
1. Anaprilin
2. Anapriline
3. Avlocardyl
4. Ay 20694
5. Ay-20694
6. Ay20694
7. Betadren
8. Dexpropranolol
9. Dociton
10. Hydrochloride, Propranolol
11. Inderal
12. Obsidan
13. Obzidan
14. Propanolol
15. Propranolol
16. Rexigen
1. 318-98-9
2. Propranolol Hcl
3. Inderal
4. Avlocardyl
5. Dociton
6. Inderalici
7. Anaprilin
8. Caridolol
9. 3506-09-0
10. Berkolol
11. Herzbase
12. Indobloc
13. Naprilin
14. Pronovan
15. Pylapron
16. Sloprolol
17. Apsolol
18. Beprane
19. Deralin
20. Ikopal
21. Obsidan
22. Tesnol
23. Kemi
24. Propranolol.hcl
25. Beta Neg
26. Innopran Xl
27. Propranolol Chloride
28. Inderex
29. Nsc-91523
30. Hemangeol
31. Innopran
32. Propranolol (hydrochloride)
33. Propanolol Hydrochloride
34. Ici 45520
35. 1-(isopropylamino)-3-(1-naphthyloxy)-2-propanol Hydrochloride
36. Ay 64043
37. 1-(isopropylamino)-3-(naphthalen-1-yloxy)propan-2-ol Hydrochloride
38. Ici-45520
39. Propranolol Hydrochloride (+/-)
40. Ay-64043
41. I 2065
42. 1-naphthalen-1-yloxy-3-(propan-2-ylamino)propan-2-ol;hydrochloride
43. (s)-propranolol (hydrochloride)
44. 1-(isopropylamino)-3-(1-naphthoxy)-propan-2-ol Hydrochloride
45. (+/-)-propranolol Hydrochloride
46. F8a3652h1v
47. Hemangiol
48. Bedranol
49. Inderol
50. Pranolol
51. Sumial
52. Indermigran
53. Proprahexal
54. Propranovitan
55. Angilol
56. Arcablock
57. Artensol
58. Biocard
59. Blocaryl
60. Cardinol
61. Corbeta
62. Detensol
63. Dibudinate
64. Dumopranol
65. Efectolol
66. Emforal
67. Farprolol
68. Frekven
69. Hemipralon
70. Kidoral
71. Nelderal
72. Noloten
73. Novopranol
74. Panolol
75. Prandol
76. Propabloc
77. Propadex
78. Propalong
79. Propayerst
80. Prophylux
81. Propral
82. Propranur
83. Rapynogen
84. Sagittol
85. Sawatol
86. Scandrug
87. Sudenol
88. Tensiflex
89. Tiperal
90. Acifol
91. Cinlol
92. Ciplar
93. Elbrol
94. Herzul
95. Oposim
96. Pranix
97. Procor
98. Prosin
99. Nedis
100. Sinal
101. Tonum
102. 1-naphthalen-1-yloxy-3-(propan-2-ylamino)propan-2-ol Hydrochloride
103. 318-98-9 (hcl)
104. Half-inderal
105. Prano-puren
106. Propra Vt Ct
107. Dsstox_cid_1198
108. Inderal Hydrochloride
109. Inderal La
110. Proberta La
111. Pur-bloka
112. Beta-neg
113. Dsstox_rid_76007
114. Dsstox_gsid_21198
115. (s)-propranolol Hydrochloride
116. 1-isopropylamino-3-(1-naphthoxy)-propan-2-ol-hydrochloride
117. Dl-propranolol Hydrochloride
118. 1-(1-naphthyloxy)-2-hydroxy-3-isopropylaminopropane Hydrochloride
119. R+c5989educor
120. (+-)-1-(isopropylamino)-3-(1-naphthyloxy)-2-propanol Hydrochloride
121. 2-propanol, 1-((1-methylethyl)amino)-3-(1-naphthalenyloxy)-, Hydrochloride
122. Propraratiopharm
123. Beta-tablinen
124. Beta-timelets
125. Dl-anapriline
126. (+/-)-1-(isopropylamino)-3-(1-naphthyloxy)-2-propanol Hydrochloride
127. [2-hydroxy-3-(naphthalen-1-yloxy)propyl](propan-2-yl)amine Hydrochloride
128. 1-[(1-methylethyl)amino]-3-(naphthalen-1-yloxy)propan-2-ol Hydrochloride
129. Chebi:8500
130. Smr000059167
131. Nsc91523
132. Ccris 1105
133. Hsdb 3176
134. Sr-01000075285
135. (r)-propranolol Hydrochloride
136. Einecs 206-268-7
137. Mfcd00012558
138. D,l-propranolol Hydrochloride
139. Servanolol
140. Efektolol
141. Migrastat
142. Unii-f8a3652h1v
143. Propranolol Hydrochloride Intensol
144. Dl-propranolol Hcl
145. Relax-b
146. Einecs 222-501-5
147. Inderal (tn)
148. Nsc 91523
149. Betacap
150. Monoprolol
151. Innopran Xl (tn)
152. (r)-(+)-propanolol Hydrochloride
153. (r)-propranolol Hcl
154. Propranolol Hydrochloride [usan:usp:jan]
155. Propranolon Hydrochloride
156. 1-(isopropylamino)-3-(1-naphthyloxy)propan-2-ol Hydrochloride
157. 1-(isopropylamino)-3-(alpha-naphthoxy)-2-propanol Hydrochloride
158. Cas-318-98-9
159. Chembl1671
160. Schembl41688
161. (y)-propranolol Hydrochloride
162. Mls000859628
163. Mls001055449
164. Mls001056753
165. Mls002222321
166. Mls002548855
167. (?)-propranolol Hydrochloride
168. Spectrum1505270
169. Propranolol Hydrochloride, 99%
170. Dtxsid3021198
171. (2-hydroxy-3-(naphthyloxy)propyl)isopropylammonium Chloride
172. Hms1570p06
173. Hms1571g12
174. Hms1571i04
175. Hms1922p19
176. Pharmakon1600-01505270
177. Act02695
178. Bcp15350
179. Bcp16675
180. Eur-1000
181. Hy-b0573
182. Kdm-1102
183. Rac-propranolol Hydrochloride
184. Tox21_201886
185. Tox21_302905
186. Tox21_500896
187. 2-propanol, 1-(isopropylamino)-3-(1-naphthyloxy)-, Hydrochloride
188. Ccg-39239
189. Ccg-39447
190. Ncs-91523
191. Nsc758950
192. S4076
193. Propranalol Hydrochloride, Dl-
194. Propranolol Hydrochloride [mi]
195. 1-(naphthalen-1-yloxy)-3-[(propan-2-yl)amino]propan-2-ol Hydrochloride
196. 2-propanol, 1-(isopropylamino)-3-(1-naphthyloxy)-, Hydrochloride, (+-)-
197. Akos005267141
198. Propranolol Hydrochloride (jp17/usp)
199. (s)-2-fmoc-6-chlorhex-4-ynoic Acid
200. Ks-1097
201. Lp00896
202. Nc00687
203. Nsc-758950
204. Propranolol Hydrochloride [jan]
205. 2-propanol, 1-((1-methylethyl)amino)-3-(1-naphthalenyloxy)-, Hydrochloride, (+-)-
206. Propranolol Hydrochloride [hsdb]
207. Propranolol Hydrochloride [usan]
208. Ncgc00024690-04
209. Ncgc00091932-01
210. Ncgc00094212-01
211. Ncgc00094212-02
212. Ncgc00094212-03
213. Ncgc00094212-04
214. Ncgc00094212-05
215. Ncgc00256554-01
216. Ncgc00259435-01
217. Ncgc00261581-01
218. Propranolol Hydrochloride [mart.]
219. Propranolol Hydrochloride [vandf]
220. Propranolol Hydrochloride [usp-rs]
221. Propranolol Hydrochloride [who-dd]
222. Propranolol Hydrochloride [who-ip]
223. Db-018092
224. Eu-0100896
225. Ft-0603377
226. Ft-0635178
227. Ft-0636788
228. P0995
229. Sw219414-1
230. Wln: L66j Bo1yq1my1 & 1 & Gh
231. Bim-0050871.0001
232. D00483
233. H10708
234. P 0884
235. Propranolol Hydrochloride [ep Monograph]
236. Propranolol Hydrochloride [orange Book]
237. Propranolol Hydrochloride [usp Monograph]
238. Propranolol Hydrochloride 100 Microg/ml In Water
239. Propranololi Hydrochloridum [who-ip Latin]
240. ( Inverted Question Mark)-propranolol Hydrochloride
241. Q-201632
242. Sr-01000075285-1
243. Sr-01000075285-3
244. W-109142
245. Q27108095
246. Z90121066
247. (+/-)-propranolol Hydrochloride, >=99% (tlc), Powder
248. (+/-)-propranolol, Hydrochloride - Cas 3506-09-0
249. (+/-)-propranolol Hydrochloride, Analytical Reference Material
250. 1-(isopropylamino)-3-(1-napthyloxy)-2-propanol Hydrochloride
251. Propranolol Hydrochloride 1.0 Mg/ml In Methanol (as Free Base)
252. (+/-)-[2-hydroxy-3-(naphthyloxy)propyl]isopropylammonium Chloride
253. 1-(1-naphthyloxy)-2-hydroxy-3-(isopropylamino)propane Hydrochloride
254. 1-(1-naphthyloxy)-2-hydroxy-3-isopropylaminopropanehydrochloride
255. 1-(alpha-naphthoxy)-3-(iso-propylamino)-2-propanol Hydrochloride
256. 1-(alpha-naphthoxy)-3-(isopropylamino)-2-propanol Hydrochloride
257. 1-(isopropylamino)-3-(.alpha.-naphthoxy)-2-propanol Hydrochloride
258. Propranolol Hydrochloride, European Pharmacopoeia (ep) Reference Standard
259. ( Inverted Question Mark)-1-(isopropylamino)-3-(1-naphthyloxy)-2-propanol Hydrochloride
260. (rs)-1-[(1-methylethyl)amino]-3-(1-naphthalenyloxy)-2-propanol Hydrochloride
261. (rs)-1-[(1-methylethyl)amino]-3-(1-naphthalenyloxy)-2-propanolhydrochloride
262. Propranolol Hydrochloride, Pharmaceutical Secondary Standard; Certified Reference Material
263. Propranolol Hydrochloride, United States Pharmacopeia (usp) Reference Standard
264. 2-propanol, 1-((1-methylethyl)amino)-3-(1-naphthalenyloxy)-, Hydrochloride, (+/-)-
265. Propranolol Hydrochloride For Performance Test, European Pharmacopoeia (ep) Reference Standard
266. Propranolol Hydrochloride Solution, 1.0 Mg/ml In Methanol (as Free Base), Ampule Of 1 Ml, Certified Reference Material
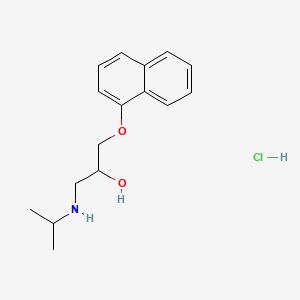
| Molecular Weight | 295.80 g/mol |
|---|---|
| Molecular Formula | C16H22ClNO2 |
| Hydrogen Bond Donor Count | 3 |
| Hydrogen Bond Acceptor Count | 3 |
| Rotatable Bond Count | 6 |
| Exact Mass | 295.1339066 g/mol |
| Monoisotopic Mass | 295.1339066 g/mol |
| Topological Polar Surface Area | 41.5 Ų |
| Heavy Atom Count | 20 |
| Formal Charge | 0 |
| Complexity | 257 |
| Isotope Atom Count | 0 |
| Defined Atom Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Undefined Atom Stereocenter Count | 1 |
| Defined Bond Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Undefined Bond Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Covalently Bonded Unit Count | 2 |
| 1 of 10 | |
|---|---|
| Drug Name | Inderal |
| PubMed Health | Propranolol (By mouth) |
| Drug Classes | Antianginal, Antiarrhythmic, Group II, Antihypertensive, Antimigraine, Cardiovascular Agent |
| Drug Label | Inderal (propranolol hydrochloride) is a synthetic beta-adrenergic receptor-blocking agent chemically described as 2-Propanol, 1-[(1-methylethyl)amino]-3-(1-naphthalenyloxy)-, hydrochloride,()-. Its molecular and structural formulae are: C16H21NO... |
| Active Ingredient | Propranolol hydrochloride |
| Dosage Form | Tablet |
| Route | oral |
| Strength | 60mg; 10mg; 80mg; 40mg; 20mg |
| Market Status | Prescription |
| Company | Akrimax Pharms |
| 2 of 10 | |
|---|---|
| Drug Name | Inderal la |
| PubMed Health | Somatropin, E coli Derived (Injection) |
| Drug Classes | Endocrine-Metabolic Agent |
| Drug Label | Inderal (propranolol hydrochloride) is a synthetic beta-adrenergic receptor-blocking agent chemically described as 2-Propanol, 1-[(1-methylethyl)amino]-3-(1-naphthalenyloxy)-, hydrochloride,()-. Its molecular and structural formulae are: C16H21NO... |
| Active Ingredient | Propranolol hydrochloride |
| Dosage Form | Capsule, extended release |
| Route | Oral |
| Strength | 160mg; 120mg; 60mg; 80mg |
| Market Status | Prescription |
| Company | Akrimax Pharms |
| 3 of 10 | |
|---|---|
| Drug Name | Innopran xl |
| PubMed Health | Propranolol |
| Drug Classes | Antianginal, Antiarrhythmic, Group II, Antihypertensive, Antimigraine, Cardiovascular Agent |
| Drug Label | INNOPRAN XL (propranolol hydrochloride) is a nonselective, beta-adrenergic receptor-blocking agent for oral administration, available as an extended release product. INNOPRAN XL is available as 80-mg and 120-mg capsules which contain sustained-releas... |
| Active Ingredient | Propranolol hydrochloride |
| Dosage Form | Capsule, extended release |
| Route | Oral |
| Strength | 120mg; 80mg |
| Market Status | Prescription |
| Company | Glaxosmithkline |
| 4 of 10 | |
|---|---|
| Drug Name | Propranolol hydrochloride |
| PubMed Health | Propranolol (Injection) |
| Drug Classes | Antianginal, Antiarrhythmic, Group II, Antihypertensive, Antimigraine, Cardiovascular Agent |
| Drug Label | hydrochloride(Propranolol is a synthetic beta-adrenergic receptor blocking agent chemically described as 2-Propanol, 1-[(1-methylethyl)amino]-3-(1-naphthalenyloxy)-, hydrochloride,()-. Its molecular and structural formulae are:C16H21NO2.HClPropr... |
| Active Ingredient | Propranolol hydrochloride |
| Dosage Form | Tablet; Injectable; Capsule, extended release; Solution |
| Route | Injection; Oral |
| Strength | 1mg/ml; 160mg; 40mg/5ml; 120mg; 60mg; 10mg; 20mg/5ml; 80mg; 40mg; 20mg |
| Market Status | Prescription |
| Company | Vintage Pharms; Upsher Smith; Bedford; Aptalis Pharmatech; Hikma Farmaceutica; Northstar Hlthcare; Sandoz; Roxane; Watson Labs; Glatt Air; Actavis Elizabeth; Baxter Hlthcare; Fresenius Kabi Usa; Ipca Labs; Zydus Pharms Usa; Pliva; Mylan |
| 5 of 10 | |
|---|---|
| Drug Name | Tev-tropin |
| Active Ingredient | Somatropin recombinant |
| Dosage Form | Injectable |
| Route | Injection |
| Strength | 5mg/vial |
| Market Status | Prescription |
| Company | Ferring |
| 6 of 10 | |
|---|---|
| Drug Name | Inderal |
| PubMed Health | Propranolol (By mouth) |
| Drug Classes | Antianginal, Antiarrhythmic, Group II, Antihypertensive, Antimigraine, Cardiovascular Agent |
| Drug Label | Inderal (propranolol hydrochloride) is a synthetic beta-adrenergic receptor-blocking agent chemically described as 2-Propanol, 1-[(1-methylethyl)amino]-3-(1-naphthalenyloxy)-, hydrochloride,()-. Its molecular and structural formulae are: C16H21NO... |
| Active Ingredient | Propranolol hydrochloride |
| Dosage Form | Tablet |
| Route | oral |
| Strength | 60mg; 10mg; 80mg; 40mg; 20mg |
| Market Status | Prescription |
| Company | Akrimax Pharms |
| 7 of 10 | |
|---|---|
| Drug Name | Inderal la |
| PubMed Health | Somatropin, E coli Derived (Injection) |
| Drug Classes | Endocrine-Metabolic Agent |
| Drug Label | Inderal (propranolol hydrochloride) is a synthetic beta-adrenergic receptor-blocking agent chemically described as 2-Propanol, 1-[(1-methylethyl)amino]-3-(1-naphthalenyloxy)-, hydrochloride,()-. Its molecular and structural formulae are: C16H21NO... |
| Active Ingredient | Propranolol hydrochloride |
| Dosage Form | Capsule, extended release |
| Route | Oral |
| Strength | 160mg; 120mg; 60mg; 80mg |
| Market Status | Prescription |
| Company | Akrimax Pharms |
| 8 of 10 | |
|---|---|
| Drug Name | Innopran xl |
| PubMed Health | Propranolol |
| Drug Classes | Antianginal, Antiarrhythmic, Group II, Antihypertensive, Antimigraine, Cardiovascular Agent |
| Drug Label | INNOPRAN XL (propranolol hydrochloride) is a nonselective, beta-adrenergic receptor-blocking agent for oral administration, available as an extended release product. INNOPRAN XL is available as 80-mg and 120-mg capsules which contain sustained-releas... |
| Active Ingredient | Propranolol hydrochloride |
| Dosage Form | Capsule, extended release |
| Route | Oral |
| Strength | 120mg; 80mg |
| Market Status | Prescription |
| Company | Glaxosmithkline |
| 9 of 10 | |
|---|---|
| Drug Name | Propranolol hydrochloride |
| PubMed Health | Propranolol (Injection) |
| Drug Classes | Antianginal, Antiarrhythmic, Group II, Antihypertensive, Antimigraine, Cardiovascular Agent |
| Drug Label | hydrochloride(Propranolol is a synthetic beta-adrenergic receptor blocking agent chemically described as 2-Propanol, 1-[(1-methylethyl)amino]-3-(1-naphthalenyloxy)-, hydrochloride,()-. Its molecular and structural formulae are:C16H21NO2.HClPropr... |
| Active Ingredient | Propranolol hydrochloride |
| Dosage Form | Tablet; Injectable; Capsule, extended release; Solution |
| Route | Injection; Oral |
| Strength | 1mg/ml; 160mg; 40mg/5ml; 120mg; 60mg; 10mg; 20mg/5ml; 80mg; 40mg; 20mg |
| Market Status | Prescription |
| Company | Vintage Pharms; Upsher Smith; Bedford; Aptalis Pharmatech; Hikma Farmaceutica; Northstar Hlthcare; Sandoz; Roxane; Watson Labs; Glatt Air; Actavis Elizabeth; Baxter Hlthcare; Fresenius Kabi Usa; Ipca Labs; Zydus Pharms Usa; Pliva; Mylan |
| 10 of 10 | |
|---|---|
| Drug Name | Tev-tropin |
| Active Ingredient | Somatropin recombinant |
| Dosage Form | Injectable |
| Route | Injection |
| Strength | 5mg/vial |
| Market Status | Prescription |
| Company | Ferring |
Adrenergic beta-Antagonists; Anti-Anxiety Agents; Anti-Arrhythmia Agents; Antihypertensive Agents; Sympatholytics; Vasodilator Agents
National Library of Medicine's Medical Subject Headings online file (MeSH, 1999)
/SRP: Former use/: Propranolol has proven to be effective in numerous cases in which digitalis, with or without quinidine and/or procainamide, failed to reduce ventricular rate, and in cases of paroxysmal atrial tachycardia attributed to digitalis toxicity.
Goodman, L.S., and A. Gilman. (eds.) The Pharmacological Basis of Therapeutics. 5th ed. New York: Macmillan Publishing Co., Inc., 1975., p. 700
Propranolol is also used in hypertrophic obstructive cardiomyopathies. In these conditions forceful contraction of myocardium along a ventricular outflow tract can greatly increase outflow resistance, particularly during exercise. .../It/ is sometimes useful in management of tachycardia and arrhythmias in patient with pheochromocytoma.
Goodman, L.S., and A. Gilman. (eds.) The Pharmacological Basis of Therapeutics. 5th ed. New York: Macmillan Publishing Co., Inc., 1975., p. 552
Medication (Vet): ...Atropine in conjunction with propranolol /was found/ to be useful in treatment of oleander poisoning.
Clarke, E.G., and M. L. Clarke. Veterinary Toxicology. Baltimore, Maryland: The Williams and Wilkins Company, 1975., p. 275
For more Therapeutic Uses (Complete) data for PROPRANOLOL HYDROCHLORIDE (25 total), please visit the HSDB record page.
.../Propranolol/ is relatively contraindicated in ...hay fever, cardiogenic shock, congestive heart failure, right ventricular failure secondary to pulmonary hypertension, and when myocardial depressant anesthetics, tricyclic antidepressants, or oral hypoglycemics are used.
Osol, A. and J.E. Hoover, et al. (eds.). Remington's Pharmaceutical Sciences. 15th ed. Easton, Pennsylvania: Mack Publishing Co., 1975., p. 835
Propranolol (1% solution) used as eye-drops .../per 1 report/, caused intense pain lasting as long as 15 min and induced hyperemia and slight miosis, but according to others these eye-drops have been well tolerated by most patients in use up to 4 times/day for 3-4 months, causing burning sensations and conjunctival hyperemia in only 8/47 eyes.
Grant, W.M. Toxicology of the Eye. 3rd ed. Springfield, IL: Charles C. Thomas Publisher, 1986., p. 768
Contraindicated in patients with cardiogenic shock, sinus bradycardia and greater than first degree block, bronchial asthma, and congestive heart failure. Adverse reactions include weakness, light headedness, depression, bradycardia, paresthesia of hands, arterial insufficiency (e.g., Raynaud type), nausea, and diarrhea. Use is best avoided in patients with bronchospastic diseases and therapy in diabetic patients must be closely monitored.
Hussar, D.A. (ed.). Modell's Drugs in Current Use and New Drugs. 38th ed. New York, NY: Springer Publishing Co., 1992., p. 140
After sudden cessation of propranolol therapy in some patients treated for angina, increased frequency, duration, and severity of angina episodes have occurred, often within 24 hr. These episodes are unstable and are not relieved by nitroglycerin. Acute and sometimes fatal myocardial infarction and sudden death have also occurred after abrupt withdrawal of propranolol therapy in some patients treated for angina. In hypertensive patients, sudden cessation of propranolol has produced a syndrome similar to florid thyrotoxicosis, characterized by tenseness, anxiety, tachycardia, and excessive perspiration; these symptoms occurred within one week of cessation of the drug and were relieved by reinstituting propranolol therapy.
McEvoy, G.K. (ed.). American Hospital Formulary Service - Drug Information 2003. Bethesda, MD: American Society of Health-System Pharmacists, Inc. 2003 (Plus Supplements)., p. 1782
For more Drug Warnings (Complete) data for PROPRANOLOL HYDROCHLORIDE (31 total), please visit the HSDB record page.
Hemangiol is indicated in the treatment of proliferating infantile haemangioma requiring systemic therapy:
- Life- or function-threatening haemangioma,
- Ulcerated haemangioma with pain and/or lack of response to simple wound care measures,
- Haemangioma with a risk of permanent scars or disfigurement.
It is to be initiated in infants aged 5 weeks to 5 months.
Adrenergic beta-Antagonists
Drugs that bind to but do not activate beta-adrenergic receptors thereby blocking the actions of beta-adrenergic agonists. Adrenergic beta-antagonists are used for treatment of hypertension, cardiac arrhythmias, angina pectoris, glaucoma, migraine headaches, and anxiety. (See all compounds classified as Adrenergic beta-Antagonists.)
Antihypertensive Agents
Drugs used in the treatment of acute or chronic vascular HYPERTENSION regardless of pharmacological mechanism. Among the antihypertensive agents are DIURETICS; (especially DIURETICS, THIAZIDE); ADRENERGIC BETA-ANTAGONISTS; ADRENERGIC ALPHA-ANTAGONISTS; ANGIOTENSIN-CONVERTING ENZYME INHIBITORS; CALCIUM CHANNEL BLOCKERS; GANGLIONIC BLOCKERS; and VASODILATOR AGENTS. (See all compounds classified as Antihypertensive Agents.)
Vasodilator Agents
Drugs used to cause dilation of the blood vessels. (See all compounds classified as Vasodilator Agents.)
Anti-Arrhythmia Agents
Agents used for the treatment or prevention of cardiac arrhythmias. They may affect the polarization-repolarization phase of the action potential, its excitability or refractoriness, or impulse conduction or membrane responsiveness within cardiac fibers. Anti-arrhythmia agents are often classed into four main groups according to their mechanism of action: sodium channel blockade, beta-adrenergic blockade, repolarization prolongation, or calcium channel blockade. (See all compounds classified as Anti-Arrhythmia Agents.)
C07AA05
Studies in man and experimental animals indicate that rapid hepatic clearance is responsible for appearance of only trace amount of unmetabolized propranolol in blood after small oral doses. With larger doses, blood levels are linearly related to dose, suggesting saturation of hepatic metabolic system.
The Chemical Society. Foreign Compound Metabolism in Mammals Volume 3. London: The Chemical Society, 1975., p. 144
Propranolol is almost completely absorbed from the GI tract; however, plasma concentrations attained are quite variable among individuals. There is no difference in the rate of absorption of the 2 isomers of propranolol. Propranolol appears in the plasma within 30 min, and peak plasma concentrations are reached about 60-90 min after oral administration of the conventional tablets. The time when peak plasma concentrations are reached may be delayed, but concentrations are not necessarily lowered, when the drug is administered with food. Oral bioavailability of the drug may be increased in children with Down's syndrome; higher than expected plasma propranolol concentrations have been observed in such children. Bioavailability of a single 40-mg oral dose of propranolol hydrochloride as a conventional tablet or oral solution reportedly is equivalent in adults.
McEvoy, G.K. (ed.). American Hospital Formulary Service - Drug Information 2003. Bethesda, MD: American Society of Health-System Pharmacists, Inc. 2003 (Plus Supplements)., p. 1785-6
Propranolol hydrochloride is slowly absorbed following administration of the drug as extended release capsules, and peak blood concentrations are reached about 6 hr after administration. When measured at steady state over a 24 hr period, the area under the plasma concentration time curve for the extended release capsules is about 60-65% of the plasma concentration time curve for a comparable divided daily dose of the conventional tablets. The lower plasma concentration time curve is probably caused by the slower rate of absorption of the drug from the extended release capsules with resultant greater hepatic metabolism. After administration of a single dose of propranolol as the extended release capsules, blood concentrations are fairly constant for about 12 hr and then decline exponentially during the following 12 hr.
McEvoy, G.K. (ed.). American Hospital Formulary Service - Drug Information 2003. Bethesda, MD: American Society of Health-System Pharmacists, Inc. 2003 (Plus Supplements)., p. 1785-6
Following iv administration of propranolol, the onset of action is almost immediate. Animal studies indicate that propranolol is rapidly absorbed after im administration.
McEvoy, G.K. (ed.). American Hospital Formulary Service - Drug Information 2003. Bethesda, MD: American Society of Health-System Pharmacists, Inc. 2003 (Plus Supplements)., p. 1786
For more Absorption, Distribution and Excretion (Complete) data for PROPRANOLOL HYDROCHLORIDE (12 total), please visit the HSDB record page.
Besides ... 4-hydroxypropranolol and naphthoxylacetic acid, 6 new urinary metabolites have... been identified... /which are/ n-deisopropylpropranolol; 1-(alpha-naphthoxy)-2,3-propyleneglycol; ring hydroxylated 1-(alpha-naphthoxy)-2,3-propyleneglycol; alpha-naphthoxyacetic acid; alpha-naphthol and 1,4-dihydroxynaphthalene.
The Chemical Society. Foreign Compound Metabolism in Mammals Volume 3. London: The Chemical Society, 1975., p. 215
Isopropylamine and hexadeuteriated isopropylamine have been identified as urinary metabolites of propranolol and hexadeuteriated propranolol, respectively; this is believed to be 1st recorded example of single-step oxidative deamination of n-isopropylamine compound.
The Chemical Society. Foreign Compound Metabolism in Mammals Volume 3. London: The Chemical Society, 1975., p. 217
During initial oral therapy (but not during iv or chronic oral therapy), an active metabolite, 4-hydroxypropranolol, is formed. 4-Hydroxypropranolol has about the same beta-adrenergic blocking potency as does propranolol and may be present in plasma in amounts about equal to propranolol. This metabolite is eliminated more rapidly than propranolol and is virtually absent from the plasma 6 hr after oral administration of the drug. Results of one study indicate that after iv administration or chronic oral administration of propranolol, 4-hydroxypropranolol is not formed to a substantial extent, and beta-adrenergic blocking activity is more closely reflected by propranolol concentrations. Individual variations in ability to hydroxylate propranolol to the active metabolite may also exist. In addition, some other metabolites of propranolol may possess antiarrhythmic activity without beta-adrenergic blocking activity.
McEvoy, G.K. (ed.). American Hospital Formulary Service - Drug Information 2003. Bethesda, MD: American Society of Health-System Pharmacists, Inc. 2003 (Plus Supplements)., p. 1786
Propranolol is almost completely metabolized in the liver and at least 8 metabolites have been identified in urine. Only 1-4% of an oral or iv dose of the drug appears in feces as unchanged drug and metabolites.
McEvoy, G.K. (ed.). American Hospital Formulary Service - Drug Information 2003. Bethesda, MD: American Society of Health-System Pharmacists, Inc. 2003 (Plus Supplements)., p. 1786
When usual therapeutic doses of propranolol are administered chronically, the half-life ranges from 3.4-6 hr. Single dose studies generally have shown a shorter half-life of 2-3 hr.
McEvoy, G.K. (ed.). American Hospital Formulary Service - Drug Information 2003. Bethesda, MD: American Society of Health-System Pharmacists, Inc. 2003 (Plus Supplements)., p. 1786
Propranolol is a nonselective beta-adrenergic blocking agent. Propranolol inhibits response to adrenergic stimuli by competitively blocking, beta-adrenergic receptors within the myocardium and within bronchial and vascular smooth muscle. Only the l-isomer of propranolol has substantial beta-adrenergic blocking activity. Propranolol has no intrinsic sympathomimetic activity.
McEvoy, G.K. (ed.). American Hospital Formulary Service - Drug Information 2003. Bethesda, MD: American Society of Health-System Pharmacists, Inc. 2003 (Plus Supplements)., p. 1785
Through its myocardial, beta-adrenergic blocking action, propranolol decreases heart rate and prevents exercise induced increases in heart rate, decreases myocardial contractility, decreases cardiac output, increases systolic ejection time, and increases cardiac volume. The drug also decreases conduction velocity through the sinoatrial and atrioventricular nodes and decreases myocardial automaticity via beta-adrenergic blockade. At blood concentrations greater than those required for beta-adrenergic blockade, propranolol has a membrane stabilizing effect on the heart which is similar to that of quinidine. The clinical importance of this effect is not clear, but it appears to be less important than its beta-adrenergic blocking activity.
McEvoy, G.K. (ed.). American Hospital Formulary Service - Drug Information 2003. Bethesda, MD: American Society of Health-System Pharmacists, Inc. 2003 (Plus Supplements)., p. 1785
beta-Adrenergic blockade may also incr peripheral resistance initially, but peripheral resistance tends to decr after chronic admin of the drug as a result of unopposed alpha-adrenergic vasoconstriction. The cardiac effects of, beta-adrenergic blockade cause an incr in sodium reabsorption because of alterations in renal hemodynamics; renal blood flow and glomerular filtration rate generally decr during chronic therapy. Plasma volume may incr if dietary sodium is not restricted. Hepatic blood flow is decreased.
McEvoy, G.K. (ed.). American Hospital Formulary Service - Drug Information 2003. Bethesda, MD: American Society of Health-System Pharmacists, Inc. 2003 (Plus Supplements)., p. 1785
The precise mechanism of propranolol's hypotensive effect has not been determined. It has been postulated that beta-adrenergic blocking agents reduce blood pressure by blocking peripheral (especially cardiac) adrenergic receptors (decreasing cardiac output), by decreasing sympathetic outflow from the CNS, and/or by suppressing renin release. In patients with high concentrations of circulating renin, low doses of the drug are associated with a fall in both blood pressure and in plasma renin concentrations, probably because of acute peripheral beta-adrenergic blockade. With higher doses of propranolol, the hypotensive effect is probably unrelated to plasma renin activity and may be caused by a delayed centrally mediated reduction of adrenergic outflow. However, there appears to be some overlap between these mechanisms, and both mechanisms seem to be operative with usual therapeutic doses. Propranolol decreases blood pressure in both the supine and standing positions.
McEvoy, G.K. (ed.). American Hospital Formulary Service - Drug Information 2003. Bethesda, MD: American Society of Health-System Pharmacists, Inc. 2003 (Plus Supplements)., p. 1785
Through its beta-adrenergic blocking action in other body systems, propranolol increases airway resistance (especially in asthmatic patients), inhibits glycogenolysis in the skeletal and cardiac muscles, blocks the release of free fatty acids and insulin by adrenergic stimulation, and increases the number of circulating eosinophils. Propranolol increases uterine activity, more in the nonpregnant than in the pregnant uterus.
McEvoy, G.K. (ed.). American Hospital Formulary Service - Drug Information 2003. Bethesda, MD: American Society of Health-System Pharmacists, Inc. 2003 (Plus Supplements)., p. 1785