

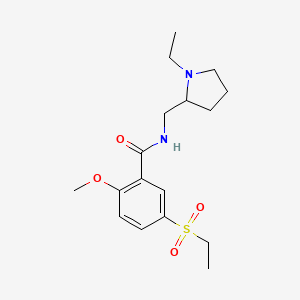

1. 4-amino-n-((1-ethyl-2-pyrrolidinyl)methyl)-5-(ethylsulfonyl)-2-methoxybenzamide
2. Amisulpride
3. Barnetil
4. Dan 2163
5. Dan-2163
6. Lin 1418
7. Lin-1418
8. N-(ethyl-1-pyrrolidinyl- 2-methyl)methoxy-2-ethylsulfonyl-5-benzamide
9. Solian
10. Sultopride Hydrochloride
1. 53583-79-2
2. Barnetil
3. Topral
4. Lin 1418
5. Sultopridum [inn-latin]
6. Lin-1418
7. Aa0g3tw31w
8. Chebi:9356
9. N-((1-ethyl-2-pyrrolidinyl)methyl)-5-(ethylsulfonyl)-o-anisamide
10. Sultopride (inn)
11. Barnotil
12. Benzamide, N-((1-ethyl-2-pyrrolidinyl)methyl)-5-(ethylsulfonyl)-2-methoxy-
13. Sultopride [inn]
14. Sultopridum
15. Sultroprida
16. Sultopride [inn:dcf]
17. N-((1-ethylpyrrolidin-2-yl)methyl)-5-(ethylsulfonyl)-2-methoxybenzamide
18. N-[(1-ethylpyrrolidin-2-yl)methyl]-5-ethylsulfonyl-2-methoxy-benzamide
19. Sultroprida [inn-spanish]
20. (+/-)-sultopride
21. Ncgc00185771-01
22. Einecs 258-641-9
23. Unii-aa0g3tw31w
24. Brn 0494772
25. Sultopride [mi]
26. Sultopride [who-dd]
27. 5-22-08-00103 (beilstein Handbook Reference)
28. Schembl149197
29. Chembl277945
30. Dtxsid9023627
31. Bdbm86720
32. Nsc_5357
33. N-[(1-ethylpyrrolidin-2-yl)methyl]-5-ethylsulfonyl-2-methoxybenzamide
34. Pdsp1_001575
35. Pdsp2_001559
36. Akos024255726
37. O-anisamide, N-((1-ethyl-2-pyrrolidinyl)methyl)-5-(ethylsulfonyl)-
38. Db13273
39. Ks-5337
40. Hy-42849
41. Cas_53583-79-2
42. Db-071706
43. Cs-0040602
44. Ft-0725190
45. D08549
46. L001065
47. Q4445779
48. (+/-)-n-((1-ethyl-2-pyrrolidinyl)methyl)-5-(ethylsulfonyl)-2-methoxybenzamide
49. N-((1-ethyl-2-pyrrolidinyl)methyl)-5-(ethylsulfonyl)-2-methoxybenzamide
50. N-[(1-ethylpyrrolidin-2-yl)methyl]-5-(ethylsulfonyl)-2-(methyloxy)benzamide
| Molecular Weight | 354.5 g/mol |
|---|---|
| Molecular Formula | C17H26N2O4S |
| XLogP3 | 1.6 |
| Hydrogen Bond Donor Count | 1 |
| Hydrogen Bond Acceptor Count | 5 |
| Rotatable Bond Count | 7 |
| Exact Mass | 354.16132849 g/mol |
| Monoisotopic Mass | 354.16132849 g/mol |
| Topological Polar Surface Area | 84.1 Ų |
| Heavy Atom Count | 24 |
| Formal Charge | 0 |
| Complexity | 517 |
| Isotope Atom Count | 0 |
| Defined Atom Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Undefined Atom Stereocenter Count | 1 |
| Defined Bond Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Undefined Bond Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Covalently Bonded Unit Count | 1 |
Antidepressive Agents, Second-Generation
A structurally and mechanistically diverse group of drugs that are not tricyclics or monoamine oxidase inhibitors. The most clinically important appear to act selectively on serotonergic systems, especially by inhibiting serotonin reuptake. (See all compounds classified as Antidepressive Agents, Second-Generation.)
Antipsychotic Agents
Agents that control agitated psychotic behavior, alleviate acute psychotic states, reduce psychotic symptoms, and exert a quieting effect. They are used in SCHIZOPHRENIA; senile dementia; transient psychosis following surgery; or MYOCARDIAL INFARCTION; etc. These drugs are often referred to as neuroleptics alluding to the tendency to produce neurological side effects, but not all antipsychotics are likely to produce such effects. Many of these drugs may also be effective against nausea, emesis, and pruritus. (See all compounds classified as Antipsychotic Agents.)
Dopamine Antagonists
Drugs that bind to but do not activate DOPAMINE RECEPTORS, thereby blocking the actions of dopamine or exogenous agonists. Many drugs used in the treatment of psychotic disorders (ANTIPSYCHOTIC AGENTS) are dopamine antagonists, although their therapeutic effects may be due to long-term adjustments of the brain rather than to the acute effects of blocking dopamine receptors. Dopamine antagonists have been used for several other clinical purposes including as ANTIEMETICS, in the treatment of Tourette syndrome, and for hiccup. Dopamine receptor blockade is associated with NEUROLEPTIC MALIGNANT SYNDROME. (See all compounds classified as Dopamine Antagonists.)
N - Nervous system
N05 - Psycholeptics
N05A - Antipsychotics
N05AL - Benzamides
N05AL02 - Sultopride