
1. Aiglonyl
2. Arminol
3. Deponerton
4. Desisulpid
5. Digton
6. Dogmatil
7. Dolmatil
8. Eglonyl
9. Ekilid
10. Guastil
11. Lebopride
12. Meresa
13. Neogama
14. Pontiride
15. Psicocen
16. Sulp
17. Sulperide
18. Sulpitil
19. Sulpivert
20. Sulpor
21. Syndil
22. Tepavil
23. Vertigo Meresa
24. Vertigo Neogama
25. Vertigo-meresa
26. Vertigo-neogama
1. 15676-16-1
2. Sulpyrid
3. Sulpirid
4. Aiglonyl
5. Dolmatil
6. Dogmatil
7. (+/-)-sulpiride
8. Guastil
9. Dobren
10. (rs)-(+/-)-sulpiride
11. Dogmatyl
12. Mirbanil
13. Misulvan
14. Sursumid
15. Abilit
16. Meresa
17. Miradol
18. Neogama
19. Omperan
20. Splotin
21. Coolspan
22. Sernevin
23. Eglonyl
24. Pyrkappl
25. Sulpitil
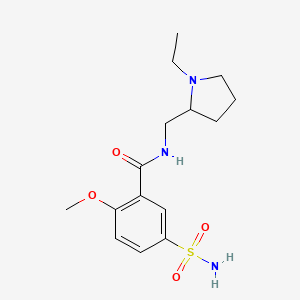
26. N-[(1-ethylpyrrolidin-2-yl)methyl]-2-methoxy-5-sulfamoylbenzamide
27. Synedil
28. Sulpiridum [inn-latin]
29. Sulpirida [inn-spanish]
30. Pyrikappl
31. Sulpirida
32. Sulpiridum
33. Sulpor
34. Dl-sulpiride
35. Rd 1403
36. N-((1-ethyl-2-pyrrolidinyl)methyl)-5-sulfamoyl-o-anisamide
37. 5-(aminosulfonyl)-n-((1-ethyl-2-pyrrolidinyl)methyl)-2-methoxybenzamide
38. (+-)-sulpiride
39. N-((1-ethyl-2-pyrrolidinyl)methyl)-2-methoxy-5-sulfamoylbenzamide
40. R.d. 1403
41. N05al01
42. Chembl26
43. Psicocen
44. Benzamide, 5-(aminosulfonyl)-n-((1-ethyl-2-pyrrolidinyl)methyl)-2-methoxy-
45. C15h23n3o4s
46. Calmoflorine
47. Championyl
48. Lisopiride
49. Stamonevrol
50. Alimoral
51. Darleton
52. Desmenat
53. Dresent
54. Eglonil
55. Equilid
56. Eusulpid
57. Fardalan
58. Fidelan
59. Isnamide
60. Kylistro
61. Mariastel
62. Norestran
63. Nufarol
64. Ozoderpin
65. Restful
66. Suprium
67. Valirem
68. Zemorcon
69. Chebi:32168
70. Enimon
71. Normum
72. O-anisamide, N-((1-ethyl-2-pyrrolidinyl)methyl)-5-sulfamoyl-
73. Omiryl
74. Levosulpiridum [inn-latin]
75. 7mne9m8287
76. N-[(1-ethylpyrrolidin-2-yl)methyl]-2-methoxy-5-sulfamoyl-benzamide
77. Levosulpirida [inn-spanish]
78. Benzamide, 5-(aminosulfonyl)-n-[(1-ethyl-2-pyrrolidinyl)methyl]-2-methoxy-
79. Nsc-757850
80. Rd-1403
81. N-((1-ethylpyrrolidin-2-yl)methyl)-2-methoxy-5-sulfamoylbenzamide
82. Sulpiride-r
83. (+)-n-[(1-ethylpyrrolidin-2-yl)methyl]-2-methoxy-5-sulfamoyl-benzamide
84. Smr000038923
85. Ccris 4248
86. Sulpiride,(+)
87. Sulpiride [usan:inn:ban:jan]
88. Sr-01000075402
89. Einecs 239-753-7
90. Brn 0494008
91. Unii-7mne9m8287
92. (s)-n-((1-ethylpyrrolidin-2-yl)methyl)-2-methoxy-5-sulfamoylbenzamide
93. (y)-sulpiride
94. Sulpiride, Slp
95. (plusmn)-sulpiride
96. Dogmatyl (tn)
97. Magnetic Resonance Imaging Sulpiride
98. (?)-sulpiride
99. Prestwick_431
100. Cas-15676-16-1
101. Mfcd00055061
102. Sulpiride [inn]
103. Sulpiride [jan]
104. Sulpiride [mi]
105. Sulpiride [usan]
106. (.+/-.)-sulpiride
107. Prestwick0_000056
108. Prestwick1_000056
109. Prestwick2_000056
110. Prestwick3_000056
111. Sulpiride,(-)
112. Biomol-nt_000037
113. Biomol-nt_000162
114. Sulpiride [mart.]
115. Schembl8421
116. Sulpiride [who-dd]
117. Dsstox_cid_22574
118. Dsstox_rid_80050
119. Dsstox_gsid_42574
120. Lopac0_001050
121. Oprea1_602476
122. Bspbio_000211
123. 5-22-08-00105 (beilstein Handbook Reference)
124. Mls000069434
125. Mls001306443
126. Divk1c_000278
127. Spbio_002132
128. Bpbio1_000233
129. Bpbio1_000463
130. Bpbio1_001255
131. Ccris-4248
132. Gtpl5501
133. Sulpiride (jp17/usan/inn)
134. Sulpiride [ep Impurity]
135. Dtxsid1042574
136. Sulpiride [ep Monograph]
137. Bdbm11638
138. Hms500n20
139. Kbio1_000278
140. Ninds_000278
141. Sulpiride 1.0 Mg/ml In Methanol
142. Hms1568k13
143. Hms2095k13
144. Hms2231k07
145. Hms3263a22
146. Hms3266p12
147. Hms3371p16
148. Hms3372o01
149. Hms3393a08
150. Hms3411d18
151. Hms3651g12
152. Hms3675d18
153. Hms3712k13
154. Hms3885j14
155. Bcp04500
156. Bcp13871
157. Hy-b1019
158. Str09321
159. ( Inverted Question Mark)-sulpiride
160. Tox21_302205
161. Tox21_501050
162. S4655
163. Stk368596
164. Sulpiride 100 Microg/ml In Methanol
165. 5-(aminosufonyl)-n-[(1-ethyl-2-pyrrolidinyl)methyl]-2-methoxybenzamide
166. Akos004912732
167. Ccg-205127
168. Cs-4534
169. Db00391
170. Lp01050
171. Nsc 757850
172. Sdccgsbi-0051020.p002
173. Idi1_000278
174. Ncgc00015966-03
175. Ncgc00015966-04
176. Ncgc00015966-05
177. Ncgc00015966-06
178. Ncgc00015966-07
179. Ncgc00015966-08
180. Ncgc00015966-16
181. Ncgc00024852-02
182. Ncgc00024852-03
183. Ncgc00024852-04
184. Ncgc00024852-05
185. Ncgc00255813-01
186. Ncgc00261735-01
187. Ac-12181
188. Db-046215
189. Eu-0001755
190. Eu-0101050
191. Ft-0630504
192. Ft-0652244
193. Ft-0674703
194. R. D. 1403
195. D01226
196. S 8010
197. 676s161
198. A809768
199. L000579
200. Q422418
201. Sr-01000075402-2
202. Sr-01000075402-3
203. Sr-01000075402-6
204. Brd-a55272860-001-03-9
205. Brd-a55272860-001-04-7
206. Brd-a55272860-001-08-8
207. Z84655412
208. Sulpiride, British Pharmacopoeia (bp) Reference Standard
209. 1-ethyl-2-(2-methoxy-5-sulfamoylbenzamidomethyl)pyrrolidine
210. Sulpiride, European Pharmacopoeia (ep) Reference Standard
211. N-(1-ethyl-pyrrolidin-2-ylmethyl)-2-methoxy-5-sulfamoyl-benzamide
212. (+/-)-n-[(1-ethylpyrrolidin-2-yl)methyl]-2-methoxy-5-sulfamoylbenzamide
213. (2r)-1-ethyl-2-((2-methoxy-5-sulfamoylbenzamido)methyl)pyrrolidin-1-ium
214. Benzamide,5-(aminosulfonyl)-n-[(1-ethyl-2-pyrrolidinyl)methyl]-2-methoxy-
215. N-(1-ethyl-2-pyrrolidinylmethyl)-2-methoxy-5-sulfamidobenzamide
216. (rs)-(+/-)-5-aminosulfonyl-n-[(1-ethyl -2-pyrrolidinyl)methyl]-2-methoxybenzamide
217. (rs)-(+/-)-5-aminosulfonyl-n-[(1-ethyl-2-pyrrolidinyl)methyl]-2-methoxybenzamide
218. ( Inverted Question Mark)-5-(aminosulfonyl)-n-[(1-ethyl-2-pyrrolidinyl)methyl]-2-methoxybenzamide
| Molecular Weight | 341.4 g/mol |
|---|---|
| Molecular Formula | C15H23N3O4S |
| XLogP3 | 0.6 |
| Hydrogen Bond Donor Count | 2 |
| Hydrogen Bond Acceptor Count | 6 |
| Rotatable Bond Count | 6 |
| Exact Mass | 341.14092740 g/mol |
| Monoisotopic Mass | 341.14092740 g/mol |
| Topological Polar Surface Area | 110 Ų |
| Heavy Atom Count | 23 |
| Formal Charge | 0 |
| Complexity | 505 |
| Isotope Atom Count | 0 |
| Defined Atom Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Undefined Atom Stereocenter Count | 1 |
| Defined Bond Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Undefined Bond Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Covalently Bonded Unit Count | 1 |
Sulpiride is indicated for the treatment of acute and chronic schizophrenia.
Sulpiride is a substituted benzamide derivative and a selective dopamine D2 antagonist indicated to treat acute and chronic schizophrenia. It has a short duration of action as it is given twice daily, and a wide therapeutic window as patients have survived single doses as high as 16g. Patients should be counselled regarding increased motor agitation, extrapyramidal reactions, and neuroleptic malignant syndrome.
Antipsychotic Agents
Agents that control agitated psychotic behavior, alleviate acute psychotic states, reduce psychotic symptoms, and exert a quieting effect. They are used in SCHIZOPHRENIA; senile dementia; transient psychosis following surgery; or MYOCARDIAL INFARCTION; etc. These drugs are often referred to as neuroleptics alluding to the tendency to produce neurological side effects, but not all antipsychotics are likely to produce such effects. Many of these drugs may also be effective against nausea, emesis, and pruritus. (See all compounds classified as Antipsychotic Agents.)
Antidepressive Agents, Second-Generation
A structurally and mechanistically diverse group of drugs that are not tricyclics or monoamine oxidase inhibitors. The most clinically important appear to act selectively on serotonergic systems, especially by inhibiting serotonin reuptake. (See all compounds classified as Antidepressive Agents, Second-Generation.)
Dopamine Antagonists
Drugs that bind to but do not activate DOPAMINE RECEPTORS, thereby blocking the actions of dopamine or exogenous agonists. Many drugs used in the treatment of psychotic disorders (ANTIPSYCHOTIC AGENTS) are dopamine antagonists, although their therapeutic effects may be due to long-term adjustments of the brain rather than to the acute effects of blocking dopamine receptors. Dopamine antagonists have been used for several other clinical purposes including as ANTIEMETICS, in the treatment of Tourette syndrome, and for hiccup. Dopamine receptor blockade is associated with NEUROLEPTIC MALIGNANT SYNDROME. (See all compounds classified as Dopamine Antagonists.)
N05AL01
S76 | LUXPHARMA | Pharmaceuticals Marketed in Luxembourg | Pharmaceuticals marketed in Luxembourg, as published by d'Gesondheetskeess (CNS, la caisse nationale de sante, www.cns.lu), mapped by name to structures using CompTox by R. Singh et al. (in prep.). List downloaded from https://cns.public.lu/en/legislations/textes-coordonnes/liste-med-comm.html. Dataset DOI:10.5281/zenodo.4587355
N - Nervous system
N05 - Psycholeptics
N05A - Antipsychotics
N05AL - Benzamides
N05AL01 - Sulpiride
Absorption
Sulpiride has an oral bioavailability of 27 9%. A 100-108 mg dose of sulpiride reaches a Cmax of 232-403 ng/mL, with a Tmax of 8.3 h. In another study, the AUC of a 100mg oral dose of sulpiride is 1156 522 h\*ng/mL and for an intravenous dose is 3981 813 h\*ng/mL.
Route of Elimination
An intravenous dose of sulpiride is 70 9% eliminated in the urine within 36 hours, while an oral dose is 27 9% eliminated in urine. In both cases, the dose is recovered as the unchanged parent compound.
Volume of Distribution
The average volume of distribution of sulpiride is 2.72 0.66 L/kg.
Clearance
The total systemic clearance of sulpiride if 415 84 mL/min, while the mean renal clearance was 310 91 mL/min.
95% of a dose of sulpiride is not metabolized.
Reports of the half life of sulpiride have only been performed with small numbers of subjects. Therefore, the average half life may be 7.15 hours to 8.3 hours.
Sulpiride is a selective dopamine D2 and D3 receptor antagonist. _In silico_ studies show that sulpiride may interact with the Asp-119 and Phe-417 amino acid residues of these receptors. It is estimated that D2 receptors should be 65-80% occupied for optimal treatment and minimal adverse effects.