

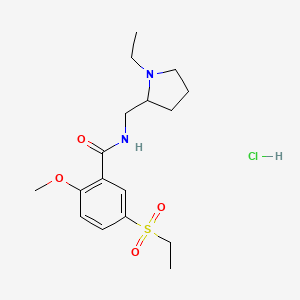

1. 4-amino-n-((1-ethyl-2-pyrrolidinyl)methyl)-5-(ethylsulfonyl)-2-methoxybenzamide
2. Amisulpride
3. Barnetil
4. Dan 2163
5. Dan-2163
6. Lin 1418
7. Lin-1418
8. N-(ethyl-1-pyrrolidinyl- 2-methyl)methoxy-2-ethylsulfonyl-5-benzamide
9. Solian
10. Sultopride
1. 23694-17-9
2. Sultopride Hcl
3. N-((1-ethylpyrrolidin-2-yl)methyl)-5-(ethylsulfonyl)-2-methoxybenzamide Hydrochloride
4. Sultopridehcl
5. Lin-1418 Hydrochloride
6. Sultopride Hydrochloride [jan]
7. Barnotil
8. N-[(1-ethyl-2-pyrrolidinyl)methyl]-5-(ethylsulphonyl)-2-methoxybenzamide Hydrochloride
9. 8q6926t32j
10. 55619-22-2
11. Dsstox_cid_28996
12. Dsstox_rid_83261
13. Dsstox_gsid_49070
14. Benzamide, N-[(1-ethyl-2-pyrrolidinyl)methyl]-5-(ethylsulfonyl)-2-methoxy-, Hydrochloride (1:1)
15. Sultopride Hydrochloride (jan)
16. Cas-23694-17-9
17. Ncgc00185771-01
18. Unii-8q6926t32j
19. N-[(1-ethyl-2-pyrrolidinyl)methyl]-5-(ethylsulfonyl)-2-methoxybenzamide Hydrochloride
20. Barnetil (tn)
21. Benzamide, N-((1-ethyl-2-pyrrolidinyl)methyl)-5-(ethylsulfonyl)-2-methoxy-, Hydrochloride (1:1)
22. N-((1-ethyl-2-pyrrolidinyl)methyl)-5-(ethylsulfonyl)-2-methoxybenzamide Hydrochloride
23. Einecs 245-829-0
24. Ncgc00184999-01
25. Sultopride Monohydrochloride
26. Schembl1417863
27. Chembl3182384
28. Dtxsid0049070
29. Ex-a3336
30. Tox21_113625
31. Tox21_113626
32. Hy-42849a
33. Sultopride Hydrochloride [mi]
34. Akos016010186
35. Ac-4565
36. Sultopride Hydrochloride [who-dd]
37. As-16926
38. Cs-0040603
39. Ft-0659859
40. D02208
41. 694s179
42. A816850
43. Sultopride Hydrochloride (lin-1418 Hydrochloride)
44. J-015185
45. Q27270888
46. N-((1-ethyl-2-pyrrolidinyl)methyl)-5-(ethylsulphonyl)-2-methoxybenzamide Monohydrochloride
47. N-(1-ethyl-2-pyrrolidinylmethyl)-2-methoxy-5-(ethylsulfonyl)benzamide Hydrochloride
48. N-[(1-ethyl-2-pyrrolidinyl)methyl]-5-(ethylsulfonyl)-2-methoxybenzamide Monohydrochloride
49. N-[(1-ethylpyrrolidin-2-yl)methyl]-5-ethylsulfonyl-2-methoxy-benzamide; Hydron; Chloride
50. N-[(1-ethylpyrrolidin-2-yl)methyl]-5-ethylsulfonyl-2-methoxybenzamide;hydrochloride
51. Benzamide, N-((1-ethyl-2-pyrrolidinyl)methyl)-5-(ethylsulfonyl)-2-methoxy-, Monohydrochloride
52. O-anisamide, N-((1-ethyl-2-pyrrolidinyl)methyl)-5-(ethylsulfonyl)-, Monohydrochloride
| Molecular Weight | 390.9 g/mol |
|---|---|
| Molecular Formula | C17H27ClN2O4S |
| Hydrogen Bond Donor Count | 2 |
| Hydrogen Bond Acceptor Count | 5 |
| Rotatable Bond Count | 7 |
| Exact Mass | 390.1380062 g/mol |
| Monoisotopic Mass | 390.1380062 g/mol |
| Topological Polar Surface Area | 84.1 Ų |
| Heavy Atom Count | 25 |
| Formal Charge | 0 |
| Complexity | 517 |
| Isotope Atom Count | 0 |
| Defined Atom Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Undefined Atom Stereocenter Count | 1 |
| Defined Bond Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Undefined Bond Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Covalently Bonded Unit Count | 2 |
Antidepressive Agents, Second-Generation
A structurally and mechanistically diverse group of drugs that are not tricyclics or monoamine oxidase inhibitors. The most clinically important appear to act selectively on serotonergic systems, especially by inhibiting serotonin reuptake. (See all compounds classified as Antidepressive Agents, Second-Generation.)
Antipsychotic Agents
Agents that control agitated psychotic behavior, alleviate acute psychotic states, reduce psychotic symptoms, and exert a quieting effect. They are used in SCHIZOPHRENIA; senile dementia; transient psychosis following surgery; or MYOCARDIAL INFARCTION; etc. These drugs are often referred to as neuroleptics alluding to the tendency to produce neurological side effects, but not all antipsychotics are likely to produce such effects. Many of these drugs may also be effective against nausea, emesis, and pruritus. (See all compounds classified as Antipsychotic Agents.)
Dopamine Antagonists
Drugs that bind to but do not activate DOPAMINE RECEPTORS, thereby blocking the actions of dopamine or exogenous agonists. Many drugs used in the treatment of psychotic disorders (ANTIPSYCHOTIC AGENTS) are dopamine antagonists, although their therapeutic effects may be due to long-term adjustments of the brain rather than to the acute effects of blocking dopamine receptors. Dopamine antagonists have been used for several other clinical purposes including as ANTIEMETICS, in the treatment of Tourette syndrome, and for hiccup. Dopamine receptor blockade is associated with NEUROLEPTIC MALIGNANT SYNDROME. (See all compounds classified as Dopamine Antagonists.)