


1. Accent
2. Glutamate, Sodium
3. Msg
4. Sodium Glutamate
5. Vestin
1. 142-47-2
2. Sodium L-glutamate
3. Sodium Glutamate
4. Ajinomoto
5. Glutacyl
6. L-glutamic Acid, Monosodium Salt
7. Monosodium L-glutamate
8. Glutavene
9. Ancoma
10. L-monosodium Glutamate
11. Chinese Seasoning
12. L-glutamic Acid Monosodium Salt
13. 16177-21-2
14. L-glutamic Acid Sodium Salt
15. Glutamic Acid, Sodium Salt
16. L(+) Sodium Glutamate
17. Glutamate Monosodium Salt
18. Sodium Hydrogen Glutamate
19. Natriumglutaminat
20. Glutamate Sodium
21. Natrium L-hydrogenglutamat
22. Monosodioglutammato
23. Glutammato Monosodico
24. Fema No. 2756
25. Vetsin
26. Zest
27. Sodium (s)-2-amino-4-carboxybutanoate
28. Rl-50
29. Msg
30. Sodium;(2s)-2-amino-5-hydroxy-5-oxopentanoate
31. Monosodium Glutamate Anhydrous
32. Sodium (2s)-2-amino-4-carboxybutanoate
33. L-glutamic Acid Monosodium
34. Accent (food Additive)
35. Glutamat Sodny [czech]
36. Glutamat Sodny
37. Sodium Glutamate (van)
38. Natriumglutaminat [german]
39. C3c196l9fg
40. Sodium L-glutamate (van)
41. Monosodioglutammato [italian]
42. Ccris 3625
43. Hsdb 580
44. Glutammato Monosodico [italian]
45. Mono Sodium Glutamate
46. Glutamic Acid, L-, Sodium Salt
47. L-glutamic Acid, Sodium Salt (1:1)
48. Glutamate Sodium [jan]
49. Einecs 205-538-1
50. L-glutamic Acid, Sodium Salt (van)
51. Nsc 135529
52. Unii-c3c196l9fg
53. Ai3-18393
54. Einecs 240-313-1
55. Glutamic Acid, Monosodium Salt, L-
56. L-glutamic Acid, Sodiumsalt (1:1)
57. H-glu-oh.na
58. 6106-04-3
59. Ec 205-538-1
60. Schembl16336
61. Dtxsid9020906
62. Akos027257231
63. Sodium 2-amino-5-hydroxy-5-oxopentanoate
64. G0188
65. J-007661
| Molecular Weight | 169.11 g/mol |
|---|---|
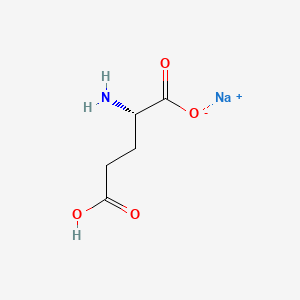
| Molecular Formula | C5H8NNaO4 |
| Hydrogen Bond Donor Count | 2 |
| Hydrogen Bond Acceptor Count | 5 |
| Rotatable Bond Count | 4 |
| Exact Mass | 169.03510202 g/mol |
| Monoisotopic Mass | 169.03510202 g/mol |
| Topological Polar Surface Area | 103 Ų |
| Heavy Atom Count | 11 |
| Formal Charge | 0 |
| Complexity | 149 |
| Isotope Atom Count | 0 |
| Defined Atom Stereocenter Count | 1 |
| Undefined Atom Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Defined Bond Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Undefined Bond Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Covalently Bonded Unit Count | 2 |
One of the FLAVORING AGENTS used to impart a meat-like flavor. Medically it has been used to reduce blood ammonia levels in ammoniacal azotemia, therapy of hepatic coma, in psychosis, and mental retardation.
National Library of Medicine - Medical Subject Headings (2007)
The large doses of sodium glutamate required for the treatment of hepatic encephalopathy may result in dangerous alkalosis and hypokalemia ... important to keep close control on the electrolyte balance during therapy.
Reynolds, J.E.F., Prasad, A.B. (eds.) Martindale-The Extra Pharmacopoeia. 28th ed. London: The Pharmaceutical Press, 1982., p. 59
Injections of sodium glutamate should be given with caution to patients with hepatic cirrhosis, impaired renal function, or liver disease not associated with hyperammonemia.
Reynolds, J.E.F., Prasad, A.B. (eds.) Martindale-The Extra Pharmacopoeia. 28th ed. London: The Pharmaceutical Press, 1982., p. 59
Food and Environmental Agents: Effect on Breast-Feeding: Monosodium glutamate: None. /from Table 7/
Report of the American Academy of Pediatrics Committee on Drugs in Pediatrics 93 (1): 142 (1994)
Flavoring Agents
Substances added to foods and medicine to improve the taste. (See all compounds classified as Flavoring Agents.)
Glutamate is absorbed from the gut by an active transport system specific for amino acids. This process is saturable, can be competitively inhibited, and is dependent on sodium ion concentration... . During intestinal absorption, a large proportion of glutamic acid is transaminated and consequently alanine levels in portal blood are elevated. If large amounts of glutamate are ingested, portal glutamate levels increase ... . This elevation results in increased hepatic metabolism of glutamate, leading to release of glucose, lactate, glutamine, and other amino acids, into systemic circulation ... . The pharmacokinetics of glutamate depend on whether it is free or incorporated into protein, and on the presence of other food components. Digestion of protein in the intestinal lumen and at the brush border produces a mixture of small peptides and amino acids; di-and tri-peptides may enter the absorptive cells where intracellular hydrolysis may occur, liberating further amino acids. Defects are known in both amino acid and peptide transport ... .. Glutamic acid in dietary protein, together with endogenous protein secreted into the gut, is digested to free amino acids and small peptides, both of which are absorbed into mucosal cells where peptides are hydrolyzed to free amino acids and some of the glutamate is metabolized. Excess glutamate and other amino acids appear in portal blood. As a consequence of the rapid metabolism of glutamate in intestinal mucosal cells and in the liver, systemic plasma levels are low, even after ingestion of large amounts of dietary protein. /Glutamic acid/
WHO Food Additive Series 22; L-Glutamic Acid and its Ammonium, Calcium, Monosodium and Potassium Salts. Available from, as of March 20, 2007: https://www.inchem.org/documents/jecfa/jecmono/v22je12.htm
... Intestinal and hepatic metabolism results in elevation of levels in systemic circulation only after extremely high doses given by gavage (>30mg/kg body weight). Ingestion of monosodium glutamate (MSG) was not associated with elevated levels in maternal milk, and glutamate did not readily pass the placental barrier. Human infants metabolized glutamate similarly to adults.
PMID:10736380 Walker R and Lupien JR; J Nutr 130 (4S Suppl): 1049S-52S (2000)
Oral administration of pharmacologically high doses of glutamate results in elevated plasma levels. The peak plasma glutamate levels are both dose and concentration dependent ... . When the same dose (1 g/kg b.w.) of monosodium glutamate (MSG) was administered by gavage in aqueous solution to neonatal rats, increasing the concentration from 2% to 10% caused a five-fold increase in the plasma area under curve; similar results were observed in mice ... . Conversely, when MSG (1.5 g/kg b.w.) was administered to 43-day-old mice by gavage at varying concentrations of 2 to 20% w/v, no correlation could be established between plasma levels and concentration ...
WHO Food Additive Series 22; L-Glutamic Acid and its Ammonium, Calcium, Monosodium and Potassium Salts. Available from, as of March 20, 2007: https://www.inchem.org/documents/jecfa/jecmono/v22je12.htm
Administration of a standard dose of 1 g/kg b.w. MSG by gavage as a 10% w/v solution resulted in a marked increase of plasma glutamate in all species studied. Peak plasma glutamate levels were lowest in adult monkeys (6 times fasting levels) and highest in mice (12-35 times fasting levels). Age-related differences between neonates and adults were observed; in mice and rats, peak plasma levels and area under curve were higher in infants than in adults while in guinea pigs the converse was observed.
WHO Food Additive Series 22; L-Glutamic Acid and its Ammonium, Calcium, Monosodium and Potassium Salts. Available from, as of March 20, 2007: https://www.inchem.org/documents/jecfa/jecmono/v22je12.htm
For more Absorption, Distribution and Excretion (Complete) data for MONOSODIUM GLUTAMATE (7 total), please visit the HSDB record page.
Glutamic acid is metabolized in the tissues by oxidative deamination ... or by transamination with pyruvate to yield oxaloacetic acid ... which, via alpha-ketoglutarate, enters the citric acid cycle ... .. Quantitatively minor but physiologically important pathways of glutamate metabolism involve decarboxylation to gamma-aminobutyrate (GABA) and amidation to glutamine ... . Decarboxylation to GABA is dependent on pyridoxal phosphate, a coenzyme of glutamic acid decarboxylase ..., as is glutamate transaminase. Vitamin B6-deficient rats have elevated serum glutamate levels and delayed glutamate clearance ... . /Glutamic acid/
WHO Food Additive Series 22; L-Glutamic Acid and its Ammonium, Calcium, Monosodium and Potassium Salts. Available from, as of March 20, 2007: https://www.inchem.org/documents/jecfa/jecmono/v22je12.htm
Oral dose of 1 g/kg monosodium glutamate given to rats was followed by only a small rise in plasma pyroglutamate levels. No incr of pyroglutamate or glutamate brain levels was observed under these conditions.
PMID:7080082 CACCIA S ET AL; TOXICOL LETT 10 (2-3): 169 (1982)
L-Glutamate and GABA supposedly act as excitatory and inhibitory transmitters, respectively, in the central nervous system. Glutamate is also involved in the synthesis of proteins. /Glutamate/
WHO Food Additive Series 22; L-Glutamic Acid and its Ammonium, Calcium, Monosodium and Potassium Salts. Available from, as of March 20, 2007: https://www.inchem.org/documents/jecfa/jecmono/v22je12.htm