

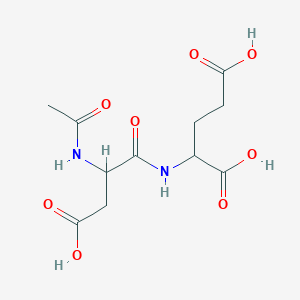

1. Isospaglumic Acid
2. N-(n-acetyl-l-alpha-aspartyl)-l-glutamic Acid
3. N-acetyl-1-asp-glu
4. N-acetyl-1-aspartylglutamic Acid
5. N-acetyl-1-aspartylglutamic Acid, (l)-isomer Ion
6. N-acetyl-1-aspartylglutamic Acid, Magnesium Salt
7. N-acetyl-aspartyl-glutamate
8. N-acetyl-aspartyl-glutamic Acid
9. N-acetyl-l-alpha-aspartylglutamic Acid
10. N-acetyl-l-aspartyl-l-glutamate
11. N-acetylaspartylglutamate
12. Naaga
13. Naaga Magnesium Salt
14. Naaga Sodium Salt
15. Naaxia
16. Zy 15106
17. Zy 15109
18. Zy-15106
19. Zy-15109
20. Zy15106
21. Zy15109
1. N-acetyl-1-aspartylglutamic Acid
2. N-acetyl-asp-glu-oh
3. Alpha-naag
4. Spectrum2_001481
5. Spectrum3_001845
6. 2-[(2-acetamido-3-carboxy-1-oxopropyl)amino]pentanedioic Acid
7. Chembl64966
8. Schembl288515
9. Spbio_001461
10. Schembl21403461
11. Chebi:95120
12. Kbio3_002730
13. Dtxsid10863103
14. Hms3266k17
15. Ccg-39200
16. Pdsp1_000259
17. Pdsp2_000258
18. Ncgc00095908-01
19. Ncgc00095908-02
20. Db-047960
21. Ft-0774474
22. N-acetyl-asp-glu, >=97% (tlc), Powder
23. L000426
24. Q27166900
| Molecular Weight | 304.25 g/mol |
|---|---|
| Molecular Formula | C11H16N2O8 |
| XLogP3 | -2.1 |
| Hydrogen Bond Donor Count | 5 |
| Hydrogen Bond Acceptor Count | 8 |
| Rotatable Bond Count | 9 |
| Exact Mass | 304.09066547 g/mol |
| Monoisotopic Mass | 304.09066547 g/mol |
| Topological Polar Surface Area | 170 Ų |
| Heavy Atom Count | 21 |
| Formal Charge | 0 |
| Complexity | 448 |
| Isotope Atom Count | 0 |
| Defined Atom Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Undefined Atom Stereocenter Count | 2 |
| Defined Bond Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Undefined Bond Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Covalently Bonded Unit Count | 1 |
Neuroprotective Agents
Drugs intended to prevent damage to the brain or spinal cord from ischemia, stroke, convulsions, or trauma. Some must be administered before the event, but others may be effective for some time after. They act by a variety of mechanisms, but often directly or indirectly minimize the damage produced by endogenous excitatory amino acids. (See all compounds classified as Neuroprotective Agents.)
Histamine H1 Antagonists
Drugs that selectively bind to but do not activate histamine H1 receptors, thereby blocking the actions of endogenous histamine. Included here are the classical antihistaminics that antagonize or prevent the action of histamine mainly in immediate hypersensitivity. They act in the bronchi, capillaries, and some other smooth muscles, and are used to prevent or allay motion sickness, seasonal rhinitis, and allergic dermatitis and to induce somnolence. The effects of blocking central nervous system H1 receptors are not as well understood. (See all compounds classified as Histamine H1 Antagonists.)
Anti-Allergic Agents
Agents that are used to treat allergic reactions. Most of these drugs act by preventing the release of inflammatory mediators or inhibiting the actions of released mediators on their target cells. (From AMA Drug Evaluations Annual, 1994, p475) (See all compounds classified as Anti-Allergic Agents.)
Bronchodilator Agents
Agents that cause an increase in the expansion of a bronchus or bronchial tubes. (See all compounds classified as Bronchodilator Agents.)
Neurotoxins
Toxic substances from microorganisms, plants or animals that interfere with the functions of the nervous system. Most venoms contain neurotoxic substances. Myotoxins are included in this concept. (See all compounds classified as Neurotoxins.)