


1. Arcylate
2. Argesic
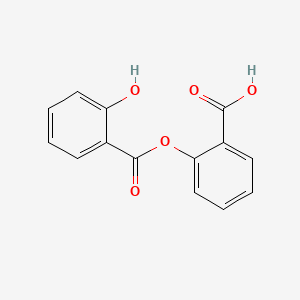
3. Benzoic Acid, 2-hydroxy-, 2-carboxyphenyl Ester
4. Disalcid
5. Disalicylic Acid
6. Mono-gesic
7. Salflex
8. Salicyl Salicylate
9. Salicylsalicylic Acid
10. Saloxium
11. Salsitab
1. 552-94-3
2. Sasapyrine
3. Salicylsalicylic Acid
4. Disalicylic Acid
5. Disalcid
6. 2-carboxyphenyl Salicylate
7. Sasapyrinum
8. Saloxium
9. Salicyloylsalicylic Acid
10. Diacesal
11. Diplosal
12. Sasapirin
13. Sasapyrin
14. Disalyl
15. Nobacid
16. Salical
17. Salina
18. Salysal
19. O-salicylsalicylic Acid
20. Sal Ester Sal
21. 2-(2-hydroxybenzoyl)oxybenzoic Acid
22. Disalicylsaeure
23. Benzoic Acid, 2-hydroxy-, 2-carboxyphenyl Ester
24. Salicylic Acid, Salicylate
25. Nsc-49171
26. Salicylic Acid, Bimolecular Ester
27. Salsalato
28. Salsalatum
29. Salflex
30. Salsalatum [inn-latin]
31. 2-((2-hydroxybenzoyl)oxy)benzoic Acid
32. Salicyloxysalicylic Acid
33. O-salicylcylsalicylsaeure
34. Disalicyclic Acid
35. Sasapyrine (jan)
36. 2-hydroxybenzoic Acid 2-carboxyphenyl Ester
37. Salicylsalicylic Acid;disalicylic Acid
38. Chebi:9014
39. V9mo595c9i
40. Salicylic Acid Bimolecular Ester
41. Nsc49171
42. Ncgc00096014-01
43. Sasapyrine [jan]
44. Dsstox_cid_3572
45. Dsstox_rid_77088
46. Dsstox_gsid_23572
47. Salsalato [inn-spanish]
48. 2-[(2-hydroxybenzoyl)oxy]benzoic Acid (salicylsalicylic Acid)
49. Mono-gesic
50. O-salicyloylsalicylic Acid
51. Disalcid (tn)
52. Cas-552-94-3
53. Salsalate (usp/inn)
54. Einecs 209-027-4
55. Mfcd00020252
56. Nsc 49171
57. 2-salicyloyloxybenzoic Acid
58. Brn 2590908
59. Unii-v9mo595c9i
60. Disalgesic
61. Salicylsalicylic Acid (2-[(2-hydroxybenzoyl)oxy]benzoic Acid)
62. Salsalate [usan:usp:inn:ban]
63. Aspirin Impurity E
64. 2-(2-hydroxybenzoyloxy)benzoic Acid
65. Carboxyphenyl Salicylate
66. Spectrum_001998
67. 2-salicylsalicylic Acid
68. Salsalate [inn]
69. Salsalate [mi]
70. Salsalate [usan]
71. Spectrum2_000693
72. Spectrum3_000173
73. Spectrum4_000940
74. Spectrum5_000670
75. Salsalate [vandf]
76. Salsalate [mart.]
77. Salsalate [usp-rs]
78. Salsalate [who-dd]
79. 2-{[(2-hydroxyphenyl)carbonyl]oxy}benzoic Acid
80. 2-salicyloyloxy-benzoic Acid
81. Schembl15562
82. Bspbio_001665
83. Kbiogr_001500
84. Kbioss_002572
85. Spectrum200331
86. Spbio_000845
87. Acetylsalicylic Acid Impurity E
88. Chembl154111
89. Zinc2062
90. Dtxsid1023572
91. Salsalate [usp Impurity]
92. Salsalate, >=98% (hplc)
93. Bdbm85244
94. Kbio2_002563
95. Kbio2_005131
96. Kbio2_007699
97. Kbio3_001165
98. Salsalate [usp Monograph]
99. Hms2091a05
100. Hms3652p07
101. Hms3885j09
102. Pharmakon1600-00200331
103. Hy-b1245
104. Nsc_5161
105. Benzoic Acid, 2-carboxyphenyl Ester
106. Tox21_111548
107. Ccg-39652
108. Nsc755823
109. S4188
110. Salicylic Acid 2-carboxyphenyl Ester
111. Akos003368478
112. Tox21_111548_1
113. 2-carboxyphenyl Salicylate, Aldrichcpr
114. Cs-4891
115. Db01399
116. Nsc-755823
117. Ncgc00096014-02
118. Ncgc00096014-03
119. Ac-18298
120. As-12645
121. Cas_552-94-3
122. 2-[(2-hydroxybenzoyl)oxy]benzoic Acid #
123. Sbi-0206687.p002
124. Db-020760
125. Ft-0632376
126. Sw219189-1
127. 2-[(2-hydroxyphenyl)carbonyloxy]benzoic Acid
128. C75590
129. D00428
130. Ab01563259_01
131. Ab01563259_02
132. A830578
133. Sr-05000001536
134. Q-100630
135. Q1320691
136. Sr-05000001536-1
137. Acetylsalicylic Acid Impurity E [ep Impurity]
138. Salsalate, United States Pharmacopeia (usp) Reference Standard
139. Aspirin Impurity E; 2-hydroxybenzoic Acid 2-carboxyphenyl Ester; Salicylic Acid Salicylate; 2-hydroxybenzoic Acid 2-carboxyphenyl Ester
140. Salsalate (aspirin Impurity E), Pharmaceutical Secondary Standard; Certified Reference Material
| Molecular Weight | 258.23 g/mol |
|---|---|
| Molecular Formula | C14H10O5 |
| XLogP3 | 3 |
| Hydrogen Bond Donor Count | 2 |
| Hydrogen Bond Acceptor Count | 5 |
| Rotatable Bond Count | 4 |
| Exact Mass | 258.05282342 g/mol |
| Monoisotopic Mass | 258.05282342 g/mol |
| Topological Polar Surface Area | 83.8 Ų |
| Heavy Atom Count | 19 |
| Formal Charge | 0 |
| Complexity | 341 |
| Isotope Atom Count | 0 |
| Defined Atom Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Undefined Atom Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Defined Bond Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Undefined Bond Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Covalently Bonded Unit Count | 1 |
For relief of the signs and symptoms of rheumatoid arthritis, osteoarthritis and related rheumatic disorders.
Salsalate is a nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory agent for oral administration. Salsalate's mode of action as an anti-inflammatory and antirheumatic agent may be due to inhibition of synthesis and release of prostaglandins. The usefulness of salicylic acid, the active in vivo product of salsalate, in the treatment of arthritic disorders has been established. In contrast to aspirin, salsalate causes no greater fecal gastrointestinal blood loss than placebo.
Anti-Inflammatory Agents, Non-Steroidal
Anti-inflammatory agents that are non-steroidal in nature. In addition to anti-inflammatory actions, they have analgesic, antipyretic, and platelet-inhibitory actions. They act by blocking the synthesis of prostaglandins by inhibiting cyclooxygenase, which converts arachidonic acid to cyclic endoperoxides, precursors of prostaglandins. Inhibition of prostaglandin synthesis accounts for their analgesic, antipyretic, and platelet-inhibitory actions; other mechanisms may contribute to their anti-inflammatory effects. (See all compounds classified as Anti-Inflammatory Agents, Non-Steroidal.)
N - Nervous system
N02 - Analgesics
N02B - Other analgesics and antipyretics
N02BA - Salicylic acid and derivatives
N02BA06 - Salsalate
Absorption
Salsalate is insoluble in acid gastric fluids (< 0.1 mg/ml at pH 1.0), but readily soluble in the small intestine where it is partially hydrolyzed to two molecules of salicylic acid. A significant portion of the parent compound is absorbed unchanged. The amount of salicylic acid available from salsalate is about 15% less than from aspirin, when the two drugs are administered on a salicylic acid molar equivalent basis (3.6 g salsalate/5 g aspirin). Food slows the absorption of all salicylates including salsalate.
Salsalate is readily soluble in the small intestine where it is partially hydrolyzed to two molecules of salicylic acid. A significant portion of the parent compound is absorbed unchanged and undergoes rapid esterase hydrolysis in the body.
The parent compound has an elimination half-life of about 1 hour. Salicylic acid (the active metabolite) biotransformation is saturated at anti-inflammatory doses of salsalate. Such capacity limited biotransformation results in an increase in the half-life of salicylic acid from 3.5 to 16 or more hours.
The mode of anti-inflammatory action of salsalate and other nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs is not fully defined, but appears to be primarily associated with inhibition of prostaglandin synthesis. This inhibition of prostaglandin synthesis is done through the inactivation of cyclooxygenase-1 (COX-1) and COX-2, which are reponsible for catalyzing the formation of prostaglandins in the arachidonic acid pathway. Although salicylic acid (the primary metabolite of salsalate) is a weak inhibitor of prostaglandin synthesis in vitro, salsalate appears to selectively inhibit prostaglandin synthesis in vivo, providing anti-inflammatory activity equivalent to aspirin and indomethacin. Unlike aspirin, salsalate does not inhibit platelet aggregation.

