

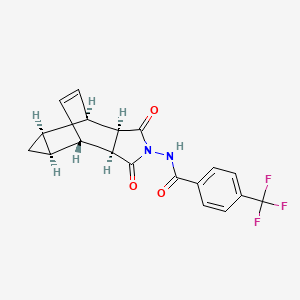

1. 4-trifluoromethyl-n-(3,3a,4,4a,5,5a,6,6a-octahydro-1,3-dioxo-4,6-ethenocycloprop(f)isoindol-2(1h)-yl)-benzamide
2. Benzamide, N-((3ar,4r,4ar,5as,6s,6as)-3,3a,4,4a,5,5a,6,6a-octahydro-1,3-dioxo-4,6-ethenocycloprop(f)isoindol-2(1h)-yl)-4-(trifluoromethyl)-, Hydrate (1:1), Rel-
3. N-((3ar,4r,4ar,5as,6s,6as)-1,3-dioxo-3,3a,4,4a,5,5a,6,6a-octahydro-4,6-ethenocyclopropa(f)isoindol-2(1h)-yl)-4-(trifluoromethyl)benzamide
4. Siga-246
5. St 246
6. St-246
7. Tecovirimat Monohydrate
8. Tpoxx
1. 869572-92-9
2. Siga-246
3. St 246
4. Tpoxx
5. St-246
6. F925rr824r
7. 816458-31-8
8. N-(3,5-dioxo-4-azatetracyclo[5.3.2.02,6.08,10]dodec-11-en-4-yl)-4-(trifluoromethyl)benzamide
9. N-[(1r,2r,6s,7s,8s,10r)-3,5-dioxo-4-azatetracyclo[5.3.2.02,6.08,10]dodec-11-en-4-yl]-4-(trifluoromethyl)benzamide
10. Benzamide, N-((3ar,4r,4ar,5as,6s,6as)-3,3a,4,4a,5,5a,6,6a-octahydro-1,3-dioxo-4,6-ethenocycloprop(f)isoindol-2(1h)-yl)-4-(trifluoromethyl)-, Rel-
11. Tecovirimat [usan]
12. Tecovirimat [usan:inn]
13. Unii-f925rr824r
14. Siga 246
15. 4-trifluoromethyl-n-(3,3a,4,4a,5,5a,6,6a-octahydro-1,3-dioxo-4,6-ethenocycloprop(f)isoindol-2(1h)-yl)-benzamide
16. Benzamide, N-[(3ar,4r,4ar,5as,6s,6as)-3,3a,4,4a,5,5a,6,6a-octahydro-1,3-dioxo-4,6-ethenocycloprop[f]isoindol-2(1h)-yl]-4-(trifluoromethyl)-, Rel-
17. N-((3ar,4r,4ar,5as,6s,6as)-1,3-dioxo-3,3a,4,4a,5,5a,6,6a-octahydro-4,6-ethenocyclopropa(f)isoindol-2(1h)-yl)-4-(trifluoromethyl)benzamide
18. Tecovirimat [mi]
19. Tecovirimat [inn]
20. Tecovirimat [who-dd]
21. Schembl404743
22. Arestvyr;iga-246;t-246
23. Chembl1257073
24. Schembl21670085
25. Tecovirimat [orange Book]
26. Dtxsid101026474
27. Ex-a4340
28. Bdbm50577060
29. S3380
30. St-246st-246
31. Zinc35323125
32. Akos030260536
33. Cs-3464
34. Db12020
35. Hy-14805
36. N-(dioxo[?]yl)-4-(trifluoromethyl)benzamide
37. 458t318
38. Q7692792
39. N-[(3ar,4r,4ar,5as,6s,6as)-1,3-dioxooctahydro-4,6-ethenocyclopropa[f]isoindol-2(1h)-yl]-4-(trifluoromethyl)benzamide
| Molecular Weight | 376.3 g/mol |
|---|---|
| Molecular Formula | C19H15F3N2O3 |
| XLogP3 | 2.6 |
| Hydrogen Bond Donor Count | 1 |
| Hydrogen Bond Acceptor Count | 6 |
| Rotatable Bond Count | 1 |
| Exact Mass | 376.10347683 g/mol |
| Monoisotopic Mass | 376.10347683 g/mol |
| Topological Polar Surface Area | 66.5 Ų |
| Heavy Atom Count | 27 |
| Formal Charge | 0 |
| Complexity | 705 |
| Isotope Atom Count | 0 |
| Defined Atom Stereocenter Count | 6 |
| Undefined Atom Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Defined Bond Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Undefined Bond Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Covalently Bonded Unit Count | 1 |
Tecovirimat is an inhibitor of the orthopoxvirus VP37 envelope wrapping protein and is indicated for the treatment of human smallpox disease in adults and pediatric patients weighing at least 13 kg. The efficacy of tecovirimat may be reduced in immunocompromised patients.
FDA Label
Tecovirimat SIGA is indicated for the treatment of the following viral infections in adults and children with body weight at least 13 kg:
- Smallpox
- Monkeypox
- Cowpox
Tecovirimat SIGA is also indicated to treat complications due to replication of vaccinia virus following vaccination against smallpox in adults and children with body weight at least 13 kg (see sections 4. 4 and 5. 1).
Tecovirimat SIGA should be used in accordance with official recommendations.
Tecovirimat prevents viral spread throughout the body. This drug inhibits its molecular target, a protein called p37, from interacting with intracellular transport components necessary for the production of enveloped virus, and therefore the spread of virus.
Antiviral Agents
Agents used in the prophylaxis or therapy of VIRUS DISEASES. Some of the ways they may act include preventing viral replication by inhibiting viral DNA polymerase; binding to specific cell-surface receptors and inhibiting viral penetration or uncoating; inhibiting viral protein synthesis; or blocking late stages of virus assembly. (See all compounds classified as Antiviral Agents.)
J05AX24
J - Antiinfectives for systemic use
J05 - Antivirals for systemic use
J05A - Direct acting antivirals
J05AX - Other antivirals
J05AX24 - Tecovirimat
Absorption
Readily absorbed following oral administration, with mean times to maximum concentration from 3 to 4 h. A study was conducted to determine the safety, tolerability, and pharmacokinetics of ST-246 administered as a single daily oral dose. Steady state was reached by day 6 (within 3 to 5 half-lives).
Route of Elimination
Less than 0.02% of the drug is excreted unchanged in the kidney, with a majority of the drug being excreted in glucuronidated form. Approximately 23% of unchanged drug is found in the feces.
Volume of Distribution
Approximately 1,356 L. Following oral administration in mice, [14C]-tecovirimat was distributed to all tissues analyzed with the highest concentrations noted in liver and gallbladder, respiratory tract tissues (i.e., nasal turbinates), and bone marrow. Studies in dogs and NHPs suggest that tecovirimat crosses the blood-brain barrier.
Clearance
Mainly renal.
In vitro studies indicate that tecovirimat is not a substrate of major cytochrome P450 (CYP) enzymes, but it is a substrate of human recombinant UGTs (specifically of UGT1A1 and 1A4). Tecovirimat was found to be metabolized into 3 most abundant metabolites, M4, M5 and TFMBA, which do not have pharmacological activity.
Approximately 20h.
Tecovirimat inhibits the production of extracellular viral forms, which are responsible for the systemic spread of infection, inhibiting virus-induced cytopathic effects. Tecovirimat does not inhibit the formation of intracellular forms of the virus (IMV); however, by inhibiting envelopment, and therefore preventing the exit of viral particles from an infected cell, the smallpox infection is slowed to a point where the immune system can eliminate the virus. Tecovirimat has shown a high level of selectivity and specificity for orthopoxviruses. Tecovirimat targets the viral p37 protein, a highly conserved protein with no homologs outside of the Orthopoxvirus genus, inhibiting its function that is necessary for required for the viral envelopment of IMV (intracellular mature virus). Tecovirimat interferes with the cellular localization of p37 viral protein and prevents its association with cellular proteins involved in membrane trafficking.