

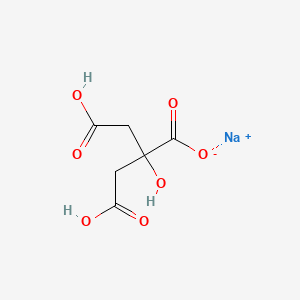

1. Anhydrous Sodium Citrate
2. Citra Ph
3. Monosodium Citrate
4. Sodium Citrate
5. Sodium Citrate Dihydrate
6. Sodium Citrate Monobasic
7. Sodium Citrate, Anhydrous
8. Trisodium Citrate Dihydrate
1. Citrofluyl
2. Monosodium Dihydrogen Citrate
3. Citric Acid, Monosodium Salt
4. Citric Acid Monosodium Salt
5. Sodium Citrate Monobasic
6. 68538up9se
7. Sodium Dihydrogen Citrate Anhydrous
8. Einecs 242-734-6
9. Unii-68538up9se
10. 1,2,3-propanetricarboxylic Acid, 2-hydroxy-, Sodium Salt (1:1)
11. Ec 242-734-6
12. E82980
| Molecular Weight | 214.10 g/mol |
|---|---|
| Molecular Formula | C6H7NaO7 |
| Hydrogen Bond Donor Count | 3 |
| Hydrogen Bond Acceptor Count | 7 |
| Rotatable Bond Count | 5 |
| Exact Mass | 214.00894684 g/mol |
| Monoisotopic Mass | 214.00894684 g/mol |
| Topological Polar Surface Area | 135 Ų |
| Heavy Atom Count | 14 |
| Formal Charge | 0 |
| Complexity | 233 |
| Isotope Atom Count | 0 |
| Defined Atom Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Undefined Atom Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Defined Bond Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Undefined Bond Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Covalently Bonded Unit Count | 2 |
Anticoagulants
Agents that prevent BLOOD CLOTTING. (See all compounds classified as Anticoagulants.)
Buffers
A chemical system that functions to control the levels of specific ions in solution. When the level of hydrogen ion in solution is controlled the system is called a pH buffer. (See all compounds classified as Buffers.)
Food Preservatives
Substances capable of inhibiting, retarding or arresting the process of fermentation, acidification or other deterioration of foods. (See all compounds classified as Food Preservatives.)