

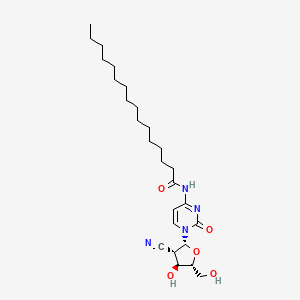

1. 2'-c-cyano-2'-deoxy-1-arabinofuranosyl-n(4)-palmitoylcytosine
2. Cndac Cpd
3. Cs-682
4. Cyc 682
5. Cyc-682
1. 151823-14-2
2. Cs-682
3. Cyc682
4. Cyc-682
5. Cs682
6. Cs 682
7. Pcndac
8. Cyc 682
9. W335p73c3l
10. N-(1-(2-cyano-2-deoxy-beta-d-arabinofuranosyl)-1,2-dihydro-2-oxo-4-pyrimidinyl)hexadecanamide
11. N-(1-((2r,3s,4s,5r)-3-cyano-4-hydroxy-5-(hydroxymethyl)tetrahydrofuran-2-yl)-2-oxo-1,2-dihydropyrimidin-4-yl)palmitamide
12. Sapacitabine [usan:inn]
13. Sapacitabina
14. Sapacitabinum
15. Unii-w335p73c3l
16. Sapacitabine (cyc682)
17. Sapacitabine (usan/inn)
18. Sapacitabine [inn]
19. Sapacitabine [usan]
20. Sapacitabine [mart.]
21. N-[1-[(2r,3s,4s,5r)-3-cyano-4-hydroxy-5-(hydroxymethyl)oxolan-2-yl]-2-oxopyrimidin-4-yl]hexadecanamide
22. Sapacitabine [who-dd]
23. Schembl711854
24. Chembl2105681
25. Dtxsid90164887
26. Chebi:145429
27. Ex-a1617
28. Nsc791785
29. Zinc14263648
30. Db06365
31. Nsc-791785
32. Ac-36130
33. Hexadecanamide, N-(1-(2-cyano-2-deoxy-beta-d-arabinofuranosyl)-1,2-dihydro-2-oxo-4-pyrimidinyl)-
34. Hy-16445
35. Cs-0006340
36. D09722
37. 823s142
38. Q7420893
39. 2'-c-cyano-2'-deoxy-1-arabinofuranosyl-n(4)-palmitoylcytosine
40. 1-(2-cyano-2-deoxy-beta-d-arabinofuranosyl)-4-(hexadecanoylamino)pyrimidin-2(1h)-one
41. Hexadecanamide, N-(1-(2-cyano-2-deoxy-.beta.-d-arabinofuranosyl)-1,2-dihydro-2-oxo-4- Pyrimidinyl)-
42. N-(1-(2-cyano-2-deoxy-.beta.-d-arabinofuranosyl)-2-oxo-1,2-dihydropyrimidin-4- Yl)hexadecanamide
43. N-[1-(2-cyano-2-deoxy-beta-d-arabinofuranosyl)-2-oxo-1,2-dihydropyrimidine-4-yl]hexadecanamide
| Molecular Weight | 490.6 g/mol |
|---|---|
| Molecular Formula | C26H42N4O5 |
| XLogP3 | 5.2 |
| Hydrogen Bond Donor Count | 3 |
| Hydrogen Bond Acceptor Count | 6 |
| Rotatable Bond Count | 17 |
| Exact Mass | 490.31552045 g/mol |
| Monoisotopic Mass | 490.31552045 g/mol |
| Topological Polar Surface Area | 135 Ų |
| Heavy Atom Count | 35 |
| Formal Charge | 0 |
| Complexity | 775 |
| Isotope Atom Count | 0 |
| Defined Atom Stereocenter Count | 4 |
| Undefined Atom Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Defined Bond Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Undefined Bond Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Covalently Bonded Unit Count | 1 |
Investigated for use/treatment in solid tumors, cutaneous t-cell lymphoma, myelodysplastic syndrome, and leukemia (lymphoid).
Antineoplastic Agents
Substances that inhibit or prevent the proliferation of NEOPLASMS. (See all compounds classified as Antineoplastic Agents.)
Sapacitabine appears to act through a dual mechanism. It interferes with DNA synthesis by causing single-strand DNA breaks and also induces arrest of cell cycle progression mainly at G2/M-Phase. Both sapacitabine and CNDAC, its major metabolite or a substance into which the drugs converts after ingestion by patients, have demonstrated potent anti-tumor activity in preclinical studies.