
1. Gr 138950
2. Gr-138950
3. Gr138950
4. Gr138950c
5. Sapri-sartan Potassium
6. Saprisartan Potassium
1. 146623-69-0
2. Gr-138950
3. Gr 138950
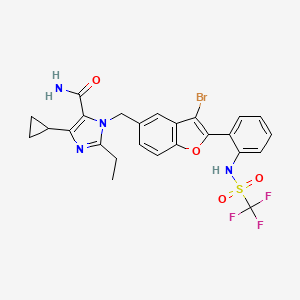
4. 3-[[3-bromo-2-[2-(trifluoromethylsulfonylamino)phenyl]-1-benzofuran-5-yl]methyl]-5-cyclopropyl-2-ethylimidazole-4-carboxamide
5. Gr138950
6. Hs64ng1g69
7. Saprisartan [inn:ban]
8. Unii-hs64ng1g69
9. 3-((3-bromo-2-(2-(trifluoromethylsulfonylamino)phenyl)-1-benzofuran-5-yl)methyl)-5-cyclopropyl-2-ethylimidazole-4-carboxamide
10. Gr-138950x
11. Saprisartan [inn]
12. Saprisartan [who-dd]
13. Schembl120388
14. Chembl305544
15. Gtpl6899
16. Dtxsid00163422
17. Chebi:190069
18. Zinc3919581
19. Bdbm50469901
20. Db01347
21. L000533
22. Q20817193
23. 1-({3-bromo-2-[2-(trifluoromethane)sulfonamidophenyl]-1-benzofuran-5-yl}methyl)-4-cyclopropyl-2-ethyl-1h-imidazole-5-carboxamide
24. 1-[[3-bromo-2-[2-[[(trifluoromethyl)sulphonyl ]amino ]phenyl]-5-benzofuranyl]methyl]-4-cyclopropyl-2-ethyl-1h-imidazole-5-carboxamide
25. 1-[[3-bromo-2-[2-[[(trifluoromethyl)sulphonyl]amino]phenyl]-5-benzofuranyl]methyl]-4-cyclopropyl-2-ethyl-1h-imidazole-5-carboxamide
26. 1h-imidazole-5-carboxamide, 1-((3-bromo-2-(2-(((trifluoromethyl)sulfonyl)amino)phenyl)-5-benzofuranyl)methyl)-4-cyclopropyl-2-ethyl-
27. 3-[[3-bromo-2-[2-(triluoromethylsulonylamino)phenyl]-1-benzouran-5-yl]methyl]-5-cyclopropyl-2-ethylimidazole-4-carboxamide
| Molecular Weight | 611.4 g/mol |
|---|---|
| Molecular Formula | C25H22BrF3N4O4S |
| XLogP3 | 5.2 |
| Hydrogen Bond Donor Count | 2 |
| Hydrogen Bond Acceptor Count | 9 |
| Rotatable Bond Count | 8 |
| Exact Mass | 610.04972 g/mol |
| Monoisotopic Mass | 610.04972 g/mol |
| Topological Polar Surface Area | 129 Ų |
| Heavy Atom Count | 38 |
| Formal Charge | 0 |
| Complexity | 979 |
| Isotope Atom Count | 0 |
| Defined Atom Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Undefined Atom Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Defined Bond Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Undefined Bond Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Covalently Bonded Unit Count | 1 |
Saprisartan is used in the treatment of hypertension and heart failure.
By inhibiting the angiotensin II receptor, this drug leades to a decrease in sodium reabsorption and a decrease in vasoconstriction. This has the combined effect of decreasing blood pressure.
Angiotensin II Type 1 Receptor Blockers
Agents that antagonize ANGIOTENSIN II TYPE 1 RECEPTOR. Included are ANGIOTENSIN II analogs such as SARALASIN and biphenylimidazoles such as LOSARTAN. Some are used as ANTIHYPERTENSIVE AGENTS. (See all compounds classified as Angiotensin II Type 1 Receptor Blockers.)
Antihypertensive Agents
Drugs used in the treatment of acute or chronic vascular HYPERTENSION regardless of pharmacological mechanism. Among the antihypertensive agents are DIURETICS; (especially DIURETICS, THIAZIDE); ADRENERGIC BETA-ANTAGONISTS; ADRENERGIC ALPHA-ANTAGONISTS; ANGIOTENSIN-CONVERTING ENZYME INHIBITORS; CALCIUM CHANNEL BLOCKERS; GANGLIONIC BLOCKERS; and VASODILATOR AGENTS. (See all compounds classified as Antihypertensive Agents.)
Saprisartan is a selective, potent, orally active and long-acting nonpeptide Angiotensin II type 1 (AT1) receptor antagonist. Saprisartan blocks the renin-angiotensin-aldosterone system (RAAS) at the level of the AT1 receptor that mediates most, if not all, of the important actions of Ang II. Saprisartan binds reversibly to the AT1 receptors in vascular smooth muscle and the adrenal gland. As angiotensin II is a vasoconstrictor, which also stimulates the synthesis and release of aldosterone, blockage of its effects results in decreases in systemic vascular resistance. AT1 receptor antagonists avoid the nonspecificity of the Ang I converting enzyme (ACE) inhibitors.