


1. Btamaze
2. Combactam
3. Cp 45899
4. Cp-45899
5. Cp45899
6. Penicillanic Acid Sulfone
7. Sodium, Sulbactam
8. Sulbactam Sodium
9. Sulfone, Penicillanic Acid
1. 68373-14-8
2. Sulbactam Acid
3. Betamaze
4. Penicillanic Acid Sulfone
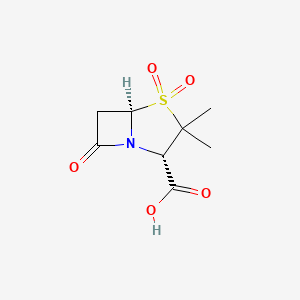
5. (2s,5r)-3,3-dimethyl-7-oxo-4-thia-1-azabicyclo[3.2.0]heptane-2-carboxylic Acid 4,4-dioxide
6. Sulbactamum
7. Penicillanic Acid 1,1-dioxide
8. (2s,5r)-3,3-dimethyl-7-oxo-4-thia-1-azabicyclo(3.2.0)heptane-2-carboxylic Acid 4,4-dioxide
9. Chembl403
10. Cp-45899
11. (2s,5r)-3,3-dimethyl-4,4,7-trioxo-4$l^{6}-thia-1-azabicyclo[3.2.0]heptane-2-carboxylic Acid
12. Cp-45,899
13. Chebi:9321
14. S4tf6i2330
15. Sulbactam (inn)
16. 68373-14-8 (free Acid)
17. Nsc-759886
18. Sulbactam 100 Microg/ml In Acetonitrile
19. Sulbactam [inn]
20. Dsstox_cid_3605
21. (2s,5r)-3,3-dimethyl-4,4,7-trioxo-4lambda6-thia-1-azabicyclo[3.2.0]heptane-2-carboxylic Acid
22. Dsstox_rid_77104
23. Dsstox_gsid_23605
24. 2,2-dimethyl-1,1-dioxidopenam-3alpha-carboxylic Acid
25. Cp-458992
26. Smr000387064
27. Cas-68373-14-8
28. Cp 45899
29. Sulbactam [inn:ban]
30. Sr-01000760610
31. Sulbactamum [inn-latin]
32. Mfcd00867005
33. Unii-s4tf6i2330
34. Sulbactam,(s)
35. (2s,5r)-3,3-dimethyl-4,4,7-trioxo-4?^{6}-thia-1-azabicyclo[3.2.0]heptane-2-carboxylic Acid
36. 0rn
37. Einecs 269-878-2
38. Sulbactam [mi]
39. Sulbactam [vandf]
40. Ncgc00159487-06
41. Sulbactam; Sulbactam Acid
42. Sulbactam [mart.]
43. Sulbactam [usp-rs]
44. Sulbactam [who-dd]
45. Schembl47781
46. Mls001048859
47. Mls001304017
48. Sodium 1,1-dioxypenicillanate
49. Dtxsid1023605
50. Gtpl10769
51. Hms2090e07
52. Hms2269a12
53. Hms3651c06
54. Hms3715b09
55. Zinc897244
56. Bcp13271
57. Ex-a2000
58. Hy-b0334
59. Tox21_113642
60. Bbl033518
61. Bdbm50021954
62. S1958
63. Stk801889
64. Akos004119988
65. Tox21_113642_1
66. Ccg-221124
67. Db09324
68. Ks-5198
69. Nsc 759886
70. (2s,5r)-3,3-dimethyl-7-oxo-4-thia-1-azabicyclo(3.2.0)heptan-2-carbonsaeure 4,4-dioxid
71. Sulbactam, Analytical Reference Material
72. Ncgc00159336-02
73. Ncgc00159336-03
74. Ncgc00159336-05
75. 4-thia-1-azabicyclo(3.2.0)heptane-2-carboxylic Acid, 3,3-dimethyl-7-oxo-, 4,4-dioxide, (2s-cis)-
76. Ac-18973
77. Bs167314
78. S0868
79. Sultamicillin Impurity A [ep Impurity]
80. C07770
81. D08533
82. Ab00698109-06
83. Ab00698109-08
84. Ab00698109_09
85. 373s148
86. A836122
87. Q423393
88. Sr-01000760610-2
89. Sr-01000760610-3
90. Brd-k44133266-001-10-0
91. Z1563146038
92. Sulbactam, European Pharmacopoeia (ep) Reference Standard
93. Sulbactam, United States Pharmacopeia (usp) Reference Standard
94. (2s,5r)-2-carboxylato-3,3-dimethyl-7-oxo-4-thia-1-azabicyclo[3.2.0]heptane4,4-dioxide
95. (2s,5r)-3,3-dimethyl-4,4,7-trioxo-4-thia-1-azabicyclo[3.2.0]heptane-2-carboxylic Acid
96. (2s,5r)-3,3-dimethyl-7-oxo-4-thia-1-azabicyclo[3.2.0]heptane-2-carboxylicacid4,4-dioxide
97. 3,3-dimethyl-4,4,7-trioxo-4lambda*6*-thia-1-aza-bicyclo[3.2.0]heptane-2-carboxylic Acid
98. Sulbactam For Peak Identification, European Pharmacopoeia (ep) Reference Standard
99. (2s,5r)-3,3-dimethyl-4,4,7-trioxo-4lambda*6*-thia-1-aza-bicyclo[3.2.0]heptane-2-carboxylic Acid
100. (2s,5r)-3,3-dimethyl-4,4,7-tris(oxidanylidene)-4$l^{6}-thia-1-azabicyclo[3.2.0]heptane-2-carboxylic Acid
101. (2s,5r)-3,3-dimethyl-7-oxo-4-thia-1-azabicyclo-[3.2.0]heptane-2-carboxylic Acid 4,4-dioxide
102. (2s,5r)?-?3,3-?dimethyl-?7-?oxo-?4-?thia-?1-?azabicyclo[3.2.0]?heptane-?2-?carboxylic Acid 4,4-dioxide
103. (s)-3,3-dimethyl-7-(r)-oxo-4,4-dioxo-4lambda*6*-thia-1-aza-bicyclo[3.2.0]heptane-2-carboxylic Acid
104. 3,3-dimethyl-4,4,7-trioxo-4lambda*6*-thia-1-aza-bicyclo[3.2.0]heptane-2-carboxylic Acid (sulbactam)
105. 4-thia-1-azabicyclo[3.2.0]heptane-2-carboxylic Acid, 3,3-dimethyl-7-oxo-,4,4-dioxide, (2s, Cis)
106. 4-thia-1-azabicyclo[3.2.0]heptane-2-carboxylic Acid,3,3-dimethyl-7-oxo-, 4,4-dioxide, (2s,5r)-
| Molecular Weight | 233.24 g/mol |
|---|---|
| Molecular Formula | C8H11NO5S |
| XLogP3 | -1 |
| Hydrogen Bond Donor Count | 1 |
| Hydrogen Bond Acceptor Count | 5 |
| Rotatable Bond Count | 1 |
| Exact Mass | 233.03579362 g/mol |
| Monoisotopic Mass | 233.03579362 g/mol |
| Topological Polar Surface Area | 100 Ų |
| Heavy Atom Count | 15 |
| Formal Charge | 0 |
| Complexity | 446 |
| Isotope Atom Count | 0 |
| Defined Atom Stereocenter Count | 2 |
| Undefined Atom Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Defined Bond Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Undefined Bond Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Covalently Bonded Unit Count | 1 |
Sulbactam is currently available in combination products with ampicillin. Within this formulation it is indicated for the treatment of infections due to susceptible strains of the designated microorganisms in the conditions listed below. Skin and Skin Structure Infections caused by beta-lactamase producing strains of Staphylococcus aureus, Escherichia coli, Klebsiella spp. (including K. pneumoniae), Proteus mirabilis, Bacteroides fragilis, Enterobacter spp., and Acinetobacter calcoaceticus. Intra-Abdominal Infections caused by beta-lactamase producing strains of Escherichia coli, Klebsiella spp. (including K. pneumoniae), Bacteroides spp. (including B. fragilis), and Enterobacter spp. Gynecological Infections caused by beta-lactamase producing strains of Escherichia coli, and Bacteroides spp. (including B. fragilis).
FDA Label
Anti-Bacterial Agents
Substances that inhibit the growth or reproduction of BACTERIA. (See all compounds classified as Anti-Bacterial Agents.)
beta-Lactamase Inhibitors
Endogenous substances and drugs that inhibit or block the activity of BETA-LACTAMASES. (See all compounds classified as beta-Lactamase Inhibitors.)
J - Antiinfectives for systemic use
J01 - Antibacterials for systemic use
J01C - Beta-lactam antibacterials, penicillins
J01CG - Beta-lactamase inhibitors
J01CG01 - Sulbactam
Absorption
Peak serum concentrations are reached almost immediately following a 15-minute intravenous infusion of sulbactam + ampicillin. Mean peak serum levels for sulbactam range from 48 to 88 mcg/mL following intravenous administration of 2000 mg of ampicillin plus 1000 mg sulbactam. After an intramuscular injection of 1000 mg ampicillin plus 500 mg sulbactam, peak sulbactam serum levels ranging from 6 to 24 mcg/mL are attained.
Route of Elimination
Approximately 75 to 85% of both ampicillin and sulbactam are excreted unchanged in the urine during the first 8 hours after administration.
Volume of Distribution
Penetration of both ampicillin and sulbactam into cerebrospinal fluid in the presence of inflamed meninges has been demonstrated after IV administration.
~1 hr
Sulbactam is an irreversible inhibitor of -lactamase; by binding and inhibiting -lactamase produced by bacterial cells, sulbactam is thereby able to prevent it from reducing antibiotic activity. Although sulbactam alone possesses little useful antibacterial activity, except against the Neisseriaceae, whole organism studies have shown that sulbactam restores ampicillin activity against beta-lactamase producing strains. In particular, sulbactam has good inhibitory activity against the clinically important plasmid mediated beta-lactamases most frequently responsible for transferred drug resistance. The presence of sulbactam in formulations with ampicillin effectively extends the antibacterial spectrum of ampicillin to include many bacteria normally resistant to it and to other beta-lactam antibacterials. Thus, products with ampicillin + sulbactam possess the properties of a broad-spectrum antibacterial and a beta-lactamase inhibitor.
