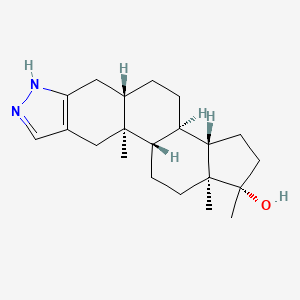

1. Androstanazol
2. Methylstanazol
3. Stanazolol
4. Stromba
5. Winstrol
1. Winstrol
2. Androstanazole
3. Androstanazol
4. 10418-03-8
5. Stromba
6. Stanazolol
7. Tevabolin
8. Winstrol Depot
9. Strombaject
10. Estazol
11. Winstroid
12. Winstrol V
13. Estanozolol
14. Stanozololum
15. Win 14833
16. Anabol
17. Stanozolol Ciii
18. Androstanazolestanazol
19. Nsc-43193
20. Win-14833
21. Nsc 233046
22. 4r1vb9p8v3
23. Chebi:9249
24. 17-methyl-2'h-5alpha-androst-2-eno(3,2-c)pyrazol-17beta-ol
25. Nsc-233046
26. (1s,3as,3br,5as,10as,10bs,12as)-1,10a,12a-trimethyl-1,2,3,3a,3b,4,5,5a,6,8,10,10a,10b,11,12,12a-hexadecahydrocyclopenta[5,6]naphtho[1,2-f]indazol-1-ol
27. Cyclopenta(7,8)phenanthro(2,3-c)pyrazol-1-ol, 1,2,3,3a,3b,4,5,5a,6,8,10,10a,10b,11,12,12a-hexadecahydro-1,10a,12a-trimethyl-
28. Stanozolo [dcit]
29. Androstanazole (van)
30. Stanozolo
31. Stanozolol (1'h Form)
32. Winstrol-v
33. Stanozololum [inn-latin]
34. Estanozolol [inn-spanish]
35. (1s,2s,10s,13r,14s,17s,18s)-2,17,18-trimethyl-6,7-diazapentacyclo[11.7.0.0^{2,10}.0^{4,8}.0^{14,18}]icosa-4(8),5-dien-17-ol
36. Cyclopenta(7,8)phenanthro(2,3-c)pyrazol-1-ol, 1,2,3,3a,3b,4,5,5a,6,7,10,10a,10b,11,12,12a-hexadecahydro-1,10a,12a-trimethyl-
37. Hsdb 3185
38. Sr-05000001522
39. Stanozolol (2'h Form)
40. 17?-methyl-5?-androstano[3,2-c]pyrazol-17?-ol
41. Einecs 233-894-8
42. Nsc 43193
43. Unii-4r1vb9p8v3
44. 17.beta.-hydroxy-17.alpha.-methyl-5.alpha.-androstano(3,2-c)pyrazole
45. Winstrol (tn)
46. 2'h-androst-2-eno(3,2-c)pyrazol-17-ol, 17-methyl-, (5alpha,17beta)-
47. 17-methyl-5alpha-androstano(3,2-c)pyrazol-17beta-ol
48. 302-96-5
49. Stanozolol [usan:usp:inn:ban:jan]
50. 17-beta-hydroxy-17-alpha-methylandrostano(3,2-c)pyrazole
51. 17beta-hydroxy-17alpha-methyl-androstano(3,2-c)pyrazole
52. 17-methyl-pyrazolo(4',3':2,3)-5alpha-androstan-17beta-ol
53. 17-methylpyrazolo(4',3':2,3)-5alpha-androstan-17beta-ol
54. 17beta-hydroxy-17-methyl-5alpha-androstano(3,2-c)pyrazole
55. Stanozolol [mi]
56. 17alpha-methyl-17beta-hydroxy-5alpha-androstano(3,2-c)pyrazole
57. Stanozolol [inn]
58. Stanozolol [jan]
59. 2'h-5alpha-androst-2-eno(3,2-c)pyrazol-17beta-ol, 17-methyl-
60. 2,3-(4',3'-pyrazolo)-5alpha-androstan-17beta-ol, 17-methyl-
61. Stanozolol [hsdb]
62. Stanozolol [usan]
63. Stanozolol [vandf]
64. Stanozolol [mart.]
65. Dsstox_cid_24128
66. Dsstox_rid_97564
67. Stanozolol [who-dd]
68. Stanozolol--dea Schedule Iii
69. Dsstox_gsid_44128
70. Schembl44099
71. Schembl44100
72. Stanozolol (jan/usp/inn)
73. 1,2,3,3a,3b,4,5,5a,6,7,10,10a,10b,11,12,12a-hexadecahydro-1,10a,12a-trimethylcyclopenta(7,8)-phenanthro(2,3-c)pyrazol-1-ol
74. Mls001424321
75. 17-methyl-2'h-5.alpha.-androst-2-eno(3,2-c)pyrazol-17.beta.-ol
76. Stanozolol, Analytical Standard
77. Stanozolol [green Book]
78. Chembl2079587
79. Dtxsid3044128
80. Stanozolol [orange Book]
81. Gtpl10369
82. Stanozolol [ep Monograph]
83. Stanozolol Ciii [usp-rs]
84. Hms2052h11
85. Hms2090p03
86. Hms3713k06
87. Stanozolol [usp Monograph]
88. Bcp12548
89. Hy-b0899
90. Nsc43193
91. Win14833
92. Zinc4097376
93. Tox21_113993
94. 1'h-androstano(3,2-c)pyrazol-17-ol, 17-methyl-, (5-alpha,17-beta)-
95. Akos005067278
96. Stanozolol 1.0 Mg/ml In Acetonitrile
97. Am84316
98. Ccg-101186
99. Ccg-220452
100. Cs-4363
101. Db06718
102. Nc00436
103. Ncgc00344550-01
104. (1s,3as,3br,5as,10as,10bs,12as)-1,10a,12a-trimethyl-1,2,3,3a,3b,4,5,5a,6,7,10,10a,10b,11,12,12a-hexadecahydrocyclopenta[5,6]naphtho[1,2-f]indazol-1-ol
105. Ac-16140
106. Ac-33164
107. As-35198
108. Cpd000058878
109. Smr000058878
110. Cas-10418-03-8
111. C07311
112. D00444
113. 17-methyl-5a-androstano[3,2-c]pyrazol-17b-ol
114. Ab00443942-03
115. Ab00443942-05
116. 418s038
117. Sr-05000001522-1
118. Sr-05000001522-2
119. W-108823
120. 17a-methyl-17b-hydroxy-5a-androstano(3,2-c)pyrazole
121. 17b-hydroxy-17-methyl-5a-androstano[3,2-c]pyrazole
122. 17b-hydroxy-17a-methyl-5a-androstano[3,2-c]pyrazole
123. Q63409446
124. 17-methyl-pyrazolo[4',3':2,3]-5a-androstan-17b-ol
125. Z1541662177
126. 17-methyl-1'h-5alpha-androstano[3,2-c]pyrazol-17beta-ol
127. Stanozolol, European Pharmacopoeia (ep) Reference Standard
128. (5a,17b)-17-methyl-2'h-androst-2-eno[3,2-c]pyrazol-17-ol
129. 2,3'-pyrazolo)-5.alpha.-androstan-17.beta.-ol, 17-methyl-
130. 5alpha-androstane-17alpha-methyl-17beta-ol-[3,2-c]pyrazole
131. 17-methyl-5.alpha.-androstano(3,2-c)pyrazol-17.beta.-ol
132. 2'h-5a-androst-2-eno[3,2-c]pyrazol-17b-ol, 17-methyl- (8ci)
133. 17alpha-methyl-17beta-hydroxy-5alpha-androst-2-eno(3,2-c)-pyrazole
134. 1'h-androstano(3,2-c)pyrazol-17-ol, 17-methyl-, (5.alpha.,17.beta.)-
135. 2'h-androst-2-eno(3,2-c)pyrazol-17-ol, 17-methyl-, (5.alpha.,17.beta.)
136. Cyclopenta[7,8]phenanthro[2,3-c]pyrazole, 2'h-androst-2-eno[3,2-c]pyrazol-17-ol Deriv.
137. (1s,2s,10s,13r,14s,17s,18s)-2,17,18-trimethyl-6,7-diazapentacyclo[11.7.0.02,10.04,8.014,18]icosa-4(8),5-dien-17-ol
138. 1,2,3,3a,3b,4,5,5a,6,7,10,10a,10b,11,12,12a-hexadecahydro-1,10a,12a-trimethyl-cyclopenta[7,8]phenanthro[2,3-c]pyrazol-1-ol
139. 17966-55-1
140. 875293-72-4
141. Cyclopenta[7,3-c]pyrazol-1-ol, 1,2,3,3a,3b,4,5,5a,6,8,10,10a,10b,11,12,12a-hexadecahydro-1,10a,12a-trimethyl-
| Molecular Weight | 328.5 g/mol |
|---|---|
| Molecular Formula | C21H32N2O |
| XLogP3 | 4.5 |
| Hydrogen Bond Donor Count | 2 |
| Hydrogen Bond Acceptor Count | 2 |
| Rotatable Bond Count | 0 |
| Exact Mass | 328.251463648 g/mol |
| Monoisotopic Mass | 328.251463648 g/mol |
| Topological Polar Surface Area | 48.9 Ų |
| Heavy Atom Count | 24 |
| Formal Charge | 0 |
| Complexity | 538 |
| Isotope Atom Count | 0 |
| Defined Atom Stereocenter Count | 7 |
| Undefined Atom Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Defined Bond Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Undefined Bond Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Covalently Bonded Unit Count | 1 |
Anabolic Steroids
National Library of Medicine's Medical Subject Headings online file (MeSH, 1999)
Stanozolol ... /is/ indicated in conditions such as chronic infections, extensive surgery, corticosteroid-induced myopathy, decubitus ulcers, burns, or severe trauma, which require reversal of catabolic processes or protein-sparing effects. /This agent is/ ... adjunct to, and not replacement for, conventional treatment of these disorders. /NOT included in US product labeling/
Thomson.Micromedex. Drug Information for the Health Care Professional. 25th ed. Volume 1. Plus Updates. Content Reviewed by the United States Pharmacopeial Convention, Inc. Greenwood Village, CO. 2005., p. 140
Stanozolol is effective in raising hemoglobin concentrations in some cases of aplastic anemia (congenital or idiopathic). /NOT included in US product labeling/
Thomson.Micromedex. Drug Information for the Health Care Professional. 25th ed. Volume 1. Plus Updates. Content Reviewed by the United States Pharmacopeial Convention, Inc. Greenwood Village, CO. 2005., p. 140
Stanozolol ... /is/ indicated in the prophylaxis of hereditary angioedema to decrease the frequency and severity of attacks. /Included in US product labeling/
Thomson.Micromedex. Drug Information for the Health Care Professional. 25th ed. Volume 1. Plus Updates. Content Reviewed by the United States Pharmacopeial Convention, Inc. Greenwood Village, CO. 2005., p. 140
For more Therapeutic Uses (Complete) data for STANOZOLOL (10 total), please visit the HSDB record page.
Vet: monitor benefits and need carefully in cardiac disease and nephritis.
Rossoff, I.S. Handbook of Veterinary Drugs. New York: Springer Publishing Company, 1974., p. 553
Use of anabolic steroids by athletes is not recommended. Objective evidence is conflicting and inconclusive as to whether these medications significantly increase athletic performance by increasing muscle strength. Weight gains reported by athletes are due in part to fluid retention, which is a potentially hazardous side effect of anabolic steroid therapy. The risk of other unwanted effects, such as testicular atrophy and suppression of spermatogenesis in males; menstrual disturbances and virilization, such as deepening of voice, development of acne, and unnatural growth of body hair in females; peliosis hepatis or other hepatotoxicity; and hepatic cancer outweigh and possible benefit received from anabolic steroids and make their use in athletes inappropriate. /Anabolic steroids/
Thomson.Micromedex. Drug Information for the Health Care Professional. 25th ed. Volume 1. Plus Updates. Content Reviewed by the United States Pharmacopeial Convention, Inc. Greenwood Village, CO. 2005., p. 140
Anabolic steroids are not recommended for use during pregnancy, since studies in animals have shown that anabolic steroids cause masculinization of the fetus. Risk-benefit must be carefully considered. /Anabolic steroids/
Thomson.Micromedex. Drug Information for the Health Care Professional. 25th ed. Volume 1. Plus Updates. Content Reviewed by the United States Pharmacopeial Convention, Inc. Greenwood Village, CO. 2005., p. 141
Contraindications: Hypersensitivity to anabolic steroids; male patients with prostate or breast carcinoma; carcinoma of the breast in females with hypercalcemia; nephrosis; the nephrotic phase of nephritis; pregnancy; to enhance physical appearance or athletic performance. /Anabolic steroids/
Novak, K.M. (ed.). Drug Facts and Comparisons 59th Edition 2005. Wolters Kluwer Health. St. Louis, Missouri 2005., p. 334
For more Drug Warnings (Complete) data for STANOZOLOL (17 total), please visit the HSDB record page.
Stanozolol is a synthetic anabolic steroid with therapeutic uses in treating C1-inhibitor deficient hereditary angioedema. C1-inhibitor is a protease that inhibits the complement system (part of the innate immune system), a biochemical chain of reactions which assists the body in removing pathogens from the body. Stanozolol may help control attacks of hereditary angioedema. Stanozolol can be administered orally or intramuscularly.
Stanozolol is a synthetic anabolic-androgenic steroid (AAS), which promotes cell growth (anabolism) and development/maintenance of masculine characteristics (androgenism).
Androgens
Compounds that interact with ANDROGEN RECEPTORS in target tissues to bring about the effects similar to those of TESTOSTERONE. Depending on the target tissues, androgenic effects can be on SEX DIFFERENTIATION; male reproductive organs, SPERMATOGENESIS; secondary male SEX CHARACTERISTICS; LIBIDO; development of muscle mass, strength, and power. (See all compounds classified as Androgens.)
Anabolic Agents
These compounds stimulate anabolism and inhibit catabolism. They stimulate the development of muscle mass, strength, and power. (See all compounds classified as Anabolic Agents.)
A - Alimentary tract and metabolism
A14 - Anabolic agents for systemic use
A14A - Anabolic steroids
A14AA - Androstan derivatives
A14AA02 - Stanozolol
It is not known whether anabolic steroids are distributed into breast milk. /Anabolic steroids/
Thomson.Micromedex. Drug Information for the Health Care Professional. 25th ed. Volume 1. Plus Updates. Content Reviewed by the United States Pharmacopeial Convention, Inc. Greenwood Village, CO. 2005., p. 141
Urinary metabolites of stanozolol (17 alpha-methyl-17 beta-hydroxy-5 alpha-androst-2-eno(3,2-c)-pyrazole) following oral administration were isolated by chromatography on XAD-2 and by preparative high-performance liquid chromatography (HPLC) and identified by gas chromatography-mass spectrometry (GC/MS) with electron impact (EI)-ionisation. Stanozolol is excreted as a conjugate but is metabolized to a large extent. All identified metabolites are hydroxylated, namely at C-3' of the pyrazole ring and at C-4 beta, C-16 alpha and C-16 beta of the steroid. Less than 5% of the metabolites are found in the unconjugated urine fraction: 3'-hydroxy-stanozolol (II) and 3'-hydroxy-17-epistanozolol (III). Conjugated excreted metabolites are 3'-hydroxystanozolol (II), stanozolol (I), 4 beta-hydroxy-stanozolol (IV), 16 beta-hydroxystanozolol (V), 16 alpha-hydroxystanozolol (VI), two isomers of 3',16-dihydroxystanozolol (VII, VIII), two isomers of 4 beta, 16-dihydroxystanozolol (IX, X) and a 3',?-dihydroxystanozolol (XI). 3'-Hydroxystanozolol, 4 alpha-hydroxystanozolol, 4 beta-hydroxystanozolol, 16 alpha-hydroxy-, 16 alpha-hydroxy-17-epi- and 16 beta-hydroxystanozolol were synthesised to confirm the structural assignment of the main metabolites.
PMID:2362445 Schanzer W et al; J Steroid Biochem 36 (1-2):153-74 (1990)
The equine phase I and phase II metabolism of the synthetic anabolic steroid stanozolol was investigated following its administration by intramuscular injection to a thoroughbred gelding. The major phase I biotransformations were hydroxylation at C16 and one other site, while phase II metabolism in the form of sulfate and beta-glucuronide conjugation was extensive.
PMID:15458725 McKinney AR et al; J Chromatogr B Analyt Technol Biomed Life Sci 811 (1): 75-83 (2004)
An analytical method has been developed in order to control the illegal use of stanozolol as growth promoter in livestock. ... Urinary metabolites were identified by mass spectrometry. Stanozolol and 16-hydroxystanozolol were detected after oral administration, while 16-hydroxystanozolol and 4,16-dihydroxystanozolol were found after subcutaneous administration.
PMID:9300863 Ferchaud V et al; J Chromatogr B Biomed Sci Appl 695 (2): 269-77 (1997)
24 hours
Stanozolol binds to androgen receptors, such as membrane bound receptor proteins LAGS and stanozolol-binding protein (STBP).
The anabolic steroid, stanozolol, is used therapeutically to treat a number of pathological conditions and its clinical effects suggest that it can modulate connective tissue breakdown. The ability of this compound to stimulate prostaglandin E2 (PGE2), collagenase, gelatinase and stromelysin production by human synovial and skin fibroblasts in vitro was examined. The results showed that stanozolol significantly stimulated, in a dose dependent manner, PGE2, collagenase and stromelysin production by skin fibroblasts. However, no stimulation was seen in the synovial cell lines. In contrast, no effect on gelatinase production was seen in either cell type, following exposure to stanozolol. The synovial and skin lines both exhibited a significant stimulation of PGE2 and all three metalloproteinases in response to interleukin-1 beta (IL-1 beta).
PMID:1529798 Ellis AJ et al; Agents Actions 35 (3-4): 232-7 (1992)
Steroid-binding proteins unrelated to the classical nuclear receptors have been proposed to play a role in non-genomic actions of the 17alpha-alkylated testosterone derivative (17alpha-AA) stanozolol (ST). We have previously reported that male rat liver endoplasmic reticulum contains two steroid-binding sites associated with high molecular mass oligomeric proteins: (1) the ST-binding protein (STBP); and (2) the low-affinity glucocorticoid-binding protein (LAGS). To further explore the role of LAGS on the mechanism of action of ST, we have now studied: (1) the interaction of ST and its hydroxylated metabolites with solubilized LAGS and the cytosolic glucocorticoid receptor (GR); and (2) the effects of hormones on the capability of STBP to bind ST. We found that, unlike 17alpha-methyltestosterone, neither ST nor its hydroxylated metabolites bind to GR. However, the 16beta-hydroxylation of ST significantly increases the capability of LAGS to bind ST. Interestingly, 3'-hydroxylation of ST abrogates the capability of LAGS to bind ST. ST (k(i)=30 nM) and 16beta-hydroxystanozolol (k(i)=13 nM) bind with high affinity to LAGS, and are capable of accelerating the rate of dissociation of previously bound dexamethasone from the LAGS. STBP and LAGS are strongly induced by ethinylestradiol. However, unlike STBP, LAGS is regulated by thyroid hormones and growth hormone, which proves that these steroid-binding activities are associated with different binding sites. These findings seem to suggest a novel mechanism for ST whereby membrane-associated glucocorticoid-binding activity is targeted by the 16beta-hydroxylated metabolite of ST. ST and its 16beta-hydroxylated metabolite modulate glucocorticoid activity in the liver through negative allosteric modulation of LAGS, with the result of this interaction an effective increase in classical GR-signaling by increasing glucocorticoid availability to the cytosolic GR.
PMID:14698206 Betancor-Hernandez E et al; J Steroid Biochem Mol Biol 87 (4-5): 253-64 (2003)
Reverses catabolic processes and negative nitrogen balance by promoting protein anabolism and stimulating appetite if there is concurrently a proper intake of calories and proteins. /Anabolic steroids/
Thomson.Micromedex. Drug Information for the Health Care Professional. 25th ed. Volume 1. Plus Updates. Content Reviewed by the United States Pharmacopeial Convention, Inc. Greenwood Village, CO. 2005., p. 141
Antianemic: Anemias due to bone marrow failure: Increases production and urinary excretion of erythropoietin. Anemias due to deficient red cell production : Stimulates erythropoietin production and may have a direct action on bone marrow. Anemias associated with renal disease: increases hemoglobin and red blood cell volume. /Anabolic steroids/
Thomson.Micromedex. Drug Information for the Health Care Professional. 25th ed. Volume 1. Plus Updates. Content Reviewed by the United States Pharmacopeial Convention, Inc. Greenwood Village, CO. 2005., p. 141
Angioedema (hereditary) prophylactic: Increases serum concentration of Cl esterase inhibitor and, as a result, C2 and C4 concentrations . /Anabolic steroids/
Thomson.Micromedex. Drug Information for the Health Care Professional. 25th ed. Volume 1. Plus Updates. Content Reviewed by the United States Pharmacopeial Convention, Inc. Greenwood Village, CO. 2005., p. 141