

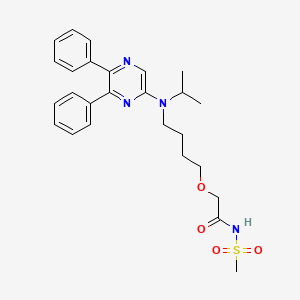

1. 2-(4-((5,6-diphenylpyrazin-2-yl)(isopropyl)amino)butoxy)-n-(methylsulfonyl)acetamide
2. Act 293987
3. Act-293987
4. Act293987
5. Ns-304
6. Uptravi
1. 475086-01-2
2. Ns-304
3. Uptravi
4. Act-293987
5. Ns 304
6. Act 293987
7. 2-(4-((5,6-diphenylpyrazin-2-yl)(isopropyl)amino)butoxy)-n-(methylsulfonyl)acetamide
8. 5exc0e384l
9. 2-[4-[(5,6-diphenylpyrazin-2-yl)-propan-2-ylamino]butoxy]-n-methylsulfonylacetamide
10. Ns-304;act-293987
11. 2-{4-[(5,6-diphenylpyrazin-2-yl)(propan-2-yl)amino]butoxy}-n-(methanesulfonyl)acetamide
12. 2-(4-((5,6-diphenylpyrazin-2-yl)(propan-2-yl)amino)butoxy}-n-(methanesulfonyl)acetamide
13. 2-[4-[(5,6-diphenyl-2-pyrazinyl)(1-methylethyl)amino]butoxy]-n-(methylsulfonyl)acetamide
14. Unii-5exc0e384l
15. Selexipag [usan:inn]
16. 2-(4-((5,6-diphenylpyrazin-2-yl)(propan-2-yl)amino)butoxy)-n-(methanesulfonyl)acetamide
17. Uptravi (tn)
18. Act293987
19. Ns-304(selexipag)
20. Selexipag(ns-304)
21. Selexipag [inn]
22. Selexipag [jan]
23. Selexipag [mi]
24. Selexipag [usan]
25. Selexipag [who-dd]
26. Selexipag (jan/usan/inn)
27. Schembl674122
28. Chembl238804
29. Gtpl7552
30. Selexipag [orange Book]
31. Chebi:90844
32. Dtxsid301027959
33. Amy10851
34. Bcp09146
35. Zinc3990451
36. Bdbm50235383
37. Mfcd10567093
38. S3726
39. Akos024457572
40. Ccg-269668
41. Cs-3774
42. Db11362
43. Sb17055
44. 2-{4-[n-(5,6-diphenylpyrazin-2-yl)-n-isopropylamino]butyloxy}-n-(methylsulfonyl)acetamide
45. Ncgc00370833-01
46. Ncgc00370833-02
47. Ac-30209
48. Bs-16872
49. Hy-14870
50. Db-119997
51. B7378
52. Ft-0776043
53. D09994
54. A857156
55. Q15424759
56. 2-(4-((5,6-diphenyl-2-pyrazinyl)(isopropyl)amino)butoxy)-n-(methylsulfonyl)acetamide
57. 2-[4-[[5,6-di(phenyl)pyrazin-2-yl]-propan-2-ylamino]butoxy]-n-methylsulfonylacetamide
58. 2-{4-[(5,6-diphenylpyrazin-2-yl)(propan-2-yl)amino]butoxy}-n-methanesulfonylacetamide
| Molecular Weight | 496.6 g/mol |
|---|---|
| Molecular Formula | C26H32N4O4S |
| XLogP3 | 3.8 |
| Hydrogen Bond Donor Count | 1 |
| Hydrogen Bond Acceptor Count | 7 |
| Rotatable Bond Count | 12 |
| Exact Mass | 496.21442669 g/mol |
| Monoisotopic Mass | 496.21442669 g/mol |
| Topological Polar Surface Area | 110 Ų |
| Heavy Atom Count | 35 |
| Formal Charge | 0 |
| Complexity | 730 |
| Isotope Atom Count | 0 |
| Defined Atom Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Undefined Atom Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Defined Bond Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Undefined Bond Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Covalently Bonded Unit Count | 1 |
Selexipag is indicated for the treatment of pulmonary arterial hypertension (PAH) to delay disease progression and reduce risk of hospitalization.
FDA Label
Uptravi is indicated for the long-term treatment of pulmonary arterial hypertension (PAH) in adult patients with WHO functional class (FC) IIIII, either as combination therapy in patients insufficiently controlled with an endothelin receptor antagonist (ERA) and/or a phosphodiesterase type 5 (PDE-5) inhibitor, or as monotherapy in patients who are not candidates for these therapies.
Efficacy has been shown in a PAH population including idiopathic and heritable PAH, PAH associated with connective tissue disorders, and PAH associated with corrected simple congenital heart disease.
At the maximum tolerated dose of 1600 mcg twice per day, selexipag was not found to prolong the QT interval to a clinically relevant extent. Both selexipag and its metabolite caused concentration-dependent inhibition of platelet aggregation in vitro with IC50 of 5.5 M and 0.21 M, respectively. However, at clinically relevant concentrations, there was no effect on platelet aggregation test parameters following multiple dose administration of selexipag in healthy patients.
Antihypertensive Agents
Drugs used in the treatment of acute or chronic vascular HYPERTENSION regardless of pharmacological mechanism. Among the antihypertensive agents are DIURETICS; (especially DIURETICS, THIAZIDE); ADRENERGIC BETA-ANTAGONISTS; ADRENERGIC ALPHA-ANTAGONISTS; ANGIOTENSIN-CONVERTING ENZYME INHIBITORS; CALCIUM CHANNEL BLOCKERS; GANGLIONIC BLOCKERS; and VASODILATOR AGENTS. (See all compounds classified as Antihypertensive Agents.)
B01AC27
B - Blood and blood forming organs
B01 - Antithrombotic agents
B01A - Antithrombotic agents
B01AC - Platelet aggregation inhibitors excl. heparin
B01AC27 - Selexipag
Absorption
After oral administration, maximum concentrations of selexipag and its metabolite were observed to be reached at 1-3 and 3-4 hours, respectively. Absorption was impaired in the presence of food, resulting in delayed time to maximum concentration as well as ~30% lower peak plasma concentration. However, exposure was not found to be significantly affected by food.
Route of Elimination
93% in feces, 12% in urine.
Clearance
On average, 35 L/hour.
Selexipag yields its active metabolite by hydrolysis of the acylsulfonamide by the enzyme hepatic carboxylesterase 1. Oxidative metabolism catalyzed by CYP3A4 and CYP2C8 results in hydroxylated and dealkylated products. UGT1A3 and UGT2B7 are involved in the glucuronidation of the active metabolite. Other than active metabolite, other metabolites in circulation do not exceed 3% of the total drug-related material.
Selexipag's terminal half life is 0.8-2.5 hours. The active metabolite's terminal half life is 6.2-13.5 hours.
Selexipag is a selective prostacyclin (IP, also called PGI2) receptor agonist. The key features of pulmonary arterial hypertension include a decrease in prostacyclin and prostacyclin synthase (enzyme that helps produce prostacyclin) in the lung. Prostacyclin is a potent vasodilator with anti-proliferative, anti-inflammatory, and anti-thrombotic effects; therefore, there is strong rationale for treatment with IP receptor agonists. Selexipag is chemically distinct as it is not PGI2 or a PGI2 analogue and has high selectivity for the IP receptor. It is metabolized by carboxylesterase 1 to yield an active metabolite (ACT-333679) that is approximately 37 times more potent than selexipag. Both selexipag and its metabolite are selective for the IP receptor over other prostanoid receptors.
