
1. Acid, Ascorbic
2. Acid, L-ascorbic
3. Ascorbate, Ferrous
4. Ascorbate, Magnesium
5. Ascorbate, Sodium
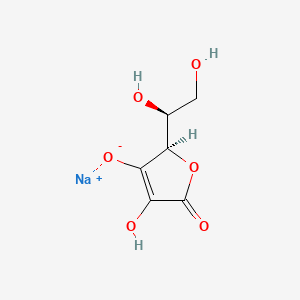
6. Ascorbic Acid
7. Ascorbic Acid, Monosodium Salt
8. Di-l-ascorbate, Magnesium
9. Ferrous Ascorbate
10. Hybrin
11. L Ascorbic Acid
12. L-ascorbic Acid
13. Magnesium Ascorbate
14. Magnesium Ascorbicum
15. Magnesium Di L Ascorbate
16. Magnesium Di-l-ascorbate
17. Magnorbin
18. Vitamin C
1. 134-03-2
2. Sodium L-ascorbate
3. L-ascorbic Acid Sodium Salt
4. Vitamin C Sodium
5. Ascorbic Acid Sodium Salt
6. Monosodium L-ascorbate
7. Vitamin C Sodium Salt
8. Ascorbicin
9. Sodascorbate
10. (+)-sodium L-ascorbate
11. L-ascorbic Acid, Monosodium Salt
12. Natrii Ascorbas
13. Vitamin C, Sodium Salt
14. Ascorbate
15. Ascorbate De Sodium
16. Ascorbin
17. Cevalin
18. L-ascorbic Acid Sodium
19. Ins No.301
20. L-ascorbic Acid (sodium Salt)
21. Ins-301
22. L-ascorbate, Sodium
23. Sodium (r)-2-((s)-1,2-dihydroxyethyl)-4-hydroxy-5-oxo-2,5-dihydrofuran-3-olate
24. S033eh8359
25. Cebitate
26. Aminofenitrooxon
27. E-301
28. Sodium (2r)-2-[(1s)-1,2-dihydroxyethyl]-4-hydroxy-5-oxo-2h-furan-3-olate
29. Iskia-c
30. Natri-c
31. Sodium (l)-ascorbate
32. Sodiumascorbate
33. Ascorbato Sodico
34. Ascorbato Sodico [dcit]
35. Sodium;(2r)-2-[(1s)-1,2-dihydroxyethyl]-4-hydroxy-5-oxo-2h-furan-3-olate
36. Mfcd00082340
37. Natrii Ascorbas [inn-latin]
38. Ascorbic Acid Sodium Derivative
39. Ccris 3291
40. Hsdb 694
41. 3-oxo-l-gulofuranolactone Sodium
42. Hbl 508
43. Ascorbate De Sodium [inn-french]
44. Einecs 205-126-1
45. Tianafacacid
46. Sodium Ascorbate [usp:inn]
47. Unii-s033eh8359
48. Sodium Derivative Of 3-oxo-l-gulofuranolactone
49. Ascorbic Acid Sodium
50. E301
51. Sodium L-ascorbate Salt
52. Dsstox_cid_105
53. Ec 205-126-1
54. Schembl3745
55. Dsstox_rid_75369
56. Dsstox_gsid_20105
57. Sodium Ascorbate [ii]
58. L(+)ascorbic Acid Sodium Salt
59. Sodium Ascorbate [fcc]
60. Sodium Ascorbate [inn]
61. Chembl591665
62. Sodium Ascorbate [hsdb]
63. Sodium Ascorbate [inci]
64. Dtxsid0020105
65. Sodium Ascorbate [vandf]
66. Hy-b0166a
67. Sodium Ascorbate [mart.]
68. Chebi:113451
69. Sodium Ascorbate [usp-rs]
70. Sodium Ascorbate [who-dd]
71. L-ascorbic Acid Sodium Salt,(s)
72. L-ascorbic Acid - Monosodium Salt
73. Tox21_300556
74. Akos015895058
75. L-ascorbic Acid, Sodium Salt (1:1)
76. Sodium Ascorbate [orange Book]
77. Ascorbic Acid Sodium Salt [mi]
78. Cs-6063
79. Db14482
80. Sodium Ascorbate [ep Monograph]
81. Sodium (2r)-2-[(1s)-1,2-dihydroxyethyl]-4-hydroxy-5-oxo-2,5-dihydrofuran-3-olate
82. Sodium Ascorbate [usp Monograph]
83. Ncgc00254355-01
84. Bp-30077
85. Cas-134-03-2
86. A0539
87. B1834
88. E80761
89. A806721
90. Q424551
91. J-006471
92. Sodium (2r)-2-[(1s)-1,2-bis(oxidanyl)ethyl]-4-oxidanyl-5-oxidanylidene-2h-furan-3-olate
93. Sodium(r)-2-((s)-1,2-dihydroxyethyl)-4-hydroxy-5-oxo-2,5-dihydrofuran-3-olate
| Molecular Weight | 198.11 g/mol |
|---|---|
| Molecular Formula | C6H7NaO6 |
| Hydrogen Bond Donor Count | 3 |
| Hydrogen Bond Acceptor Count | 6 |
| Rotatable Bond Count | 2 |
| Exact Mass | 198.01403222 g/mol |
| Monoisotopic Mass | 198.01403222 g/mol |
| Topological Polar Surface Area | 110 Ų |
| Heavy Atom Count | 13 |
| Formal Charge | 0 |
| Complexity | 237 |
| Isotope Atom Count | 0 |
| Defined Atom Stereocenter Count | 2 |
| Undefined Atom Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Defined Bond Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Undefined Bond Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Covalently Bonded Unit Count | 2 |
Antioxidants; Free Radical Scavengers
National Library of Medicine's Medical Subject Headings online file (MeSH, 1999)
Ascorbic acid and calcium and sodium ascorbates are used as antoxidants in pharmaceutical manufacturing and in the food industry.
Sweetman SC (ed), Martindale: The Complete Drug Reference. London: Pharmaceutical Press (2009), p.1985.
In 20 patients in acute asthmatic crisis, 16 recovered promptly after receiving 6 g sodium ascorbate iv. Chronic oral treatment (0.6-1 g/day/60 days) with Na ascorbate prevented asthmatic symptoms in 18/25 asthmatic patients.
Miyares C et al; Rev Cubana Med 10 (5): 469 (1971)
8 patients with hyphema were treated with iv glycerin in combination with sodium ascorbate. The results showed that glycerol in combination with sodium ascorbate diminished the hemorrhage in eye within 12-24 hr.
PMID:7272018 Latinovic S et al; Boll Chim Farm 120: 156-8 (1981)
For more Therapeutic Uses (Complete) data for Sodium ascorbate (6 total), please visit the HSDB record page.
Each gram of sodium ascorbate contains approximately 5 mEq of sodium; this should be considered when the drug is used in patients on salt-restricted diets.
American Society of Health System Pharmacists; AHFS Drug Information 2009. Bethesda, MD. (2009)
Antioxidants
Naturally occurring or synthetic substances that inhibit or retard oxidation reactions. They counteract the damaging effects of oxidation in animal tissues. (See all compounds classified as Antioxidants.)
Vitamins
Organic substances that are required in small amounts for maintenance and growth, but which cannot be manufactured by the human body. (See all compounds classified as Vitamins.)
Ascorbic acid, the reduced form of vitamin C, functions as a potent antioxidant as well as in cell differentiation. Ascorbate is taken up by mammalian cells through the specific sodium/ascorbate co-transporters SVCT1 and SVCT2. Although skeletal muscle contains about 50% of the whole-body vitamin C, the expression of SVCT transporters has not been clearly addressed in this tissue. ... This work ... analyzed the expression pattern of SVCT2 during embryonic myogenesis using the chick as model system. ... Immunohistochemical analyses showed that SVCT2 is preferentially expressed by type I slow-twitch muscle fibers throughout chick myogenesis as well as in post-natal skeletal muscles of several species, including human...
Low M et al; Histochem Cell Biol 131 (5): 565-74 (2009). Available from, as of March 15, 2010: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/entrez/query.fcgi?cmd=Retrieve&db=pubmed&dopt=Abstract&list_uids=19125272
Humans use two sodium-ascorbate cotransporters (hSVCT1 and hSVCT2) for transporting the dietary essential micronutrient ascorbic acid, the reduced and active form of vitamin C. Although the human liver plays a pivotal role in regulating and maintaining vitamin C homeostasis, vitamin C transport physiology and regulation of the hSVCT systems in this organ have not been well defined. Thus, this research used a human hepatic cell line (HepG2), confirming certain results with primary human hepatocytes and determined the initial rate of ascorbic acid uptake to be Na(+) gradient, pH dependent, and saturable as a function of concentration over low and high micromolar ranges. Additionally, hSVCT2 protein and mRNA are expressed at higher levels in HepG2 cells and native human liver, and the cloned hSVCT2 promoter has more activity in HepG2 cells. Results using short interfering RNA suggest that in HepG2 cells, decreasing hSVCT2 message levels reduces the overall ascorbic acid uptake process more than decreasing hSVCT1 message levels. Activation of PKC intracellular regulatory pathways caused a downregulation in ascorbic acid uptake not mediated by a single predicted PKC-specific amino acid phosphorylation site in hSVCT1 or hSVCT2. However, PKC activation causes internalization of hSVCT1 but not hSVCT2. Examination of other intracellular regulatory pathways on ascorbic acid uptake determined that regulation also potentially occurs by PKA, PTK, and Ca(2+)/calmodulin, but not by nitric oxide-dependent pathways...
Reidling JC et al; Am J Physiol. Gastrointest Liver Physiol 295 (6): 1217-27 (2008). Available from, as of March 15, 2010: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/entrez/query.fcgi?cmd=Retrieve&db=pubmed&dopt=Abstract&list_uids=18845575
... Adrenal cortex is closely associated with ascorbate metabolism ... Hydrocortisone was reported ... to stimulate synthesis of ascorbate from gluconolactone, but deoxycorticosterone or aldosterone caused ... increase in ascorbate excretion in normal or adrenalectomized rats...
The Chemical Society. Foreign Compound Metabolism in Mammals Volume 3. London: The Chemical Society, 1975., p. 607
Mechanism of action of ascorbate is a superoxide radical scavenger.
Amdur, M.O., J. Doull, C.D. Klaasen (eds). Casarett and Doull's Toxicology. 4th ed. New York, NY: Pergamon Press, 1991., p. 524
... Sodium ascorbate decreases cellular iron uptake by melanoma cells in a dose- and time-dependent fashion, indicating that intracellular iron levels may be a critical factor in sodium ascorbate-induced apoptosis. Indeed, sodium ascorbate-induced apoptosis is enhanced by the iron chelator, desferrioxamine (DFO) while it is inhibited by the iron donor, ferric ammonium citrate (FAC). Moreover, the inhibitory effects of sodium ascorbate on intracellular iron levels are blocked by addition of transferrin, suggesting that transferrin receptor (TfR) dependent pathway of iron uptake may be regulated by sodium ascorbate. Cells exposed to sodium ascorbate demonstrated down-regulation of TfR expression and this precedes sodium ascorbate-induced apoptosis. Taken together, sodium ascorbate-mediated apoptosis appears to be initiated by a reduction of TfR expression, resulting in a down-regulation of iron uptake followed by an induction of apoptosis...
Kang JS et al; J Cell Physiol 204 (1): 192-7 (2005). Available from, as of March 15, 2010: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/entrez/query.fcgi?cmd=Retrieve&db=pubmed&dopt=Abstract&list_uids=15672419
Humans use two sodium-ascorbate cotransporters (hSVCT1 and hSVCT2) for transporting the dietary essential micronutrient ascorbic acid, the reduced and active form of vitamin C. Although the human liver plays a pivotal role in regulating and maintaining vitamin C homeostasis, vitamin C transport physiology and regulation of the hSVCT systems in this organ have not been well defined. Thus, this research used a human hepatic cell line (HepG2), confirming certain results with primary human hepatocytes and determined the initial rate of ascorbic acid uptake to be Na(+) gradient, pH dependent, and saturable as a function of concentration over low and high micromolar ranges. Additionally, hSVCT2 protein and mRNA are expressed at higher levels in HepG2 cells and native human liver, and the cloned hSVCT2 promoter has more activity in HepG2 cells. Results using short interfering RNA suggest that in HepG2 cells, decreasing hSVCT2 message levels reduces the overall ascorbic acid uptake process more than decreasing hSVCT1 message levels. Activation of PKC intracellular regulatory pathways caused a downregulation in ascorbic acid uptake not mediated by a single predicted PKC-specific amino acid phosphorylation site in hSVCT1 or hSVCT2. However, PKC activation causes internalization of hSVCT1 but not hSVCT2. Examination of other intracellular regulatory pathways on ascorbic acid uptake determined that regulation also potentially occurs by PKA, PTK, and Ca(2+)/calmodulin, but not by nitric oxide-dependent pathways...
Reidling JC et al; Am J Physiol. Gastrointest Liver Physiol 295 (6): 1217-27 (2008). Available from, as of March 15, 2010: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/entrez/query.fcgi?cmd=Retrieve&db=pubmed&dopt=Abstract&list_uids=18845575