


1. Disodium Carbonate, 14c-labeled Cpd
2. Disodium Carbonate, Heptahydrate
3. Disodium Carbonate, Monohydrate
4. Monosodium Carbonate, 14c-labeled Cpd
5. Monosodium Carbonate, Monohydrate
6. Sodium Carbonate (2:3), Dihydrate
7. Sodium Carbonate (4:5)
8. Sodium Carbonate Decahydrate
9. Sodium Carbonate, Hydrate
1. 497-19-8
2. Soda Ash
3. Disodium Carbonate
4. Carbonic Acid Disodium Salt
5. Sodium Carbonate, Anhydrous
6. Calcined Soda
7. Solvay Soda
8. Sodium Carbonate Anhydrous
9. Carbonic Acid, Disodium Salt
10. Carbonic Acid Sodium Salt (1:2)
11. Carbonic Acid Sodium Salt
12. Soda-ash
13. Natrum Carbonicum
14. Crystol Carbonate
15. Natriumkarbonat
16. Bisodium Carbonate
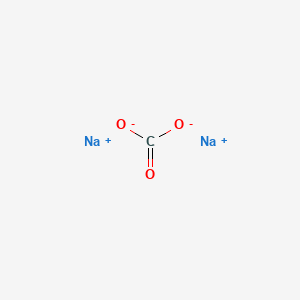
17. Na2co3
18. Anhydrous Sodium Carbonate
19. Soda Ash Light
20. Na-x
21. Sodium Carbonate (anhydrous)
22. Sodium Salt Of Carbonic Acid
23. Soda
24. Sodium Carbonate (2:1)
25. Sodium Carbonate [nf]
26. Mfcd00003494
27. Sodium Carbonate (na2(co3))
28. Anhydrous Soda
29. Ins No.500(i)
30. Chebi:29377
31. Ins-500(i)
32. 45p3261c7t
33. Nsc-156204
34. E-500(i)
35. Sodium Carbonate (nf)
36. Soda (van)
37. Soda, Calcined
38. Snowlite I
39. Light Ash
40. V Soda
41. Soda Ash Light 4p
42. Suprapur 6395
43. Caswell N0 752
44. Dynamar L 13890
45. Disodium;carbonate
46. Natrium Carbonicum Siccatum
47. Natrium Carbonicum Calcinatum
48. Disodium Carbonate (na2co3)
49. Ccris 7319
50. Hsdb 5018
51. V 20n
52. Einecs 207-838-8
53. Epa Pesticide Chemical Code 073506
54. Nsc 156204
55. Sodium Carbonate, Anhydrous Astm D458
56. Sodium Carbonate, Acs
57. Sodium Cabonate
58. Sodium Carbonat
59. Carbonate Sodium
60. Sodium-carbonate
61. Soda Ash Dense
62. Unii-45p3261c7t
63. Sodium Carbonate, Anhydrous Ge Materials D4d5
64. Dried Sodium Carbonate
65. Caswell No. 752
66. Sodium Carbonate Sodium
67. Sodium Sodium Carbonate
68. Sodium Carbonate, Dried
69. Sodium Carbonate, Dense
70. Disodium Trioxidocarbonate
71. Schembl25
72. Sodium Carbonate Solution
73. Soda Ash [ii]
74. Carbonic Acid, Sodium Salt
75. Ec 207-838-8
76. Sodium Carbonate [ii]
77. Sodium Carbonate [mi]
78. Sodium Carbonate Nanoparticles
79. Sodium Carbonate [fcc]
80. Chembl186314
81. Sodium Carbonate [hsdb]
82. Sodium Carbonate [inci]
83. Dried Sodium Carbonate (jp17)
84. Dtxsid1029621
85. Natrum Carbonicum [hpus]
86. Sodium Carbonate [vandf]
87. Sodium Carbonate [mart.]
88. Anhydrous Soda,99.999%,powder
89. Sodium Carbonate, Biochemical Grade
90. Einecs 231-420-4
91. Dried Sodium Carbonate [jan]
92. Akos009158235
93. Sodium Carbonate [orange Book]
94. Db09460
95. Sodium Carbonate [ep Monograph]
96. Sodium Carbonate, Anhydrous, Acs Powder
97. Carbonate-buffered Saline (5x), Ph 9.0
98. Sodium Carbonate Anhydrous [mart.]
99. Carbonate, 0.5m Buffer Solution, Ph 9.4
100. Carbonate, 0.5m Buffer Solution, Ph 9.5
101. Carbonate, 0.5m Buffer Solution, Ph 9.6
102. Db-017706
103. Sodium Carbonate Anhydrous [usp-rs]
104. Sodium Carbonate Anhydrous [who-dd]
105. Sodium Carbonate, Anhydrous, Puratronic(r)
106. Carbonate, 0.5m Buffer Solution, Ph 10.0
107. Ft-0645109
108. S0560
109. D05283
110. Sodium Carbonate, 0.05n Standardized Solution
111. Q190227
112. Sodium Carbonate, Anhydrous [ep Impurity]
113. Sodium Carbonate 5% W/v Solution In Water (+/- 0.3%)
114. Sodium Carbonate, Anhydrous, Granular Trace Metals Grade, 99.99%
115. Soda Ash, (99% As Sodium Carbonate Or 58% As Sodium Oxide), Technical Grade, Light
116. Sodium Carbonate Concentrate, 0.1 M Na2co3 In Water, Eluent Concentrate For Ic
117. Sodium Carbonate, Acculute Standard Volumetric Solution, Final Concentration 0.1n
118. 1332-57-6
119. 7542-12-3
120. Sodium Carbonate Concentrate, Na2co3 72 Mm In Water, Ic Eluent Concentrate (20x) For Metrosep A Supp 7
| Molecular Weight | 105.988 g/mol |
|---|---|
| Molecular Formula | CNa2O3 |
| Hydrogen Bond Donor Count | 0 |
| Hydrogen Bond Acceptor Count | 3 |
| Rotatable Bond Count | 0 |
| Exact Mass | 105.96428242 g/mol |
| Monoisotopic Mass | 105.96428242 g/mol |
| Topological Polar Surface Area | 63.2 Ų |
| Heavy Atom Count | 6 |
| Formal Charge | 0 |
| Complexity | 18.8 |
| Isotope Atom Count | 0 |
| Defined Atom Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Undefined Atom Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Defined Bond Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Undefined Bond Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Covalently Bonded Unit Count | 3 |
Used topically for dermatitides, mouthwash, vaginal douche; veterinary use as emergency emetic.
National Library of Medicine's Medical Subject Headings. Sodium carbonate. Online file (MeSH, 2017). Available from, as of October 23, 2017: https://www.nlm.nih.gov/mesh/2017/mesh_browser/MBrowser.html
Occasionally, for dermatitides topically as a lotion.
Troy, D.B. (Ed); Remmington The Science and Practice of Pharmacy. 21 st Edition. Lippincott Williams & Williams, Philadelphia, PA 2005, p. 1089
Medication (Vet): Has been used as an emetic. In solution to cleanse skin, in eczema, to soften scabs of ringworm.
O'Neil, M.J. (ed.). The Merck Index - An Encyclopedia of Chemicals, Drugs, and Biologicals. Cambridge, UK: Royal Society of Chemistry, 2013., p. 1596
Sodium bicarbonate infusion is widely recommended ... for patients who present with self-poisoning from tricyclic antidepressives. Cardiac conduction disorders could also be treated or prevented by means of such an infusion. The scientific basis for these recommendations was investigated by using Medline to search for publications about clinical studies that supported the use of sodium carbonate; 111 articles were scrutinized. Observational studies and case reports mention a rapid improvement in hypotension and cardiac arrhythmias following the administration of sodium bicarbonate. Results from animal experiments are contentious; it is not clear whether alkalinization or the administration of extra sodium causes the effect. Randomized studies in patients have not been carried out. As the toxicity of sodium bicarbonate is low, and its potential benefit appears to be high, /the authors/ recommend its use, despite the lack of scientific evidence. No recommendations concerning dosing, concentration and the length of the therapy can be provided on the basis of the literature.
PMID:11561485 Vrijlandt PJ et al; Ned Tijdschr Geneeskd 145 (35): 1686-9 (2001)
For more Therapeutic Uses (Complete) data for Sodium carbonate (8 total), please visit the HSDB record page.
Used topically for dermatitides, mouthwash, vaginal douche; veterinary use as emergency emetic.Occasionally, for dermatitides topically as a lotion. Medication (Vet): In solution to cleanse skin, in eczema, to soften scabs of ringworm.
Alkalizing buffering action: Sodium bicarbonate is an alkalinizing agent that dissociates to provide bicarbonate ion. Bicarbonate in excess of that needed to buffer hydrogen ions causes systemic alkalinization and, when excreted, urine alkalinization as well. Oral antacid action: Taken orally, sodium bicarbonate neutralizes stomach acid by the above mechanism.
Absorption
The uptake of sodium, via exposure to sodium carbonate, is much less than the uptake of sodium via food. Therefore, sodium carbonate is not expected to be systemically available in the body. Furthermore, an oral uptake of sodium carbonate will result in a neutralization in the stomach due to the gastric acid.
Route of Elimination
Filtered and reabsorbed by the kidney; less than 1% of filtered bicarbonate is excreted.
Volume of Distribution
Distribution occurs naturally and is confined to the systemic circulation.
The major extracellular buffer in the blood and the interstitial fluid of vertebrates is the bicarbonate buffer system ... . Carbon dioxide from the tissues diffuses rapidly into red blood cells, where it is hydrated with water to form carbonic acid. This reaction is accelerated by carbonic anhydrase, an enzyme present in high concentrations in red blood cells. The carbonic acid formed dissociates into bicarbonate and hydrogen ions. Most of the bicarbonate ions diffuse into the plasma. Since the ratio of H2CO3 to dissolved CO2 is constant at equilibrium, pH may be expressed in terms of bicarbonate ion concentration and partial pressure of CO2 by means of the Henderson-Hasselbach equation: pH = pk + log [HCO3-]/aPCO2. The blood plasma of /humans/ normally has a pH of 7.40. Should the pH fall below 7.0 or rise above 7.8, irreversible damage may occur. Compensatory mechanisms for acid-base disturbances function to alter the ratio of HCO3 - to PCO2 , returning the pH of the blood to normal. ... The uptake of sodium, via exposure to sodium carbonate, is much less than the uptake of sodium via food. Therefore, sodium carbonate is not expected to be systemically available in the body. Furthermore ... an oral uptake of sodium carbonate will result in a neutralization in the stomach due to the gastric acid.
OECD; Screening Information Data Set (SIDS) Inital Assessment Report for SIDS Initial Assessment Meeting (SIAM) 15, Sodium carbonate (497-19-8) p.11 (October 2002). Available from, as of October 23, 2017: https://www.inchem.org/pages/sids.html
None.
Carbon dioxide from the tissues diffuses rapidly into red blood cells, where it is hydrated with water to form carbonic acid. This reaction is accelerated by carbonic anhydrase, an enzyme present in high concentrations in red blood cells. The carbonic acid formed dissociates into bicarbonate and hydrogen ions. Most of the bicarbonate ions diffuse into the plasma. Since the ratio of H2CO3 to dissolved CO2 is constant at equilibrium, pH may be expressed in terms of bicarbonate ion concentration and partial pressure of CO2 by means of the Henderson-Hasselbach equation: pH = pk + log [HCO3-]/aPCO2