


1. Laserphyrin
2. Mono-l-aspartyl Chlorin E6
3. Monoaspartyl Chlorin E6
4. N-aspartyl Chlorin E6
5. N-aspartylchlorin E6
6. Npe6
7. Talaporfin
1. Laserphyrin
2. 220201-34-3
3. Taporfin Sodium
4. Mono-l-aspartyl Chlorin E6
5. Npe6
6. Ls-11
7. Talaporfin Sodium [usan]
8. Talaporfin Tetrasodium Salt
9. Me-2906
10. L63605pz70
11. Me 2906
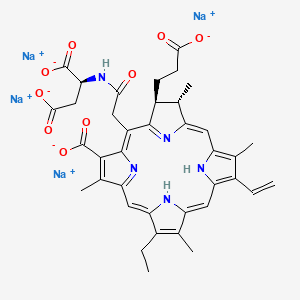
12. Tetrasodium (2s)-2-((((7s,8s)-3-carboxylato-7-(2-carboxylatoethyl)-13-ethenyl-18-ethyl-2,8,12,17-tetramethyl-7,8-dihydroporphyrin-5-yl)acetyl)amino)butanedioate
13. Tetrasodium;(2s)-2-[[2-[(2s,3s)-7-carboxylato-3-(2-carboxylatoethyl)-17-ethenyl-12-ethyl-2,8,13,18-tetramethyl-2,3,23,24-tetrahydroporphyrin-5-yl]acetyl]amino]butanedioate
14. Aptocine
15. L-aspartic Acid, N-(((7s,8s)-3-carboxy-7-(2-carboxyethyl)-13-ethenyl-18-ethyl-7,8-dihydro-2,8,12,17-tetramethyl-21h,23h-porphin-5-yl)acetyl)-, Tetrasodium Salt
16. Talaporfinsodium
17. Laserphyrin (tn)
18. Ls 11 (photosensitizer)
19. Ls11
20. Talaporfin Sodium (jan/usan)
21. Talaporfin Sodium [jan]
22. Chembl2107806
23. Unii-l63605pz70
24. Dtxsid70420519
25. Talaporfin Sodium [mart.]
26. Talaporfin Sodium [who-dd]
27. Me2906
28. At34139
29. Talaporfin Tetrasodium Salt [mi]
30. D01985
31. Q27282754
32. 220680-62-6
| Molecular Weight | 799.7 g/mol |
|---|---|
| Molecular Formula | C38H37N5Na4O9 |
| Hydrogen Bond Donor Count | 3 |
| Hydrogen Bond Acceptor Count | 11 |
| Rotatable Bond Count | 8 |
| Exact Mass | 799.21820490 g/mol |
| Monoisotopic Mass | 799.21820490 g/mol |
| Topological Polar Surface Area | 247 Ų |
| Heavy Atom Count | 56 |
| Formal Charge | 0 |
| Complexity | 1340 |
| Isotope Atom Count | 0 |
| Defined Atom Stereocenter Count | 3 |
| Undefined Atom Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Defined Bond Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Undefined Bond Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Covalently Bonded Unit Count | 5 |
Investigated for use/treatment in macular degeneration.
Antineoplastic Agents
Substances that inhibit or prevent the proliferation of NEOPLASMS. (See all compounds classified as Antineoplastic Agents.)
Photosensitizing Agents
Drugs that are pharmacologically inactive but when exposed to ultraviolet radiation or sunlight are converted to their active metabolite to produce a beneficial reaction affecting the diseased tissue. These compounds can be administered topically or systemically and have been used therapeutically to treat psoriasis and various types of neoplasms. (See all compounds classified as Photosensitizing Agents.)
Light Sciences Oncology (LSO) aims to en-light-en cancer patients. Light Sciences has developed Light Infusion Therapy (Litx) which is a novel treatment for solid tumors. The therapy involves inserting a flexible light-emitting diode (LED) into a tumor, followed by an injection of LS11 (talaporfin sodium), a light-activated drug. Once the LED activates LS11, molecular oxygen is converted into singlet oxygen, killing tissue within the LED's scope and shutting down the blood supply to the area. The treatment is designed for use on three types of cancers: hepatoma (liver cancer), metastatic colorectal cancer, and Gioma (brain tumor).