


1. Kpt-330
2. Xpovio
1. Kpt-330
2. 1393477-72-9
3. Xpovio
4. Selinexor (kpt-330)
5. Selinexor Free Base
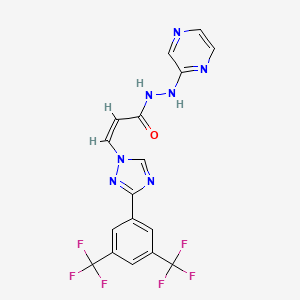
6. (z)-3-(3-(3,5-bis(trifluoromethyl)phenyl)-1h-1,2,4-triazol-1-yl)-n'-(pyrazin-2-yl)acrylohydrazide
7. Kpt 330
8. 31tz62fo8f
9. 2-propenoic Acid, 3-(3-(3,5-bis(trifluoromethyl)phenyl)-1h-1,2,4-triazol-1-yl)-, 2-(2-pyrazinyl)hydrazide, (2z)-
10. (z)-3-[3-[3,5-bis(trifluoromethyl)phenyl]-1,2,4-triazol-1-yl]-n'-pyrazin-2-ylprop-2-enehydrazide
11. 1621865-82-4
12. 2-propenoic Acid, 3-[3-[3,5-bis(trifluoromethyl)phenyl]-1h-1,2,4-triazol-1-yl]-, 2-(2-pyrazinyl)hydrazide, (2z)-
13. Selinexor [usan:inn]
14. Unii-31tz62fo8f
15. Nexpovio
16. Selinexor [inn]
17. Kpt330;selinexor
18. Xpovio (tn)
19. Kpt-330(selinexor)
20. Selinexor [mi]
21. Selinexor (usan/inn)
22. Selinexor [usan]
23. Selinexor [who-dd]
24. Selinexor [orange Book]
25. Chembl3545185
26. Schembl14678327
27. Gtpl10036
28. Ex-a870
29. Dtxsid801026013
30. Bdbm50527778
31. Mfcd27987944
32. Nsc780203
33. Nsc781780
34. Zinc96170454
35. Ccg-269161
36. Db11942
37. Nsc-780203
38. Nsc-781780
39. Ncgc00386310-01
40. Ncgc00386310-03
41. Ac-33645
42. Bs-15022
43. Compound 70 [wo2013019561a1]
44. N-hydroxy-n'-(2-phenylethyl)isophthalamide
45. S7252
46. Sw219336-1
47. D11222
48. A857179
49. J-690156
50. Q27256082
51. (2z)-2-(2-pyrazinyl)hydrazide-3-[3-[3,5-bis(trifluoromethyl)phenyl]-1h-1,2,4-triazol-1-yl]-2-propenoic Acid
52. Selinexor;(z)-3-(3-(3,5-bis(trifluoromethyl)phenyl)-1h-1,2,4-triazol-1-yl)-n'-(pyrazin-2-yl)acrylohydrazide
| Molecular Weight | 443.3 g/mol |
|---|---|
| Molecular Formula | C17H11F6N7O |
| XLogP3 | 3 |
| Hydrogen Bond Donor Count | 2 |
| Hydrogen Bond Acceptor Count | 12 |
| Rotatable Bond Count | 5 |
| Exact Mass | 443.09292697 g/mol |
| Monoisotopic Mass | 443.09292697 g/mol |
| Topological Polar Surface Area | 97.6 Ų |
| Heavy Atom Count | 31 |
| Formal Charge | 0 |
| Complexity | 621 |
| Isotope Atom Count | 0 |
| Defined Atom Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Undefined Atom Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Defined Bond Stereocenter Count | 1 |
| Undefined Bond Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Covalently Bonded Unit Count | 1 |
Selinexor is indicated for the treatment of relapsed or refractory multiple myeloma in combination with dexamethasone. Patients must have received at least 4 prior therapies and have disease which is refractory to least two proteasome inhibitors, at least two immunomodulatory agents, and an antiCD38 monoclonal antibody.
FDA Label
NEXPOVIO is indicated
- in combination with bortezomib and dexamethasone for the treatment of adult patients with multiple myeloma who have received at least one prior therapy.
- in combination with dexamethasone for the treatment of multiple myeloma in adult patients who have received at least four prior therapies and whose disease is refractory to at least two proteasome inhibitors, two immunomodulatory agents and an anti-CD38 monoclonal antibody, and who have demonstrated disease progression on the last therapy.
Selinexor causes cell cycle arrest and apoptosis in cancer cells.
L01XX66
L - Antineoplastic and immunomodulating agents
L01 - Antineoplastic agents
L01X - Other antineoplastic agents
L01XX - Other antineoplastic agents
L01XX66 - Selinexor
Absorption
A single 80 mg dose of selinexor produces a mean Cmax of 680 ng/mL and a mean AUC of 5386 ng*h/mL. This relationship is dose proportion over the range of 3-85 mg/m2 which encompasses the range of 0.06-1.8 times the approved dosage. The official FDA labeling reports the Tmax as 4 hours but phase 1 studies have found a range of 2-4 hours. Administering selinexor with food, either a high or low fat meal, results in an increase in the AUC of approximately 15-20% but this is not expected to be clinically significant.
Volume of Distribution
The mean apparent volume of distribution is 125 L. A phase 1 study reported mean apparent volumes of distribution ranging from 1.9-2.9 L/kg in their investigation of food and formulation effects.
Clearance
Selinexor has a mean apparent clearance of 17.9 L/h.
Selinexor is known to be metabolized through CYP3A4, UDPglucuronosyltransferases, and glutathione S-transferases although the metabolite profile has yet to be characterized in published literature. The primary metabolites found in urine and plasma are glucuronide conjugates.
Selinexor has a mean half-life of elimination of 6-8 hours.
Selinexor binds to and inhibits exportin-1 (XPO1). XPO1 is a nuclear exporter protein which contains a pocket to which nuclear proteins can bind. When complexed with these proteins and Ran, activated through guanosine triphosphate (GTP) binding, the XPO1-protein-Ran-GTP complex is able to exit the nucleus through a nuclear pore. Once outside, GTP is hydrolyzed and the complex dissociates. The inhibition of this process in cancer cells allows the targets of XPO1, many of which are tumor suppressors, to collect in the nucleus and result in increased transcription of tumor suppressor genes. Tumor suppressor proteins known to be affected by XPO1 inhibition include p53, p73, adenomatous polyposis coli, retinoblastoma, forkhead box protein O, breast cancer 1, nucleophosmin, and merlin. Regulators of cell cycle progression are also affected, namely p21, p27, galectin-3, and Tob. Inhibitor of NFB also collects in the nucleus as a result leading to reduced activity of NFB, a known contributor to cancer. XPO1 participates in the formation of a complex with eukaryotic initiation factor 4E and contributes to the transport of messenger RNA for several oncegenes including cell cycle promotors, cyclin D1, cyclin E, and CDK2/4/6, as well as antiapoptotic proteins, Mcl-1 and Bcl-xL. These wide ranging changes in protein expression and gene transcription culminate in cell cycle arrest and the promotion of apoptosis in cancer cells.