethoxyberbine
29. 13a-alpha-berbine, 2,3,9,10-tetramethoxy-
30. (-)-2,3,9,10-tetramethoxyberbine
31. Tetrahydropalmatine L-form
32. (s)-5,8,13,13a-tetrahydro-2,3,9,10-tetramethoxy-6h-dibenzo(a,g)quinolizine
33. 6h-dibenzo(a,g)quinolizine, 5,8,13,13a-tetrahydro-2,3,9,10-tetramethoxy-, (s)-
34. Schembl230850
35. Chembl487182
36. Dtxsid701020650
37. Hms3656m19
38. Hms3884j17
39. Hy-n0096
40. Tetrahydropalmatine [who-dd]
41. Bdbm50424077
42. Mfcd03265591
43. S2437
44. Zinc19535049
45. Akos000277105
46. Ac-8007
47. Ccg-268100
48. Cs-8092
49. Db12093
50. Tetrahydropalmatine L-form [mi]
51. 6h-dibenzo[a,g]quinolizine, 5,8,13,13a-tetrahydro-2,3,9,10-tetramethoxy-, (13as)-
52. Ncgc00346591-01
53. Ac-16039
54. As-17459
55. As-82762
56. (-)-tetrahydropalmatine, >=98% (hplc)
57. N1727
58. Sw219613-1
59. T3311
60. C02890
61. 483t147
62. A913918
63. Q-100022
64. Q-100371
65. Q7706555
66. (13as)-2,3,9,10-tetramethoxy-5,8,13,13a-tetrahydro-6h-dibenzo[a,g]quinolizine
67. (13as)-2,3,9,10-tetramethoxy-6,8,13,13a-tetrahydro-5h-isoquinolino[3,2-a]isoquinoline
68. (s)-2,3,9,10-tetramethoxy-5,8,13,13a-tetrahydro-6h-isoquinolino[3,2-a]isoquinoline
69. 2-(2,3-dimethoxy-benzyl)-1-ethyl-6,7-dimethoxy-1,2,3,4-tetrahydro-isoquinoline
70. 5,8,13,13a(s)-tetrahydro-2,3,9,10-tetramethoxy-6h-dibenzo[a,g]quinolizine
71. 5,8,13,13a-tetrahydro-(s)-2,3,9,10-tetramethoxy-6h-dibenzo(a,g)quinolizine
| Molecular Weight | 355.4 g/mol |
|---|---|
| Molecular Formula | C21H25NO4 |
| XLogP3 | 3.2 |
| Hydrogen Bond Donor Count | 0 |
| Hydrogen Bond Acceptor Count | 5 |
| Rotatable Bond Count | 4 |
| Exact Mass | 355.17835828 g/mol |
| Monoisotopic Mass | 355.17835828 g/mol |
| Topological Polar Surface Area | 40.2 Ų |
| Heavy Atom Count | 26 |
| Formal Charge | 0 |
| Complexity | 475 |
| Isotope Atom Count | 0 |
| Defined Atom Stereocenter Count | 1 |
| Undefined Atom Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Defined Bond Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Undefined Bond Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Covalently Bonded Unit Count | 1 |
Anti-Arrhythmia Agents
Agents used for the treatment or prevention of cardiac arrhythmias. They may affect the polarization-repolarization phase of the action potential, its excitability or refractoriness, or impulse conduction or membrane responsiveness within cardiac fibers. Anti-arrhythmia agents are often classed into four main groups according to their mechanism of action: sodium channel blockade, beta-adrenergic blockade, repolarization prolongation, or calcium channel blockade. (See all compounds classified as Anti-Arrhythmia Agents.)
Calcium Channel Blockers
A class of drugs that act by selective inhibition of calcium influx through cellular membranes. (See all compounds classified as Calcium Channel Blockers.)
Antihypertensive Agents
Drugs used in the treatment of acute or chronic vascular HYPERTENSION regardless of pharmacological mechanism. Among the antihypertensive agents are DIURETICS; (especially DIURETICS, THIAZIDE); ADRENERGIC BETA-ANTAGONISTS; ADRENERGIC ALPHA-ANTAGONISTS; ANGIOTENSIN-CONVERTING ENZYME INHIBITORS; CALCIUM CHANNEL BLOCKERS; GANGLIONIC BLOCKERS; and VASODILATOR AGENTS. (See all compounds classified as Antihypertensive Agents.)
Antipsychotic Agents
Agents that control agitated psychotic behavior, alleviate acute psychotic states, reduce psychotic symptoms, and exert a quieting effect. They are used in SCHIZOPHRENIA; senile dementia; transient psychosis following surgery; or MYOCARDIAL INFARCTION; etc. These drugs are often referred to as neuroleptics alluding to the tendency to produce neurological side effects, but not all antipsychotics are likely to produce such effects. Many of these drugs may also be effective against nausea, emesis, and pruritus. (See all compounds classified as Antipsychotic Agents.)
Adrenergic Agents
Drugs that act on adrenergic receptors or affect the life cycle of adrenergic transmitters. Included here are adrenergic agonists and antagonists and agents that affect the synthesis, storage, uptake, metabolism, or release of adrenergic transmitters. (See all compounds classified as Adrenergic Agents.)
Analgesics, Non-Narcotic
A subclass of analgesic agents that typically do not bind to OPIOID RECEPTORS and are not addictive. Many non-narcotic analgesics are offered as NONPRESCRIPTION DRUGS. (See all compounds classified as Analgesics, Non-Narcotic.)
Dopamine Antagonists
Drugs that bind to but do not activate DOPAMINE RECEPTORS, thereby blocking the actions of dopamine or exogenous agonists. Many drugs used in the treatment of psychotic disorders (ANTIPSYCHOTIC AGENTS) are dopamine antagonists, although their therapeutic effects may be due to long-term adjustments of the brain rather than to the acute effects of blocking dopamine receptors. Dopamine antagonists have been used for several other clinical purposes including as ANTIEMETICS, in the treatment of Tourette syndrome, and for hiccup. Dopamine receptor blockade is associated with NEUROLEPTIC MALIGNANT SYNDROME. (See all compounds classified as Dopamine Antagonists.)