


1. Euler Gaddum Substance P
2. Euler-gaddum Substance P
3. Hypothalamic Substance P
4. Sp(1-11)
5. Substance P, Euler-gaddum
6. Substance P, Hypothalamic
1. 33507-63-0
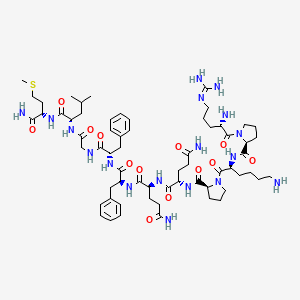
2. Arg-pro-lys-pro-gln-gln-phe-phe-gly-leu-met-nh2
3. 12769-48-1
4. Chembl235363
5. 11035-08-8
6. Neurokinin P
7. Arg-pro-lys-pro-gln-gln-phe-phe-gly-leu-met-nh2 3acoh 5h2o
8. H-arg-pro-lys-pro-gln-gln-phe-phe-gly-leu-met-nh2
9. Ccris 7229
10. Einecs 251-545-8
11. Unii-675vgv5j1d
12. Crofelemer
13. P Substance
14. Substance-p
15. Substanz-p
16. Neurokinin-1
17. Substance P Tfa
18. Neurokinin P Tfa
19. Neuropeptide Sp-1
20. Sh-oligopeptide-73
21. Substance P Analogue
22. [3h]-substance P
23. [125i]-substance P
24. Neurokinin Pneurokinin P
25. Substance P Acetate Salt
26. Substance P (1-11)
27. Tachykinin Substance P (sp)
28. 675vgv5j1d
29. Gtpl2098
30. Gtpl3805
31. Gtpl3835
32. Schembl1116347
33. [3h]sp (human, Mouse, Rat)
34. Schembl20844802
35. Chebi:80308
36. [3h]-sp
37. Argprolysproglnglnphepheglyleumet
38. [125i]sp (human, Mouse, Rat)
39. [125i]-sp
40. Bdbm50001450
41. Mfcd00076780
42. Akos024456424
43. Ncgc00167123-01
44. As-77493
45. Q411041
46. Arg-pro-lys-pro-gln-gln-phe-phe-gly-leu-met Nh2
47. Arg-pro-lys-pro-gln-gln-phe-phe-gly-leu-met-amine
48. (sp)arg-pro-lys-pro-gln-gln-phe-phe-gly-leu-met-nh2
49. H-arg-pro-lys-pro-gln-gln-phe-d-phe-gly-leu-met-nh2
50. Arg-pro-lys-pro-gln-gln-phe-phe-gly-leu-met-nh2(substance P)
51. Arg-pro-lys-pro-gln-gln-phe-phe-gly-leu-met-nh2.(substance P)
52. H-arg-pro-lys-pro-gln-gln-phe-phe-gly-leu-met-nh2(substance P)
53. Substance P (arg-pro-lys-pro-gln-gln-phe-phe-gly-leu-metnh2)
54. 148470-19-3
| Molecular Weight | 1347.6 g/mol |
|---|---|
| Molecular Formula | C63H98N18O13S |
| XLogP3 | -2.3 |
| Hydrogen Bond Donor Count | 15 |
| Hydrogen Bond Acceptor Count | 17 |
| Rotatable Bond Count | 42 |
| Exact Mass | 1346.72814643 g/mol |
| Monoisotopic Mass | 1346.72814643 g/mol |
| Topological Polar Surface Area | 544 Ų |
| Heavy Atom Count | 95 |
| Formal Charge | 0 |
| Complexity | 2620 |
| Isotope Atom Count | 0 |
| Defined Atom Stereocenter Count | 10 |
| Undefined Atom Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Defined Bond Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Undefined Bond Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Covalently Bonded Unit Count | 1 |
For the symptomatic treatment of non-infectious diarrhea in adult patients with HIV/AIDS who are taking antiretroviral therapy.
FDA Label
Crofelemer is an inhibitor of secretory diarrhea via inhibition of the CFTR chloride transporter. Crofelemer is not an antimicrobial, and therefore does not drive the emergence of resistance; it does not inhibit motility, and therefore does not cause constipation or rebound diarrhea; and it is not systemically absorbed, reducing the potential for adverse drug interactions and toxicity.
Neurotransmitter Agents
Substances used for their pharmacological actions on any aspect of neurotransmitter systems. Neurotransmitter agents include agonists, antagonists, degradation inhibitors, uptake inhibitors, depleters, precursors, and modulators of receptor function. (See all compounds classified as Neurotransmitter Agents.)
A - Alimentary tract and metabolism
A07 - Antidiarrheals, intestinal antiinflammatory/antiinfective agents
A07X - Other antidiarrheals
A07XA - Other antidiarrheals
A07XA06 - Crofelemer
Absorption
The absorption of crofelemer is minimal and crofelemer concentrations in plasma are below the level of quantitation (50 ng/mL).
Route of Elimination
Since crofelemer is not significantly absorbed, the route of elimination has not been identified.
Volume of Distribution
Since crofelemer is not significantly absorbed, volume of distribution was not quantified.
Clearance
Since crofelemer is not significantly absorbed, clearance was not determined.
Since crofelemer is not significantly absorbed, no metabolites have been identified.
Since crofelemer is not significantly absorbed, the half life was not determined.
Crofelemer is an inhibitor of the cystic fibrosis transmembrane regulator chloride channel (CFTR), as evidenced by its activity on cell cultures, single cell patch clamps, single CFTR channels, and elaboration of mouse intestinal fluid secretion. Crofelemer also inhibits calcium activated chloride channels (CaCC), which in combination with CFTR, are expressed on the luminal side of intestinal cells. Crofelemer inhibition of both of these channels prevents water loss from diarrhea by inhibiting chloride secretion.
