


1. D-306
2. Diacomit
1. 49763-96-4
2. Diacomit
3. Bcx 2600
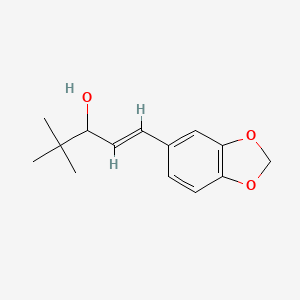
4. 1-(1,3-benzodioxol-5-yl)-4,4-dimethyl-1-penten-3-ol
5. 137767-55-6
6. Bcx-2600
7. 1-(benzo[d][1,3]dioxol-5-yl)-4,4-dimethylpent-1-en-3-ol
8. 4,4-dimethyl-1-((3,4-methylenedioxy)phenyl)-1-penten-3-ol
9. (1e)-1-(2h-1,3-benzodioxol-5-yl)-4,4-dimethylpent-1-en-3-ol
10. Ncgc00185769-01
11. Estiripentol
12. 1-penten-3-ol, 4,4-dimethyl-1-(3,4-methylenedioxyphenyl)-
13. (e)-1-(benzo[d][1,3]dioxol-5-yl)-4,4-dimethylpent-1-en-3-ol
14. 1-penten-3-ol, 1-(1,3-benzodioxol-5-yl)-4,4-dimethyl-
15. Stiripentolum
16. Stiripentol [mi]
17. Stiripentol [inn]
18. Stiripentol [jan]
19. Stiripentol [usan:inn]
20. Stiripentol [usan]
21. Stiripentolum [inn-latin]
22. Estiripentol [inn-spanish]
23. Stiripentol [mart.]
24. 4,4-dimethyl-1-(3,4-methylenedioxyphenyl)-1-penten-3-ol
25. Smr000449279
26. Stiripentol [who-dd]
27. Stiripentol [ema Epar]
28. R02xot8v8i
29. Einecs 256-480-9
30. Mfcd00869310
31. Brn 1313047
32. (e)-1-(1,3-benzodioxol-5-yl)-4,4-dimethylpent-1-en-3-ol
33. Diacomit (tn)
34. Me-2080
35. Cpd000449279
36. Dsstox_cid_28994
37. Dsstox_rid_83259
38. Dsstox_gsid_49068
39. 5-19-02-00640 (beilstein Handbook Reference)
40. Mls000758313
41. Mls001424144
42. Schembl216436
43. Stiripentol (jan/usan/inn)
44. Gtpl5469
45. Schembl2533815
46. Chembl1983350
47. Chebi:94435
48. Stiripentol, >=98% (hplc)
49. Dtxsid80860609
50. Stiripentol [orange Book]
51. Hms2052k07
52. Hms2232p06
53. Hms3886m17
54. Bcp10434
55. Tox21_113622
56. Bdbm50504273
57. S5266
58. Akos025149123
59. Akos027255159
60. Ccg-101092
61. Ccg-266819
62. Cs-7801
63. Db09118
64. Nc00342
65. Ncgc00185769-02
66. Bs-16863
67. Cas-49763-96-4
68. Hy-103392
69. D05928
70. W10731
71. Bcx2600; Bcx-2600; Bcx 2600
72. 763s964
73. Q412182
74. (1e)-1-(1,3-benzodioxol-5-yl)-4,4-dimethyl-1-penten-3-ol
75. (e)-1-(3,4-methylenedioxyphenyl)-4,4-dimethyl-1-penten-3-ol
76. 131206-47-8
| Molecular Weight | 234.29 g/mol |
|---|---|
| Molecular Formula | C14H18O3 |
| XLogP3 | 3.6 |
| Hydrogen Bond Donor Count | 1 |
| Hydrogen Bond Acceptor Count | 3 |
| Rotatable Bond Count | 3 |
| Exact Mass | 234.125594432 g/mol |
| Monoisotopic Mass | 234.125594432 g/mol |
| Topological Polar Surface Area | 38.7 Ų |
| Heavy Atom Count | 17 |
| Formal Charge | 0 |
| Complexity | 280 |
| Isotope Atom Count | 0 |
| Defined Atom Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Undefined Atom Stereocenter Count | 1 |
| Defined Bond Stereocenter Count | 1 |
| Undefined Bond Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Covalently Bonded Unit Count | 1 |
Indicated for use in conjunction with clobazam and valproate as adjunctive therapy of refractory generalized tonic-clonic seizures in patients with severe myoclonic epilepsy in infancy (SMEI, Dravets syndrome) whose seizures are not adequately controlled with clobazam and valproate.
Diacomit is indicated for use in conjunction with clobazam and valproate as adjunctive therapy of refractory generalized tonic-clonic seizures in patients with severe myoclonic epilepsy in infancy (SMEI, Dravet's syndrome) whose seizures are not adequately controlled with clobazam and valproate.
Stiripentol is an orphan drug that effectively reduces seizure frequency in infantile epilepsy as an adjunct therapy and also exhibits a therapeutic advantage in improving the efficacy of other antiepileptic drugs. It potentiates GABA transmission by elevating the levels of the inhibitory neurotransmitters in the brain. Stiripentol is a positive allosteric modulator of GABA-A receptors in the brain that enhances the opening duration of the channel by binding to a site different than the benzodiazepine binding site. Reduced synaptosomal uptake of GABA and/or inhibition of GABA transaminase may also explain the role of stiripentol in reducing the events of seizure. The anticonvulsant activity of stiripentol is age-dependent, with increased efficacy in younger patients.
Anticonvulsants
Drugs used to prevent SEIZURES or reduce their severity. (See all compounds classified as Anticonvulsants.)
N03AX17
N - Nervous system
N03 - Antiepileptics
N03A - Antiepileptics
N03AX - Other antiepileptics
N03AX17 - Stiripentol
Absorption
Absorption of stiripentol is quick with the peak plasma concentration reached within 1.5 hours following oral administration. The systemic exposure increases in a dose-proportional relationship. It is rapidly taken up into the brain and enters the cerebellum and medulla. It displays low bioavailability due to water insolubility and metabolism.
Route of Elimination
Renal elimination is mainly responsible for excretion of stiripentol. About 73% of total administered dose is found in urine as metabolites, while further 13-24% of the total dose is recovered in faeces as unchanged substance.
Volume of Distribution
The average volume of distribution is 1.03 L/kg but does not display a dose-dependent relationship. It is expected to be distributed into the extravascular space and with a high degree of tissue binding.
Clearance
Plasma clearance decreases markedly at high doses; it falls from approximately 40 L/kg/day at the dose of 600 mg/day to about 8 L/kg/day at the dose of 2,400 mg. Decreased clearance is probably explained by inhibition of the cytochrome P450 isoenzymes that catalyzes stiripentol metabolism.
There are 13 metabolites from extensive metabolism stiripentol that are found in urine. The predominant metabolic pathways involve demethylenation and glucuronidation. Other metabolic pathways are oxidative cleavage of the methylenedioxy ring system, O-methylation of catechol metabolites, hydroxylation of the t-butyl group and conversion of the allylic alcohol side-chain to the isomeric 3-pentanone structure. Based on in vitro studies, phase I metabolism of stiripentol involves enzymatic activity of CYP1A2, CYP2C19 and CYP3A4.
Elimination half life is approximately ranges from 4.5 to 13 hours, in a dose-dependent manner.
Stiripentol enhances GABAergic inhibition and prolongs the open duration of GABA-A receptor chloride channels by a barbiturate-like mechanism. It binds to GABA-A receptors containing any of the , , , or -subunits but displays strongest potency when bound to receptors containing 3 or subunits. Stiripentol is an inhibitor of lactate dehydrogenase (LDH), which plays a physiological role in energy metabolism of neurons and regulation of neuronal excitation. It binds to the site separate from lactate and pyruvate binding sites of the enzyme and inhibits both pyruvate-to-lactate conversion and lactate-to-pyruvate conversion. LDH inhibitors including stiripentol as antiepileptic treatments mimic ketogenic diet, where the energy source in the brain is switched from glucose to mainly ketone bodies. The ketone bodies directly regulate neuronal excitation and seizures via ATP-sensitive potassium channels and vesicular glutamate transporters. As a potent inhibitor of hepatic cytochrome P450 enzymes, mainly CYP3A4 and CYP2C19, stiripentol co-administration with other antiepileptic drugs elevates the free unchanged active drugs (such as carbamazepine, sodium valproate, phenytoin, phenobarbital and many benzodiazepines) in the circulation to mediate their therapeutic actions.
