

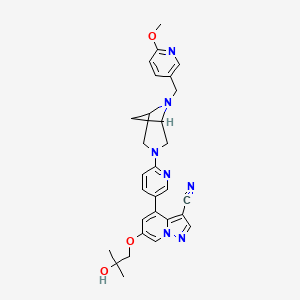

1. 6-(2-hydroxy-2-methylpropoxy)-4-(6-(6-((6-methoxypyridin-3-yl)methyl)-3,6-diazabicyclo(3.1.1)heptan-3-yl)pyridin-3-yl)pyrazolo(1,5-a)pyridine-3-carbonitrile
2. Loxo-292
3. Serpercatinib
1. 2152628-33-4
2. Loxo-292
3. Retevmo
4. Selpercatinib [inn]
5. Cegm9ybngd
6. Selpercatinib [usan]
7. Ly3527723
8. Ret Inhibitor Loxo-292
9. Loxo292
10. 6-(2-hydroxy-2-methylpropoxy)-4-[6-[6-[(6-methoxypyridin-3-yl)methyl]-3,6-diazabicyclo[3.1.1]heptan-3-yl]pyridin-3-yl]pyrazolo[1,5-a]pyridine-3-carbonitrile
11. 6-(2-hydroxy-2-methylpropoxy)-4-(6-(6-((6-methoxypyridin-3-yl)methyl)-3,6-diazabicyclo[3.1.1]heptan-3-yl)pyridin-3-yl)pyrazolo[1,5-a]pyridine-3-carbonitrile
12. Ly-3527723
13. 6-(2-hydroxy-2-methylpropoxy)-4-[6-[6-[(6-methoxy-3-pyridinyl)methyl]-3,6-diazabicyclo[3.1.1]hept-3-yl]-3-pyridinyl]pyrazolo[1,5-a]pyridine-3-carbonitrile
14. 6-(2-hydroxy-2-methylpropoxy)-4-(6-(6-((6-methoxypyridin-3-yl)methyl)-3,6-diazabicyclo(3.1.1)heptan-3-yl)pyridin-3-yl)pyrazolo(1,5-a)pyridine-3-carbonitrile
15. Pyrazolo(1,5-a)pyridine-3-carbonitrile, 6-(2-hydroxy-2-methylpropoxy)-4-(6-(6-((6-methoxy-3-pyridinyl)methyl)-3,6-diazabicyclo(3.1.1)hept-3-yl)-3-pyridinyl)-
16. Serpercatinib
17. Retevmo (tn)
18. Unii-cegm9ybngd
19. Selpercatinib [mi]
20. Selpercatinib [jan]
21. Loxo-292; Selpercatinib
22. Selpercatinib(loxo-292)
23. Selpercatinib [who-dd]
24. Chembl4559134
25. Schembl20071478
26. Selpercatinib (jan/usan/inn)
27. Gtpl10318
28. Bdbm296429
29. Dtxsid901026442
30. Selpercatinib [orange Book]
31. Bcp29047
32. Cld62833
33. Ex-a2859
34. Nsc818434
35. S8781
36. Who 10967
37. Zb1574
38. Us10112942, Example 163
39. Us10112942, Example 166
40. Us10112942, Example 183
41. Akos037649115
42. Nsc-818434
43. Ac-31588
44. Bs-16622
45. Loxo-292;loxo 292;loxo292
46. Selpercatinib (loxo-292, Arry-192)
47. Example 163 [wo2018071447a1]
48. Hy-114370
49. Cs-0084279
50. D11713
51. D77980
52. A929273
| Molecular Weight | 525.6 g/mol |
|---|---|
| Molecular Formula | C29H31N7O3 |
| XLogP3 | 2.5 |
| Hydrogen Bond Donor Count | 1 |
| Hydrogen Bond Acceptor Count | 9 |
| Rotatable Bond Count | 8 |
| Exact Mass | 525.24883788 g/mol |
| Monoisotopic Mass | 525.24883788 g/mol |
| Topological Polar Surface Area | 112 Ų |
| Heavy Atom Count | 39 |
| Formal Charge | 0 |
| Complexity | 885 |
| Isotope Atom Count | 0 |
| Defined Atom Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Undefined Atom Stereocenter Count | 2 |
| Defined Bond Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Undefined Bond Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Covalently Bonded Unit Count | 1 |
Selpercatinib is indicated for the treatment of _RET_ fusion-positive non-small cell lung cancer in adult patients. Selpercatinib is also indicated for the systemic treatment of advanced or metastatic _RET_-mutant medullary thyroid cancer and for the systemic treatment of _RET_ fusion-positive radioactive iodine-refractory thyroid cancer in both adult and pediatric patients aged 12 and over. Selpercatinib is currently approved for these indications under an accelerated approval scheme and continued approval may be contingent on future confirmatory trials.
FDA Label
Treatment of all conditions included in the category of malignant neoplasms (except haematopoietic and lymphoid tissue neoplasms)
Retsevmo as monotherapy is indicated for the treatment of adults and adolescents 12 years and older with advanced RET-mutant medullary thyroid cancer (MTC)
- advanced RET fusion-positive non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) not previously treated with a RET inhibitor
- advanced RET fusion-positive thyroid cancer who require systematic therapy following prior treatment
Selpercatinib exerts anti-tumour activity in specific cancers through inhibition of mutated forms of RET tyrosine kinases. Due to its increased specificity for RET over other tyrosine kinases, selpercatinib is thought to have an improved safety profile compared to other multi-kinase inhibitors. Despite this, selpercatinib treatment is associated with hepatotoxicity, hypertension, QT interval prolongation, hemorrhagic events, risk of impaired wound healing, and embryo-fetal toxicity; some patients may also exhibit hypersensitivity to selpercatinib.
L01EX22
L - Antineoplastic and immunomodulating agents
L01 - Antineoplastic agents
L01E - Protein kinase inhibitors
L01EX - Other protein kinase inhibitors
L01EX22 - Selpercatinib
Absorption
In patients with locally advanced or metastatic solid tumours receiving 160 mg of selpercatinib twice daily, steady-state was achieved after approximately 7 days, with a Cmax of 2,980 (CV 53%) and AUC0-24h of 51,600 (CV 58%). The absolute bioavailability is between 60 and 82% (mean 73%), and the median tmax is two hours. Food has no apparent effect on the AUC or Cmax of selpercatinib. Patients with hepatic impairment display a concomitant increase in AUC0-INF for mild (7%), moderate (32%), and severe (77%) impairment.
Route of Elimination
Selpercatinib administered as a single 160 mg dose in healthy individuals was primarily recovered in feces (69%, 14% unchanged) and urine (24%, 12% unchanged).
Volume of Distribution
Selpercatinib has an apparent volume of distribution of 191 L; the volume of distribution increases with increasing body weight.
Clearance
Selpercatinib has an apparent clearance of 6L/h; the clearance increases with increasing body weight.
Selpercatinib is predominantly metabolized in the liver by CYP3A4.
Selpercatinib has a half-life of 32 hours in healthy individuals.
Rearranged during transfection (RET) is a transmembrane receptor tyrosine kinase containing extracellular, transmembrane, and intracellular domains whose activity is required for normal kidney and nervous system development. Constitutive RET activation is primarily achieved through chromosomal rearrangements producing 5' fusions of dimerizable domains to the 3' _RET_ tyrosine kinase domain, such as _KIF5B-RET_ and _CCDC6-RET_, resulting in constitutive dimerization and subsequent autophosphorylation. Constitutive activation leads to increased downstream signalling and is associated with tumour invasion, migration, and proliferation. Selpercatinib is a direct RET kinase inhibitor, exhibiting IC50 values between 0.92 and 67.8 nM depending on the exact _RET_ genotype. Information based on natural as well as induced resistance mutations and molecular modelling suggests that selpercatinib directly inhibits RET autophosphorylation by competing with ATP for binding. Various single amino acid mutations at position 810 inhibit selpercatinib binding without significantly altering ATP binding, potentially leading to treatment failures. Selpercatinib is also reported to inhibit other tyrosine kinase receptors, including VEGFR1, VEGFR3, FGFR1, FGFR2, and FGFR3, at clinically relevant concentrations. The significance of these effects is not well studied.
