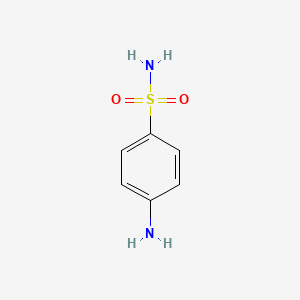

1. 4 Aminobenzenesulfonamide
2. 4-aminobenzenesulfonamide
3. Azol Polvo
4. Sulfanilamide Barium Salt
5. Sulfanilamide Cadmium Salt
6. Sulfanilamide Hydrochloride
7. Sulfanilamide Lithium Salt
8. Sulfanilamide Magnesium Salt
9. Sulfanilamide Monohydrate
10. Sulfanilamide Silver Salt
11. Sulfanilamide Sodium
12. Sulfanilamide Sodium Salt
13. Sulfanilamide Strontium Salt
14. Sulfanilamide Zinc Salt
15. Sulphanilamide
1. 4-aminobenzenesulfonamide
2. 63-74-1
3. Sulphanilamide
4. Sulfamine
5. P-aminobenzenesulfonamide
6. Sulphonamide
7. Sulfonylamide
8. P-aminobenzenesulfamide
9. Prontylin
10. Prontosil Album
11. 4-aminobenzene-1-sulfonamide
12. Bacteramid
13. Streptasol
14. Streptocid
15. P-sulfamoylaniline
16. Sulfonamide P
17. Prontosil I
18. Benzenesulfonamide, 4-amino-
19. Estreptocida
20. Exoseptoplix
21. Streptoclase
22. P-sulfamidoaniline
23. Sulfamidyl
24. Sulfanalone
25. Sulfanidyl
26. Sulfanil
27. Sulfocidine
28. Sulfana
29. 4-sulfamoylaniline
30. Sulfanilimidic Acid
31. P-anilinesulfonamide
32. P-aminophenylsulfonamide
33. Ambeside
34. Antistrept
35. Astreptine
36. Astrocid
37. Bactesid
38. Collomide
39. Colsulanyde
40. Copticide
41. Deseptyl
42. Ergaseptine
43. Erysipan
44. Gombardol
45. Lysococcine
46. Neococcyl
47. Orgaseptine
48. Prontalbin
49. Proseptal
50. Proseptine
51. Proseptol
52. Pysococcine
53. Septanilam
54. Septinal
55. Septolix
56. Septoplex
57. Septoplix
58. Strepamide
59. Strepsan
60. Streptagol
61. Streptamid
62. Streptamin
63. Streptocide
64. Streptocom
65. Strepton
66. Streptopan
67. Streptosil
68. Streptozol
69. Streptozone
70. Streptrocide
71. Sulfocidin
72. Therapol
73. Albexan
74. Albosal
75. Dipron
76. Gerison
77. Infepan
78. Sanamid
79. Stramid
80. Tolder
81. Lusil
82. Prontosil White
83. Pronzin Album
84. Septamide Album
85. Stopton Album
86. Streptocid Album
87. 4-aminophenylsulfonamide
88. Rubiazol A
89. White Streptocide
90. Pabs
91. Streptocide White
92. P-aminobenzenesulfonylamide
93. Aniline-p-sulfonic Amide
94. Fourneau 1162
95. Sulfanilamide Vaginal Cream
96. Benzenesulfonamide, P-amino-
97. 4-azanylbenzenesulfonamide
98. 4-amino-benzenesulfonamide
99. Mfcd00007939
100. P-aminobenzensulfonamide
101. Sulphanilamidum
102. 1162 F
103. 4-(aminosulfonyl)aniline
104. Para-aminobenzenesulfonamide
105. A-349
106. F 1162
107. Chebi:45373
108. 4-aminobenzene Sulfonic Acid Amide
109. Nsc-7618
110. Chembl21
111. P-amino Benzene Sulfonamide
112. (4-(aminosulfonyl)phenyl)amine
113. Avc
114. Streptocidum
115. Nsc7618
116. Sulfanilamide Melting Point Standard
117. Sulfanilamide (inn)
118. 21240mf57m
119. Cas-63-74-1
120. Ncgc00016285-02
121. Ncgc00016285-05
122. Sulfanilamida
123. Sulfanilamidum
124. 4-aminobenzenesulphonamide (sulphanilamide)
125. Sulfanilamide, >=99%
126. Dsstox_cid_3622
127. Sulfanilamide [inn]
128. Dsstox_rid_77115
129. Dsstox_gsid_23622
130. Streptocide (van)
131. Solfanilamide [dcit]
132. Caswell No. 809a
133. Solfanilamide
134. Hsdb 223
135. Sulfanilamidum [inn-latin]
136. Sulfanilamida [inn-spanish]
137. Smr000059035
138. Ccris 764
139. Sr-01000763435
140. Nsc 7618
141. Einecs 200-563-4
142. Epa Pesticide Chemical Code 077902
143. Brn 0511852
144. Sulfanilamine
145. Sulfanimide
146. Sulfanilamide [inn:dcf:nf]
147. Ai3-00952
148. Sulphanilic Amide
149. 4-sulphanilamide
150. Unii-21240mf57m
151. Sulfanimide,(s)
152. F-1162
153. Streptocid (tn)
154. Delta-sulfanilamide
155. Prestwick_36
156. 4-sulfamoyl-aniline
157. Sulfanilamide Reagent
158. Sulfanilamide-reagent
159. 4-sulphamoyl Aniline
160. Spectrum_000489
161. 4-aminobenzensulfonamide
162. Wln: Zswr Dz
163. 4-aminobenzenesulphonamide
164. P-aminobenzene Sulfonamide
165. Prestwick0_000729
166. Prestwick1_000729
167. Prestwick2_000729
168. Prestwick3_000729
169. Spectrum2_000846
170. Spectrum3_001406
171. Spectrum4_000398
172. Spectrum5_001081
173. 4-aminobenzene Sulfonamide
174. 4-aminobenzene-sulfonamide
175. P-aminosulfonyl Phenylamine
176. Schembl740
177. Sulfanilamide [mi]
178. 4-amino-benzenesulphonamide
179. Epitope Id:122232
180. Avc (tn)
181. Sulfanilamide [hsdb]
182. Oprea1_273157
183. P-aminobenzene Sulfonyl Amide
184. Bspbio_000658
185. Bspbio_003052
186. Kbiogr_000955
187. Kbioss_000969
188. Sulfanilamide [vandf]
189. 4-14-00-02658 (beilstein Handbook Reference)
190. Mls001074682
191. Mls002152940
192. Bidd:gt0170
193. Divk1c_000528
194. Spectrum1500646
195. Sulfanilamide [mart.]
196. Sulphanilamidum [hpus]
197. Spbio_000831
198. Spbio_002597
199. Sulfanilamide [usp-rs]
200. Sulfanilamide [who-dd]
201. Aromatic Sulfonamide Compound 5
202. Bpbio1_000724
203. Halogenosulfanilamide Deriv. 5a
204. Zinc2101
205. Dtxsid4023622
206. Schembl11880061
207. Bdbm10857
208. Hms501k10
209. Kbio1_000528
210. Kbio2_000969
211. Kbio2_003537
212. Kbio2_006105
213. Kbio3_002272
214. Sulfanilamide, P.a., 99.0%
215. Ninds_000528
216. Hms1570a20
217. Hms1921o07
218. Hms2092e20
219. Hms2097a20
220. Hms2233b19
221. Hms3370j16
222. Hms3655k19
223. Hms3714a20
224. Hms3744m13
225. Pharmakon1600-01500646
226. Ro13354
227. Sulfanilamide [orange Book]
228. Hy-b0242
229. Sulfanilamide [ep Monograph]
230. Tox21_110351
231. Tox21_201331
232. Tox21_303336
233. Ac9456
234. Aromatic/heteroaromatic Sulfonamide 2
235. Bbl005257
236. C1264
237. Ccg-40302
238. Nsc757404
239. S1685
240. Stk298902
241. Uk-124
242. Akos000119305
243. Tox21_110351_1
244. Db00259
245. Nsc-757404
246. Idi1_000528
247. Ncgc00016285-01
248. Ncgc00016285-03
249. Ncgc00016285-04
250. Ncgc00016285-06
251. Ncgc00016285-08
252. Ncgc00091144-01
253. Ncgc00091144-02
254. Ncgc00091144-03
255. Ncgc00257174-01
256. Ncgc00258883-01
257. Sulfanilamide 100 Microg/ml In Methanol
258. As-13239
259. Bp-12552
260. Sulfanilamide (4-aminobenzenesulfonamide)
261. Sy009959
262. Sbi-0051575.p002
263. Ab00052138
264. Ft-0657032
265. Ft-0674702
266. S0381
267. Sulfadiazine Impurity D [ep Impurity]
268. Sw196353-3
269. Sulfadimidine Impurity D [ep Impurity]
270. Sulfanilamide, Jis Special Grade, >=99.7%
271. Sulfanilamide, Vetec(tm) Reagent Grade, 97%
272. C07458
273. D08543
274. Ab00052138-10
275. Ab00052138_11
276. Ab00052138_12
277. Sulfadimethoxine Impurity E [ep Impurity]
278. Sulfamethoxazole Impurity E [ep Impurity]
279. A834498
280. Ac-907/25014139
281. Q423423
282. Sulfanilamide, Vetranal(tm), Analytical Standard
283. Sr-01000763435-2
284. Sr-01000763435-3
285. Sr-01000763435-4
286. Sulfacetamide Sodium Impurity A [ep Impurity]
287. Sulfanilamide (166 Degrees C) Melting Point Standard
288. F2190-0451
289. Benzenesulfonic Acid,4-amino,amide Sulfanilamide
290. Ethyl1-(aminomethyl)-6,8-dimethoxyisoquinoline-4-carboxylate
291. Sulfanilamide, European Pharmacopoeia (ep) Reference Standard
292. Sulfanilamide, Puriss. P.a., >=99% (calc. To The Dried Substance)
293. Sulfanilamide, United States Pharmacopeia (usp) Reference Standard
294. Reagecon Melting Point Sulphanilamide +164 To +166 Degrees C Standard
295. Sulfadimethoxine Sodium For Veterinary Use Impurity E [ep Impurity]
296. Sulfanilamide Melting Point Standard, United States Pharmacopeia (usp) Reference Standard
297. 1337-39-9
298. Sulfanilamide Melting Point Standard, Pharmaceutical Secondary Standard; Certified Reference Material
| Molecular Weight | 172.21 g/mol |
|---|---|
| Molecular Formula | C6H8N2O2S |
| XLogP3 | -0.6 |
| Hydrogen Bond Donor Count | 2 |
| Hydrogen Bond Acceptor Count | 4 |
| Rotatable Bond Count | 1 |
| Exact Mass | 172.03064868 g/mol |
| Monoisotopic Mass | 172.03064868 g/mol |
| Topological Polar Surface Area | 94.6 Ų |
| Heavy Atom Count | 11 |
| Formal Charge | 0 |
| Complexity | 211 |
| Isotope Atom Count | 0 |
| Defined Atom Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Undefined Atom Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Defined Bond Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Undefined Bond Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Covalently Bonded Unit Count | 1 |
| 1 of 2 | |
|---|---|
| Drug Name | Avc |
| PubMed Health | Sulfanilamide (Vaginal) |
| Drug Classes | Antibacterial |
| Drug Label | AVC is a preparation for vaginal administration for the treatment of Candida albicans infections and available in the following forms:AVC CreamEach tube contains:Sulfanilamide........................................................................... |
| Active Ingredient | Sulfanilamide |
| Dosage Form | Cream |
| Route | Vaginal |
| Strength | 15% |
| Market Status | Prescription |
| Company | Meda Pharms |
| 2 of 2 | |
|---|---|
| Drug Name | Avc |
| PubMed Health | Sulfanilamide (Vaginal) |
| Drug Classes | Antibacterial |
| Drug Label | AVC is a preparation for vaginal administration for the treatment of Candida albicans infections and available in the following forms:AVC CreamEach tube contains:Sulfanilamide........................................................................... |
| Active Ingredient | Sulfanilamide |
| Dosage Form | Cream |
| Route | Vaginal |
| Strength | 15% |
| Market Status | Prescription |
| Company | Meda Pharms |
The US FDA announced on May 31, 1979, that their Anti-infective and Topical Drugs Advisory Committee and Fertility and Maternal Health Advisory Committee, as well as other studies, had concluded there was no adequate evidence that the then-available vaginal sulfonamides formulations were effective either for the treatment of vulvovaginitis caused by Candida albicans, Trichomonas vaginalis, or Gardnerella vaginalis (Hemophilus vaginalis) or for relief of the symptoms of these conditions. /Sulfonamides (vaginal)/
USP Convention. USPDI - Drug Information for the Health Care Professional. 15 th ed. Volume 1. Rockville, MD: United States Pharmacopeial Convention, Inc., 1995. (Plus updates.), p. 2547
/Applied topically/ for the treatment of vaginitis caused by Garderella (Hemophilus) vaginalis, Trichomonas and Candida
GENNARO. REMINGTON'S PHARM SCI 17TH ED 1985 p.1176
Antibacterial
Budavari, S. (ed.). The Merck Index - Encyclopedia of Chemicals, Drugs and Biologicals. Rahway, NJ: Merck and Co., Inc., 1989., p. 1409
MEDICATION (VET): antimicrobial.
Budavari, S. (ed.). The Merck Index - Encyclopedia of Chemicals, Drugs and Biologicals. Rahway, NJ: Merck and Co., Inc., 1989., p. 1409
VET: INSURE ADEQUATE FLUID INTAKE. USE CAUTIOUSLY IN RENAL DISEASE.
Rossoff, I.S. Handbook of Veterinary Drugs. New York: Springer Publishing Company, 1974., p. 573
.../IN ONE OF 2 CASES/ A NEW-BORN CHILD BECAME JAUNDICED ON...1ST DAY OF LIFE & DIED ON 8TH DAY; POST MORTEM REVEALED LIVER NECROSIS & FOCAL NECROSES IN ADRENALS & SPLEEN. SECOND CASE RECOVERED AFTER SEVERE JAUNDICE & ANEMIA, COMMENCING ON 4TH DAY OF LIFE. IN BOTH INSTANCES MOTHER HAD BEEN TREATED WITH SULFANILAMIDE...
The Chemical Society. Foreign Compound Metabolism in Mammals Volume 3. London: The Chemical Society, 1975., p. 671
Sulfonamides are absorbed from the vaginal mucosa and are distributed into breast milk. Use is not recommended in nursing mothers since sulfonamides may cause hyperbilirubinemia in the infant. In addition, sulfonamides may cause hemolytic anemia in glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase-deficient neonates. /Sulfonamides (vaginal)/
USP Convention. USPDI - Drug Information for the Health Care Professional. 15 th ed. Volume 1. Rockville, MD: United States Pharmacopeial Convention, Inc., 1995. (Plus updates.), p. 2548
Side/Adverse Effects: Those indicating need for medical attention: Incidence less frequent: Hypersensitivity (itching, burning, skin rash, redness, swelling, or other sign of irritation not present before therapy). Those indicating need for medical attention only if they continue or are bothersome: Incidence less frequent are: Rash or irritation of penis of sexual partner. /Sulfonamides (vaginal)/
USP Convention. USPDI - Drug Information for the Health Care Professional. 15 th ed. Volume 1. Rockville, MD: United States Pharmacopeial Convention, Inc., 1995. (Plus updates.), p. 2548
For more Drug Warnings (Complete) data for SULFANILAMIDE (6 total), please visit the HSDB record page.
3. 3= MODERATELY TOXIC: PROBABLE ORAL LETHAL DOSE (HUMAN) 0.5-5 G/KG, BETWEEN 1 OZ & 1 PINT (OR 1 LB) FOR 70 KG PERSON (150 LB).
Gosselin, R.E., H.C. Hodge, R.P. Smith, and M.N. Gleason. Clinical Toxicology of Commercial Products. 4th ed. Baltimore: Williams and Wilkins, 1976., p. II-238
For the treatment of vulvovaginitis caused by Candida albicans.
Sulfanilamide is a sulfonamide antibiotic. The sulfonamides are synthetic bacteriostatic antibiotics with a wide spectrum against most gram-positive and many gram-negative organisms. However, many strains of an individual species may be resistant. Sulfonamides inhibit multiplication of bacteria by acting as competitive inhibitors of p-aminobenzoic acid in the folic acid metabolism cycle. Bacterial sensitivity is the same for the various sulfonamides, and resistance to one sulfonamide indicates resistance to all. Most sulfonamides are readily absorbed orally. However, parenteral administration is difficult, since the soluble sulfonamide salts are highly alkaline and irritating to the tissues. The sulfonamides are widely distributed throughout all tissues. High levels are achieved in pleural, peritoneal, synovial, and ocular fluids. Although these drugs are no longer used to treat meningitis, CSF levels are high in meningeal infections. Their antibacterial action is inhibited by pus.
Anti-Bacterial Agents
Substances that inhibit the growth or reproduction of BACTERIA. (See all compounds classified as Anti-Bacterial Agents.)
D - Dermatologicals
D06 - Antibiotics and chemotherapeutics for dermatological use
D06B - Chemotherapeutics for topical use
D06BA - Sulfonamides
D06BA05 - Sulfanilamide
J - Antiinfectives for systemic use
J01 - Antibacterials for systemic use
J01E - Sulfonamides and trimethoprim
J01EB - Short-acting sulfonamides
J01EB06 - Sulfanilamide
Absorption
Sulfonamides are absorbed through the vaginal mucosa. There are no pharmacokinetic data available describing how much of an intravaginal dose reaches the systemic circulation.
SULFANILAMIDE DIFFUSES INTO ALL TISSUES & SECRETIONS OF BODY, INCL MILK & FETAL PRODUCTS, & CEREBROSPINAL FLUID, IN CONCN APPROX THOSE FOUND IN BLOOD.
Thienes, C., and T.J. Haley. Clinical Toxicology. 5th ed. Philadelphia: Lea and Febiger, 1972., p. 210
ABSORPTION /OF SULFONAMIDES/ FROM SKIN & VAGINA IS ERRATIC. ONCE INTO BLOODSTREAM, SULFONAMIDES BIND TO SERUM ALBUMIN TO VARYING DEGREES... PROTEIN-BINDING LIMITS PENETRANCE INTO TISSUES & GLOMERULAR FILTRATION &...IS DETERMINANT OF DISTRIBUTION & RATE OF EXCRETION. /SULFONAMIDES/
Osol, A. and J.E. Hoover, et al. (eds.). Remington's Pharmaceutical Sciences. 15th ed. Easton, Pennsylvania: Mack Publishing Co., 1975., p. 1105
Sulfonamides are eliminated from the body partly as the unchanged drug and partly as metabolic products. The largest fraction is excreted in the urine, and the half life of sulfonamides in the body is thus dependent on renal function. Small amounts are eliminated in the feces and in bile, milk, and other secretions. /Sulfonamides/
Gilman, A.G., T.W. Rall, A.S. Nies and P. Taylor (eds.). Goodman and Gilman's The Pharmacological Basis of Therapeutics. 8th ed. New York, NY. Pergamon Press, 1990., p. 1049
Except for sulfonamides especially designed for their local effects in the bowel, this class of drugs is rapidly absorbed from the gastrointestinal tract. Approximately 70 to 100% of an oral dose is absorbed, and sulfonamide can be found in the urine within 30 minutes of ingestion. The small intestine is the major site of absorption, but some of the drug is absorbed from the stomach. Absorption from other sites, such as the vagina, respiratory tract, or abraded skin, is variable and unreliable, but a sufficient amount may enter the body to cause toxic reactions in susceptible persons or to produce sensitization. /Sulfonamides/
Gilman, A.G., T.W. Rall, A.S. Nies and P. Taylor (eds.). Goodman and Gilman's The Pharmacological Basis of Therapeutics. 8th ed. New York, NY. Pergamon Press, 1990., p. 1049
For more Absorption, Distribution and Excretion (Complete) data for SULFANILAMIDE (8 total), please visit the HSDB record page.
...DOGS...ACETYLATE SULFAMOYL GROUP & EXCRETE...N1-ACETYLSULFANILAMIDE...
The Chemical Society. Foreign Compound Metabolism in Mammals. Volume 1: A Review of the Literature Published Between 1960 and 1969. London: The Chemical Society, 1970., p. 424
When sulfanilamide, p-aminobenzoic acid, 4-aminobiphenyl, 2-aminofluorene or 1-aminopyrene was given orally to dogs, the corresponding N-acetyl and N-formyl derivatives were isolated from urine or feces. ... Dog intestinal flora and several bacterial strains exhibited both N-acetylating and N-formylating activities, in varying degrees, toward all of the arylamines tested. ... The results /show/ that the intestinal microflora plays an important role in the formation of N-acyl derivatives from arylamines in dogs.
PMID:7834807 Okumura F et al; Carcinogenesis 16 (1): 71-6 (1995)
Sulfanilamide is a competitive inhibitor of bacterial enzyme dihydropteroate synthetase. This enzyme normally uses para-aminobenzoic acid (PABA) for synthesizing the necessary folic acid. The inhibited reaction is normally necessary in these organisms for the synthesis of folic acid. Without it, bacteria cannot replicate.
Sulfonamides are structural analogs and competitive antagonist of para-aminobenzoic acid ... and thus prevent normal bacterial utilization of para-aminobenzoic acid for the synthesis of folic acid (pteroylglutamic acid). ... More specifically, sulfonamides are competitive inhibitors of dihydropteroate synthase, the bacterial enzyme responsible for the incorporation of para-aminobenzoic acid into dihydropteroic acid, the immediate precursor of folic acid. /Sulfonamides/
Gilman, A.G., T.W. Rall, A.S. Nies and P. Taylor (eds.). Goodman and Gilman's The Pharmacological Basis of Therapeutics. 8th ed. New York, NY. Pergamon Press, 1990., p. 1048