

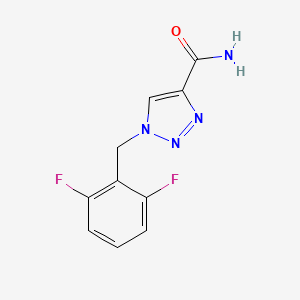

1. 1-(2,6-difluorobenzyl)-1h-1,2,3-triazole-4-carboxamide
2. Cgp 33101
3. Cgp-33101
4. Inovelon
1. 106308-44-5
2. Banzel
3. Inovelon
4. 1-(2,6-difluorobenzyl)-1h-1,2,3-triazole-4-carboxamide
5. Cgp 33101
6. Cgp-33101
7. 1-[(2,6-difluorophenyl)methyl]-1h-1,2,3-triazole-4-carboxamide
8. Ruf 331
9. Xilep
10. Ruf-331
11. 1-[(2,6-difluorophenyl)methyl]triazole-4-carboxamide
12. E-2080
13. E2080
14. E 2080
15. Wfw942pr79
16. 1h-1,2,3-triazole-4-carboxamide, 1-[(2,6-difluorophenyl)methyl]-
17. Ncgc00165883-02
18. 1h-1,2,3-triazole-4-carboxamide, 1-((2,6-difluorophenyl)methyl)-
19. Dsstox_cid_26506
20. Dsstox_rid_81675
21. Dsstox_gsid_46506
22. 1-[(2,6-difluorophenyl)methyl]-1h-1,2,3-triazole-4 Carboxamide
23. Smr000857122
24. C10h8f2n4o
25. Cas-106308-44-5
26. Unii-wfw942pr79
27. Rufinamide [usan:inn:ban]
28. Syn111
29. Syn-111
30. Cgp33101
31. Banzel (tn)
32. Mfcd00865314
33. Rufinamide (banzel)
34. Cgp 33,101
35. Rufinamide [mi]
36. Rufinamide [inn]
37. Rufinamide [jan]
38. Rufinamide [usan]
39. Rufinamide [vandf]
40. Rufinamide [mart.]
41. Rufinamide [usp-rs]
42. Rufinamide [who-dd]
43. Rufinamide (jan/usp/inn)
44. Mls001332513
45. Mls001332514
46. Rufinamide [ema Epar]
47. Schembl230448
48. Gtpl7470
49. Zinc7782
50. Chembl1201754
51. Dtxsid1046506
52. Rufinamide [orange Book]
53. Chebi:134966
54. Hms2232m19
55. Hms3262o14
56. Hms3371a06
57. Hms3651o05
58. Hms3884g07
59. Rufinamide [usp Monograph]
60. Bcp21828
61. Hy-a0042
62. Tox21 112267
63. Tox21_112267
64. Tox21_500796
65. Bdbm50515492
66. S1256
67. Akos005145897
68. Rufinamide, >=98% (hplc), Powder
69. Tox21_112267_1
70. Ac-1429
71. Ccg-222100
72. Cs-1455
73. Db06201
74. Lp00796
75. Sb18904
76. Sdccgsbi-0633757.p001
77. Ncgc00165883-01
78. Ncgc00165883-03
79. Ncgc00165883-04
80. Ncgc00165883-11
81. Ncgc00261481-01
82. As-13861
83. Ft-0656828
84. Ft-0674479
85. R0143
86. Sw219770-1
87. C71253
88. D05775
89. Ab00918347-05
90. Ab00918347_06
91. 308r445
92. A801414
93. Q408565
94. Sr-01000842156
95. J-001568
96. Sr-01000842156-4
97. 1-[(2,6-difluorophenyl)methyl]-4-triazolecarboxamide
98. F0001-2404
99. Z1541638521
100. 1-(2,6-difluorobenzyl)-1h-1,2,3-triazol-4-carboxamide
101. Rufinamide, United States Pharmacopeia (usp) Reference Standard
102. 1-[[2,6-bis(fluoranyl)phenyl]methyl]-1,2,3-triazole-4-carboxamide
| Molecular Weight | 238.19 g/mol |
|---|---|
| Molecular Formula | C10H8F2N4O |
| XLogP3 | 0.7 |
| Hydrogen Bond Donor Count | 1 |
| Hydrogen Bond Acceptor Count | 5 |
| Rotatable Bond Count | 3 |
| Exact Mass | 238.06661722 g/mol |
| Monoisotopic Mass | 238.06661722 g/mol |
| Topological Polar Surface Area | 73.8 Ų |
| Heavy Atom Count | 17 |
| Formal Charge | 0 |
| Complexity | 282 |
| Isotope Atom Count | 0 |
| Defined Atom Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Undefined Atom Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Defined Bond Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Undefined Bond Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Covalently Bonded Unit Count | 1 |
| 1 of 2 | |
|---|---|
| Drug Name | Banzel |
| PubMed Health | Rufinamide (By mouth) |
| Drug Classes | Anticonvulsant |
| Drug Label | BANZEL (rufinamide) is a triazole derivative structurally unrelated to currently marketed antiepileptic drugs (AEDs). Rufinamide has the chemical name 1-[(2,6-difluorophenyl)methyl]-1H-1,2,3-triazole-4 carboxamide. It has an empirical formula of C10H... |
| Active Ingredient | Rufinamide |
| Dosage Form | Tablet; Suspension |
| Route | Oral |
| Strength | 200mg; 40mg/ml; 400mg |
| Market Status | Prescription |
| Company | Eisai |
| 2 of 2 | |
|---|---|
| Drug Name | Banzel |
| PubMed Health | Rufinamide (By mouth) |
| Drug Classes | Anticonvulsant |
| Drug Label | BANZEL (rufinamide) is a triazole derivative structurally unrelated to currently marketed antiepileptic drugs (AEDs). Rufinamide has the chemical name 1-[(2,6-difluorophenyl)methyl]-1H-1,2,3-triazole-4 carboxamide. It has an empirical formula of C10H... |
| Active Ingredient | Rufinamide |
| Dosage Form | Tablet; Suspension |
| Route | Oral |
| Strength | 200mg; 40mg/ml; 400mg |
| Market Status | Prescription |
| Company | Eisai |
Adjunct therapy for treatment of seizures associated with Lennox-Gastaut syndrome.
FDA Label
Inovelon is indicated as adjunctive therapy in the treatment of seizures associated with Lennox Gastaut syndrome in patients 4 years of age and older.
At high concentrations will inhibit action of mGluR5 subtype receptors thus preventing the production of glutamate.
Voltage-Gated Sodium Channel Blockers
A class of drugs that inhibit the activation of VOLTAGE-GATED SODIUM CHANNELS. (See all compounds classified as Voltage-Gated Sodium Channel Blockers.)
Anticonvulsants
Drugs used to prevent SEIZURES or reduce their severity. (See all compounds classified as Anticonvulsants.)
N03AF03
N03AF03
S76 | LUXPHARMA | Pharmaceuticals Marketed in Luxembourg | Pharmaceuticals marketed in Luxembourg, as published by d'Gesondheetskeess (CNS, la caisse nationale de sante, www.cns.lu), mapped by name to structures using CompTox by R. Singh et al. (in prep.). List downloaded from https://cns.public.lu/en/legislations/textes-coordonnes/liste-med-comm.html. Dataset DOI:10.5281/zenodo.4587355
N - Nervous system
N03 - Antiepileptics
N03A - Antiepileptics
N03AF - Carboxamide derivatives
N03AF03 - Rufinamide
Absorption
The oral suspension and tablet are bioequivalent on a mg per mg basis. Rufinamide is well absorbed but the rate is slow and the extent of absorption decreases as dose is increases. Based on urinary excretion, the extent of absorption was at least 85% following oral administration of a single dose of 600 mg rufinamide tablet under fed conditions. Bioavailability= 70%-85% (decreases with increasing doses); Tmax, fed and fasted states= 4-6 hours; Cmax, 10 mg/kg/day= 4.01 L/mL; Cmax, 30mg/kg/day= 8.68 L/mL; AUC (0h-12h), 10mg/kg/day= 37.847 gh/mL; AUC (0h-12h), 30mg/kg/day= 89.359 gh/mL.
Route of Elimination
Renally (91%; 66% as CGP 47292, 2% as unchanged drug) and fecally (9%) eliminated.
Volume of Distribution
Rufinamide was evenly distributed between erythrocytes and plasma. The apparent volume of distribution is dependent upon dose and varies with body surface area. The apparent volume of distribution was about 50 L at 3200 mg/day. Volume of distribution is similar between adults and children and is non-linear.
Rufinamide is extensively metabolized but has no active metabolites. Metabolism by carboxyesterases into inactive metabolite CGP 47292, a carboxylic acid derivative, via hydrolysis is the primary biotransformation pathway. A few minor additional metabolites were detected in urine, which appeared to be acyl-glucuronides of CGP 47292. The cytochrome P450 enzyme system or glutathiones are not involved with the metabolism of rufinamide. Rufinamide is a weak inhibitor of CYP 2E1. Rufinamide is a weak inducer of CYP 3A4 enzymes.
Elimination half-life, healthy subjects and patients with epilepsy = 6-10 hours.
Rufinamide is a triazole derivative antiepileptic that prolongs the inactive state of voltage gated sodium channels thus stabilizing membranes, ultimately blocking the spread of partial seizure activity.