
1. Arry 142886
2. Arry-142886
3. Arry142886
4. Azd 6244
5. Azd-6244
6. Azd6244
1. 606143-52-6
2. Azd6244
3. Arry-142886
4. Azd 6244
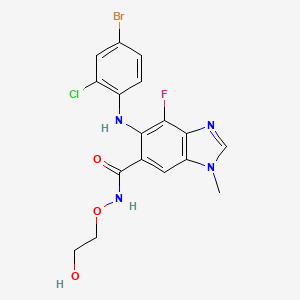
5. 5-[(4-bromo-2-chlorophenyl)amino]-4-fluoro-n-(2-hydroxyethoxy)-1-methyl-1h-benzimidazole-6-carboxamide
6. Azd-6244
7. Selumetinib (azd6244)
8. Arry 142886
9. Arry-886
10. Azd6244 (selumetinib)
11. 5-((4-bromo-2-chlorophenyl)amino)-4-fluoro-n-(2-hydroxyethoxy)-1-methyl-1h-benzo[d]imidazole-6-carboxamide
12. Koselugo
13. 5-(4-bromo-2-chlorophenylamino)-4-fluoro-n-(2-hydroxyethoxy)-1-methyl-1h-benzo[d]imidazole-6-carboxamide
14. Chembl1614701
15. Chebi:90227
16. 6uh91i579u
17. Nsc741078
18. Ncgc00189073-01
19. Ncgc00189073-02
20. 6-(4-bromo-2-chloroanilino)-7-fluoro-n-(2-hydroxyethoxy)-3-methylbenzimidazole-5-carboxamide
21. Dsstox_cid_28870
22. Dsstox_rid_83139
23. Dsstox_gsid_48944
24. 1h-benzimidazole-6-carboxamide, 5-[(4-bromo-2-chlorophenyl)amino]-4-fluoro-n-(2-hydroxyethoxy)-1-methyl-
25. 6-[(4-bromo-2-chlorophenyl)amino]-7-fluoro-n-(2-hydroxyethoxy)-3-methylbenzimidazole-5-carboxamide
26. Azd 6244;5-((4-bromo-2-chlorophenyl)amino)-4-fluoro-n-(2-hydroxyethoxy)-1-methyl-1h-benzo[d]imidazole-6-carboxamide;6-(4-bromo-2-chlorophenylamino)-7-fluoro-n-(2-hydroxyethoxy)-3-methyl-3h-benzo[d]imidazole-5-carboxamide
27. Cas-606143-52-6
28. Arry142886
29. Selumetinib [usan:inn]
30. Selumetinibum
31. Unii-6uh91i579u
32. 1h-benzimidazole-6-carboxamide, 5-((4-bromo-2-chlorophenyl)amino)-4-fluoro-n-(2-hydroxyethoxy)-1-methyl-
33. 3ew
34. 5-((4-bromo-2-chlorophenyl)amino)-4-fluoro-n-(2-hydroxyethoxy)-1-methyl-1h-benzimidazole-6-carboxamide
35. Selumetinib [mi]
36. Selumetinib [inn]
37. Selumetinib (usan/inn)
38. Selumetinib [usan]
39. Azd6244 - Selumetinib
40. Selumetinib [who-dd]
41. Schembl155456
42. Gtpl5665
43. Selumetinib, Arry-142886
44. Dtxsid3048944
45. Ex-a020
46. Bcpp000367
47. Hms3244g03
48. Hms3244g04
49. Hms3244h03
50. Hms3265k01
51. Hms3265k02
52. Hms3265l01
53. Hms3265l02
54. Hms3654o03
55. Nsc 741o78
56. Bcp01739
57. Tox21_113362
58. Bdbm50355497
59. Mfcd11977472
60. Nsc800882
61. S1008
62. Zinc31773258
63. Akos015904255
64. Tox21_113362_1
65. Bcp9000354
66. Ccg-264774
67. Cs-0059
68. Db11689
69. Ex-8621
70. Nsc-741078
71. Nsc-800882
72. Sb14707
73. Ncgc00189073-07
74. 6-(4-bromo-2-chloro-anilino)-7-fluoro-n-(2-hydroxyethoxy)-3-methyl-benzimidazole-5-carboxamide
75. Ac-25059
76. Am808016
77. Azd6244,selumetinib, Arry-142886
78. Hy-50706
79. Selumetinib (arry142886/azd6244)
80. Azd6244 (selumetinib,arry-142886)
81. Ft-0674552
82. Sw202561-3
83. D09666
84. 143a526
85. Q-101405
86. Q7448840
87. Brd-k57080016-001-01-9
88. 1h-benzimidazole-6-carboxamide, 5-((4-bromo-2-chlorophenyl)amino)-4-fluoro-n-(2- Hydroxyethoxy)-1-methyl-
89. 5-[(4-bromo-2-chlorophenyl)amino]-4-fluoro-n-(2-hydroxyethoxy)-1-methyl-1h-1,3-benzodiazole-6-carboxamide
90. 6-(4-bromo-2-chloro-phenylamino)-7-fluoro-3-methyl-3h-benzoimidazole-5-carboxylic Acid (2-hydroxy -ethoxy)-amide
91. 6-(4-bromo-2-chloro-phenylamino)-7-fluoro-3-methyl-3h-benzoimidazole-5-carboxylic Acid (2-hydroxy-ethoxy)-amide
92. 6-(4-bromo-2-chloro-phenylamino)-7-fluoro-3-methyl-3h-benzoimidazole-5-carboxylic Acid(2-hydroxy-ethoxy)-amide
93. 6-(4-bromo-2-chlorophenylamino)-7-fluoro-3-methyl-3h-benzoimidazole-5-carboxylic Acid (2-hydroxyethoxy)-amide
94. 6-(4-bromo-2-chlorophenylamino)-7-fluoro-3-methyl-3h-benzoimidazole-5-carboxylic Acid(2-hydroxyethoxy)-amide
95. 6-(4-bromo-2chloro-phenylamino)-7-fluoro-3-methyl-3h-benzoimidazole-5-carboxylic Acid (2-hydroxy-ethoxy)-amide
| Molecular Weight | 457.7 g/mol |
|---|---|
| Molecular Formula | C17H15BrClFN4O3 |
| XLogP3 | 3.6 |
| Hydrogen Bond Donor Count | 3 |
| Hydrogen Bond Acceptor Count | 6 |
| Rotatable Bond Count | 6 |
| Exact Mass | 456.00001 g/mol |
| Monoisotopic Mass | 456.00001 g/mol |
| Topological Polar Surface Area | 88.4 Ų |
| Heavy Atom Count | 27 |
| Formal Charge | 0 |
| Complexity | 523 |
| Isotope Atom Count | 0 |
| Defined Atom Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Undefined Atom Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Defined Bond Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Undefined Bond Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Covalently Bonded Unit Count | 1 |
Although selumetinib has been investigated for the treatment of several types of cancer, it is currently only indicated for the treatment of neurofibromatosis type 1 (NF1) in patients 2 years who have symptomatic, inoperable plexiform neurofibromas (PN).
FDA Label
Koselugo as monotherapy is indicated for the treatment of symptomatic, inoperable plexiform neurofibromas (PN) in paediatric patients with neurofibromatosis type 1 (NF1) aged 3 years and above
Selumetinib is a non-ATP-competitive mitogen-activated protein kinase kinase 1 and 2 (MEK1 and MEK2) inhibitor. By selectively targeting MEK1 and MEK2, selumetinib is able to inhibit oncogenic downstream effects of the Raf-MEK-ERK signaling pathway, which is often overactive in certain types of cancer. Indeed, a study investigating the effects of selumetinib in children with NF-1 found that treatment with the anti-neoplastic resulted in reduced tumor size. Decreases in tumor-associated pain and improvements in overall function were also subjectively reported. Selumetinib has minimal off-target activity, contributing to its impressive safety profile.
L - Antineoplastic and immunomodulating agents
L01 - Antineoplastic agents
L01E - Protein kinase inhibitors
L01EE - Mitogen-activated protein kinase (mek) inhibitors
L01EE04 - Selumetinib
Absorption
Based on several studies investigating selumetinib at various doses in both pediatric and adult populations, the Tmax generally ranges between 1- 1.5 hours. In healthy adults, the mean absolute oral bioavailability was reported to be 62%. Selumetinib should be administered on an empty stomach since food significantly decreases serum concentrations of the drug.
Route of Elimination
Approximately 59% of selumetinib is eliminated in the feces, while 33% is eliminated in the urine.
Volume of Distribution
The mean apparent volume of distribution of selumetinib at steady state in pediatric patients ranged from 78 L to 171 L. A study in healthy adult males found a mean apparent volume of distribution of 146 L. Another study observing the pharmacokinetic effects of various selumetinib doses and regimens in select Japanese patients found that the apparent volume of distribution values at steady-state ranged from 73.2 - 148.1 L.
Clearance
The clearance of selumetinib in pediatric patients is 8.8 L/hr. A study in healthy adult males found a clearance value of 15.7 L/hr. Another study observing the pharmacokinetic effects of various selumetinib doses and regimens in select Japanese patients found clearance values that ranged from 9.2 - 15.9 L/hr.
Selumetinib is heavily metabolized in the liver and the proposed metabolic pathway is as follows: Hydrolysis of selumetinibs amide functional group produces M15 (AZ13326637), which contains a carboxylic acid. Elimination of the ethanediol moiety from the parent compound results in the formation of the primary amide M14 (AZ12791138) metabolite. Amide hydrolysis transforms M14 into M15, glucuronidation and further oxidation of M14 leads to M2, M6 and M1, and N-demethylation of M14 produces M12. The amide glucuronide (M2) is thought to be the major circulating metabolite. Demethylation of selumetinib produces the pharmacologically active M8 (AZ12442942), and further oxidation of M8 leads to M11. Glucuronidation of M8 produces M3 or M5, and elimination of the ethanediol moiety from M8 results in a primary amide, producing M12. Although the N-demethylated metabolite (M8) accounts for <10% of the circulating metabolites, it is responsible for approximately 21-35% of any observed pharmacological activity. Ribose conjugation transforms M12 into M9, while oxidation of M12 leads to M10 and M13 metabolites. Glucuronidation of M10 produces M1. Direct glucuronidation of selumetinib produces M4 or M7, which can both eventually transform into M3 and M5 metabolites.
Selumetinib is characterized by a short half-life. The elimination half-life associated with a dose of 25 mg/m2 in pediatric patients is 6.2 hours. In a study observing the pharmacokinetic effects of various selumetinib regimens in select Japanese patients, the half-life ranged from 9.2- 10.6 hours. In other studies where selumetinib 75 mg is administered twice daily, the half-life is reported to be approximately 13 hours.
The Ras-Raf-MEK-ERK signaling cascade is known to be activated in several types of cancer, and regulates the transcription of proteins involved in apoptosis. In addition, studies have shown that mutations of the Raf component of the pathway can contribute to chemotherapy drug resistance. Ras as well as several kinases and phosphatases are responsible for regulating the Raf-MEK-ERK pathway. Often in cancers, Ras (a G-protein coupled receptor) is deregulated, allowing downstream signalling to proceed unchecked. Through several complex steps, Raf phosphorylates and activates MEK, which then phosphorylates and activates ERK. ERK is then able to exert its effects on several downstream targets. As such, therapies inhibiting upstream components of this pathway have become attractive targets for cancer treatment. Selumetinib exerts its effects by selectively inhibiting MEK1 and MEK2 which can effectively blunt the pleiotropic effects of the Ras-Raf-MEK-ERK cascade. By inhibiting this oncogenic pathway, selumetinib reduces cell proliferation, and promotes pro-apoptotic signal transduction.