


1. Imagotan
2. Psychoson
3. Inofal
4. 14759-06-9
5. Thioridazine 2-sulfone
6. Thioridazine-2-sulfone
7. Tpn-12
8. Thioridazine Sulfone
9. Thioridazine Sulphone
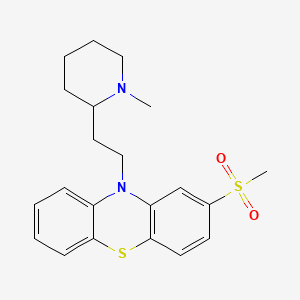
10. 10-(2-(1-methyl-2-piperidyl)ethyl)-2-methylsulfonylphenothiazine
11. 10-[2-(1-methylpiperidin-2-yl)ethyl]-2-methylsulfonylphenothiazine
12. 10h-phenothiazine, 10-[2-(1-methyl-2-piperidinyl)ethyl]-2-(methylsulfonyl)-
13. B7599i244x
14. Phenothiazine, 10-(2-(1-methyl-2-piperidyl)ethyl)-2-methylsulfonyl-
15. Solforidazina [dcit]
16. Solforidazina
17. Sulforidazina
18. Sulforidazinum
19. Tpn 12
20. Sulforidazine [inn:dcf]
21. 10h-phenothiazine, 10-(2-(1-methyl-2-piperidinyl)ethyl)-2-(methylsulfonyl)-
22. Sulforidazinum [inn-latin]
23. Sulforidazina [inn-spanish]
24. Einecs 238-818-7
25. Brn 1230366
26. 2-methylsulfonyl-10-[2-(1-methyl-2-piperidyl)ethyl]phenothiazine
27. (+/-)-thioridazine-2-sulfone
28. 2-methylsulfonyl-10-(2-(1-methyl-2-piperidyl)ethyl)phenothiazine
29. Unii-b7599i244x
30. 2-methylsulfonyl-10-(2-(1-methyl-2-piperidyl)ethyl)phenothiazin
31. Sulforidazine [mi]
32. Sulforidazine [inn]
33. Schembl145025
34. Sulforidazine [mart.]
35. Sulforidazine [who-dd]
36. Chembl2107268
37. Bdbm86723
38. Dtxsid30864531
39. Chebi:135644
40. Nsc_31765
41. Akos030239787
42. Cas_14759-06-9
43. Ft-0675190
44. Thioridazine Impurity E [ep Impurity]
45. L000789
46. J-008369
47. Q7636215
48. Thioridazine Hydrochloride Impurity E [ep Impurity]
49. 10-[2-(1-methyl-2-piperidinyl)ethyl]-2-methylsulfonylphenothiazine
50. 10-(2-(1-methyl-2-piperidinyl)ethyl)-2-(methylsulfonyl)-10h-phenothiazine
51. 10-[2-(1-methyl-2-piperidinyl)ethyl]-2-(methylsulfonyl)-10h-phenothiazine #
52. 2-methanesulfonyl-10-[2-(1-methylpiperidin-2-yl)ethyl]-10h-phenothiazine
53. Phenothiazine, 10-(2-(1-methyl-2-piperidyl)ethyl)-2-(methylsulfonyl)-
| Molecular Weight | 402.6 g/mol |
|---|---|
| Molecular Formula | C21H26N2O2S2 |
| XLogP3 | 4.6 |
| Hydrogen Bond Donor Count | 0 |
| Hydrogen Bond Acceptor Count | 5 |
| Rotatable Bond Count | 4 |
| Exact Mass | 402.14357042 g/mol |
| Monoisotopic Mass | 402.14357042 g/mol |
| Topological Polar Surface Area | 74.3 Ų |
| Heavy Atom Count | 27 |
| Formal Charge | 0 |
| Complexity | 606 |
| Isotope Atom Count | 0 |
| Defined Atom Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Undefined Atom Stereocenter Count | 1 |
| Defined Bond Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Undefined Bond Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Covalently Bonded Unit Count | 1 |
Antidepressive Agents
Mood-stimulating drugs used primarily in the treatment of affective disorders and related conditions. Several MONOAMINE OXIDASE INHIBITORS are useful as antidepressants apparently as a long-term consequence of their modulation of catecholamine levels. The tricyclic compounds useful as antidepressive agents (ANTIDEPRESSIVE AGENTS, TRICYCLIC) also appear to act through brain catecholamine systems. A third group (ANTIDEPRESSIVE AGENTS, SECOND-GENERATION) is a diverse group of drugs including some that act specifically on serotonergic systems. (See all compounds classified as Antidepressive Agents.)
Antipsychotic Agents
Agents that control agitated psychotic behavior, alleviate acute psychotic states, reduce psychotic symptoms, and exert a quieting effect. They are used in SCHIZOPHRENIA; senile dementia; transient psychosis following surgery; or MYOCARDIAL INFARCTION; etc. These drugs are often referred to as neuroleptics alluding to the tendency to produce neurological side effects, but not all antipsychotics are likely to produce such effects. Many of these drugs may also be effective against nausea, emesis, and pruritus. (See all compounds classified as Antipsychotic Agents.)
