
1. 3 Hydroxydiazepam
2. 3-hydroxydiazepam
3. Apo Temazepam
4. Apo-temazepam
5. Dasuen
6. Euhypnos
7. Gen Temazepam
8. Gen-temazepam
9. Hydroxydiazepam
10. Levanxol
11. Methyloxazepam
12. Nocturne
13. Norkotral Tema
14. Normison
15. Normitab
16. Nortem
17. Novo Temazepam
18. Novo-temazepam
19. Nu Temazepam
20. Nu-temazepam
21. Oxydiazepam
22. Planum
23. Pms Temazepam
24. Pms-temazepam
25. Pronervon T
26. Remestan
27. Restoril
28. Ro 5 5345
29. Ro-5-5345
30. Ro55345
31. Sah 47 603
32. Sah 47-603
33. Sah 47603
34. Signopam
35. Tema, Norkotral
36. Temaze
37. Temazep Von Ct
38. Temtabs
39. Tenox
40. Von Ct, Temazep
41. Wy 3917
42. Wy-3917
43. Wy3917
1. Restoril
2. Hydroxydiazepam
3. Methyloxazepam
4. Levanxol
5. Oxydiazepam
6. Levanxene
7. Crisonar
8. Euhypnos
9. Signopam
10. 846-50-4
11. N-methyloxazepam
12. Mabertin
13. Normison
14. Remestan
15. Planum
16. 3-hydroxydiazepam
17. Cerepax
18. Euipnos
19. Temaz
20. Tenox
21. Wy-3917
22. Temazepamum
23. Er 115
24. (rs)-temazepam
25. Ro 5-5345
26. Wy 3917
27. Temazepam, Pharmaceutical Grade
28. K-3917
29. Temazepam Civ
30. 2h-1,4-benzodiazepin-2-one, 7-chloro-1,3-dihydro-3-hydroxy-1-methyl-5-phenyl-
31. Nsc 246303
32. 7-chloro-3-hydroxy-1-methyl-5-phenyl-3h-1,4-benzodiazepin-2-one
33. Chb1qd2qss
34. Nocturne
35. Normitab
36. Temtabs
37. Dasuen
38. Nortem
39. Norkotral Tema
40. Nsc-246303
41. Temazep Von Ct
42. Pronervon T
43. 1,3-dihydro-7-chloro-3-hydroxy-1-methyl-5-phenyl-2h-1,4-benzodiazepin-2-one
44. Chebi:9435
45. Nomapam
46. Temador
47. Lenal
48. Uvamin Retard
49. Neodorm Sp
50. 7-chloro-3-hydroxy-1-methyl-5-phenyl-1,3-dihydro-2h-1,4-benzodiazepin-2-one
51. Ncgc00159440-02
52. Gelthix
53. Levanzene
54. Perdorm
55. Dsstox_cid_1309
56. Dsstox_rid_76071
57. Dsstox_gsid_21309
58. Temazepamum [inn-latin]
59. Strazepam
60. 7-chloro-3-hydroxy-1-methyl-5-phenyl-2,3-dihydro-1h-1,4-benzodiazepin-2-one
61. Restoril (tn)
62. Cas-846-50-4
63. Ccris 1954
64. Temazepam (usp/inn)
65. K3917
66. Unii-chb1qd2qss
67. Einecs 212-688-1
68. Brn 0759300
69. Dea No. 2925
70. Temazepam [usan:usp:inn:ban]
71. Diazepam, 3-hydroxy
72. (+/-)-temazepam
73. Wy 2917
74. Temazepam [inn]
75. Temazepam [mi]
76. Temazepam [iarc]
77. Temazepam [usan]
78. Temazepam [vandf]
79. Chembl967
80. Temazepam [mart.]
81. Temazepam [who-dd]
82. Schembl29463
83. 5-25-02-00242 (beilstein Handbook Reference)
84. Mls003899242
85. Divk1c_000989
86. Temazepam, Analytical Standard
87. Gtpl7300
88. Temazepam [orange Book]
89. Temazepam Civ [usp-rs]
90. Dtxsid8021309
91. Temazepam [ep Monograph]
92. Hms503e19
93. Kbio1_000989
94. Temazepam [usp Monograph]
95. Ninds_000989
96. Temazepam 1.0 Mg/ml In Methanol
97. Tox21_111670
98. Tox21_200044
99. Bdbm50408032
100. Nsc246303
101. Ccg-213642
102. Db00231
103. Ro-5-5354
104. Idi1_000989
105. Ncgc00159440-03
106. Ncgc00257598-01
107. Smr000238146
108. Wln: T67 Gnv Jn Ihj Cg G1 Iq Kr
109. C07125
110. D00370
111. Ab01563160_01
112. Q414796
113. Temazepam, British Pharmacopoeia (bp) Reference Standard
114. 2h-1, 7-chloro-1,3-dihydro-3-hydroxy-1-methyl-5-phenyl-
115. Temazepam, United States Pharmacopeia (usp) Reference Standard
116. Temazepam; T8275_sigma; Divk1c_000989; Ninds_000989
117. 1-methyl-7-chloro-3-hydroxy-5-phenyl-1,3-dihydro-2h-1,4-benzodiazepine-2-one
118. 2h-1,4-benzodiazepin-2-one, 1,3-dihydro-7-chloro-3-hydroxy-1-methyl-5-phenyl-
119. 3-hydroxy-1,3-dihydro-1-methyl-7-chloro-5-phenyl-2h-1,4-benzodiazepin-2-one
120. 7-chloro-3-hydroxy-1-methyl-5-phenyl-1,3-dihydro-2h-1,4-benzodiazepin-2-one #
121. 7-chloro-3-hydroxy-1-methyl-5-phenyl-1,3-dihydro-2h-benzo[e][1,4]diazepin-2-one
122. Temazepam Solution, 1.0 Mg/ml In Methanol, Ampule Of 1 Ml, Certified Reference Material
| Molecular Weight | 300.74 g/mol |
|---|---|
| Molecular Formula | C16H13ClN2O2 |
| XLogP3 | 2.2 |
| Hydrogen Bond Donor Count | 1 |
| Hydrogen Bond Acceptor Count | 3 |
| Rotatable Bond Count | 1 |
| Exact Mass | 300.0665554 g/mol |
| Monoisotopic Mass | 300.0665554 g/mol |
| Topological Polar Surface Area | 52.9 Ų |
| Heavy Atom Count | 21 |
| Formal Charge | 0 |
| Complexity | 434 |
| Isotope Atom Count | 0 |
| Defined Atom Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Undefined Atom Stereocenter Count | 1 |
| Defined Bond Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Undefined Bond Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Covalently Bonded Unit Count | 1 |
| 1 of 4 | |
|---|---|
| Drug Name | Restoril |
| PubMed Health | Temazepam (By mouth) |
| Drug Classes | Antianxiety, Hypnotic |
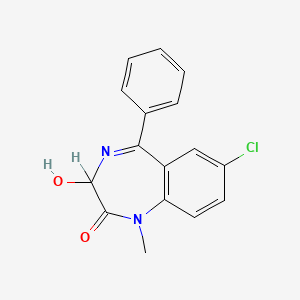
| Drug Label | Restoril (temazepam) is a benzodiazepine hypnotic agent. The chemical name is 7-chloro-1,3-dihydro-3-hydroxy-1-methyl-5-phenyl-2H-1,4-benzodiazepin-2-one, and the structural formula is: Temazepam is a white, crystalline substance, very slightly so... |
| Active Ingredient | Temazepam |
| Dosage Form | Capsule |
| Route | Oral |
| Strength | 22.5mg; 7.5mg; 30mg; 15mg |
| Market Status | Prescription |
| Company | Mallinckrodt |
| 2 of 4 | |
|---|---|
| Drug Name | Temazepam |
| PubMed Health | Temazepam (By mouth) |
| Drug Classes | Antianxiety, Hypnotic |
| Drug Label | DESCRIPTIONTemazepam is a benzodiazepine hypnotic agent. The chemical name is 7-chloro1,3-dihydro-3-hydroxy-1-methyl-5-phenyl-2H-1,4-benzodiazepin-2-one, and the structural formula is:C16H13ClN2O2... |
| Active Ingredient | Temazepam |
| Dosage Form | Capsule |
| Route | Oral |
| Strength | 22.5mg; 7.5mg; 30mg; 15mg |
| Market Status | Prescription |
| Company | Sandoz; Novel Labs; Actavis Elizabeth; Mutual Pharm; Mylan |
| 3 of 4 | |
|---|---|
| Drug Name | Restoril |
| PubMed Health | Temazepam (By mouth) |
| Drug Classes | Antianxiety, Hypnotic |
| Drug Label | Restoril (temazepam) is a benzodiazepine hypnotic agent. The chemical name is 7-chloro-1,3-dihydro-3-hydroxy-1-methyl-5-phenyl-2H-1,4-benzodiazepin-2-one, and the structural formula is: Temazepam is a white, crystalline substance, very slightly so... |
| Active Ingredient | Temazepam |
| Dosage Form | Capsule |
| Route | Oral |
| Strength | 22.5mg; 7.5mg; 30mg; 15mg |
| Market Status | Prescription |
| Company | Mallinckrodt |
| 4 of 4 | |
|---|---|
| Drug Name | Temazepam |
| PubMed Health | Temazepam (By mouth) |
| Drug Classes | Antianxiety, Hypnotic |
| Drug Label | DESCRIPTIONTemazepam is a benzodiazepine hypnotic agent. The chemical name is 7-chloro1,3-dihydro-3-hydroxy-1-methyl-5-phenyl-2H-1,4-benzodiazepin-2-one, and the structural formula is:C16H13ClN2O2... |
| Active Ingredient | Temazepam |
| Dosage Form | Capsule |
| Route | Oral |
| Strength | 22.5mg; 7.5mg; 30mg; 15mg |
| Market Status | Prescription |
| Company | Sandoz; Novel Labs; Actavis Elizabeth; Mutual Pharm; Mylan |
Temazepam is specifically indicated only for the short-term management of insomnia,. Furthermore, such management is generally predominantly associated with the symptomatic relief of transient and short-term insomnia characterized by difficulty in falling asleep, frequent nocturnal awakenings and/or early morning awakenings. In particular, the official prescribing information for temazepam typically specifies that the instructions issued for dispensed prescriptions of the medication should indicate specifically that patients are only expected to use the therapy for short periods of time - usually 7-10 days in general. Subsequently, treatment with temazepam should usually not exceed 7 to 10 consecutive days and nor should it be prescribed in quantities exceeding a one-month supply. Some regional prescribing information also notes that temazepam may be used for premedication prior to minor surgery or other related procedures.
FDA Label
Temazepam is a benzodiazepine used as a hypnotic agent in the management of insomnia. Temazepam produces CNS depression at limbic, thalamic, and hypothalamic levels of the CNS. Temazepam increases the affinity of the neurotransmitter gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA) for GABA receptors by binding to benzodiazepine receptors. Results are sedation, hypnosis, skeletal muscle relaxation, anticonvulsant activity, and anxiolytic action. In sleep laboratory studies, the effect of temazepam was compared to placebo during a two week period. The studies demonstrated a linear dose-response improvement in total sleep time and sleep latency with substantial drug-placebo differences apparent for total sleep time and for sleep latency at higher doses of temazepam. Regardless, REM sleep was ultimately unchanged but slow wave sleep was decreased. Moreover, a transient syndrome, known as "rebound insomnia", wherein the symptoms that led to treatment with temazepam in the first place recur in an enhanced form, may happen on withdrawal of temazepam treatment. The possibility of this occurrence is in part why long term use of temazepam is not recommended due to worries over tolerance and dependence wherein patients' bodies become physiologically accustomed to the regular presence and pharmacological effect of higher and higher doses of the benzodiazepine used. The duration of hypnotic effect and the profile of unwanted adverse effects may be influenced by the distribution and elimination half-lives of the administered temazepam and any active metabolites that may be formed. When such half-lives are long, the drug or its metabolite(s) may accumulate during periods of nightly administration and be associated with impairments of cognitive and motor performance during waking hours. Conversely, if half-lives are short, the drug and metabolites would be cleared before the next dose is ingested, and carry-over effects related to sedation or CNS depression should be minimal or not present at all. However, during nightly use and for an extended period, pharmacodynamic tolerance or adaptation to some effects of benzodiazepine hypnotics may develop - which may also contribute to the possibility of 'rebound insomnia'. Consequently, if the drug has a very short elimination half-life, it is possible that a relative deficiency (for example, in relation to benzodiazepine GABA(a) receptor sites) may occur at some point in the interval between each night's use. This sequence of events may account for certain clinical findings reported happening after several weeks of nightly use of rapidly eliminated benzodiazepine hypnotics, including increased wakefulness during the last third of the night and the appearance of increased daytime anxiety.
GABA Modulators
Substances that do not act as agonists or antagonists but do affect the GAMMA-AMINOBUTYRIC ACID receptor-ionophore complex. GABA-A receptors (RECEPTORS, GABA-A) appear to have at least three allosteric sites at which modulators act: a site at which BENZODIAZEPINES act by increasing the opening frequency of GAMMA-AMINOBUTYRIC ACID-activated chloride channels; a site at which BARBITURATES act to prolong the duration of channel opening; and a site at which some steroids may act. GENERAL ANESTHETICS probably act at least partly by potentiating GABAergic responses, but they are not included here. (See all compounds classified as GABA Modulators.)
Anti-Anxiety Agents
Agents that alleviate ANXIETY, tension, and ANXIETY DISORDERS, promote sedation, and have a calming effect without affecting clarity of consciousness or neurologic conditions. ADRENERGIC BETA-ANTAGONISTS are commonly used in the symptomatic treatment of anxiety but are not included here. (See all compounds classified as Anti-Anxiety Agents.)
Hypnotics and Sedatives
Drugs used to induce drowsiness or sleep or to reduce psychological excitement or anxiety. (See all compounds classified as Hypnotics and Sedatives.)
N - Nervous system
N05 - Psycholeptics
N05C - Hypnotics and sedatives
N05CD - Benzodiazepine derivatives
N05CD07 - Temazepam
Absorption
Studies demonstrate that between 90 to 100% of an orally administered temazepam dose is absorbed, making the medication very well absorbed. The oral administration of 15 to 45 mg temazepam resulted in rapid absorption with significant blood levels achieved in 30 minutes and peak levels at 2-3 hours. In particular, direct studies following the oral ingestion of 30 mg of temazepam revealed measurable plasma concentrations were obtained 10-20 minutes after dosing with peak plasma levels ranging between 666-982 ng/mL (with a mean of 865 ng/mL) presenting approximately 1.2-1.6 hours (with a mean of 1.5 hours) after the dosing. Finally, a dose-proportional relationship was established for the area under the plasma concentration/time curve over the 15 to 30 mg dose range.
Route of Elimination
Following a single dose, 80-90% of the dose appears in the urine, predominantly as the O-conjugate metabolite, and 3-13% of the dose appears in the faeces. Less than 2% of the dose is excreted unchanged or as N-desmethyltemazepam in the urine.
Volume of Distribution
The volume of distribution documented for temazepam is 1.3-1.5 L/kg body weight - and in particular, 43-68 L/kg for the unbound fraction.
Clearance
Studies regarding the clearance of temazepam have recorded the values of 1.03 ml/min/kg and 31 ml/min/kg for the clearance of total temazepam and the clearance of unbound temazepam, respectively.
First-pass metabolism of temazepam is minimal at approximately 5-8% of an administered dose. Nevertheless, temazepam is principally metabolized in the liver where most of the unchanged drug is directly conjugated to glucuronide and excreted in the urine. In particular, the primary metabolite present in the blood is the O-conjugate of temazepam. Less than 5% of the drug is demethylated to oxazepam and subsequently eliminated as the glucuronide. Regardless, the glucuronides of temazepam have no demonstrable CNS activity and it is believed that no active metabolites are formed in general. Since temazepam mainly undergoes Phase II conjugation reactions, it is proposed that it is devoid of CYP450 interactions.
Temazepam is a known human metabolite of diazepam.
S73 | METXBIODB | Metabolite Reaction Database from BioTransformer | DOI:10.5281/zenodo.4056560
The terminal half-life determined for temazepam is recorded as being between 3.5-18 hours, with a mean of 9 hours.
Gamma-Aminobutyric acid (GABA) is considered the principal inhibitory neurotransmitter in the human body. When GABA binds to GABA(a) receptors found in neuron synapses, chloride ions are conducted across neuron cell membranes via an ion channel in the receptors. With enough chloride ions conducted, the local, associated neuron membrane potentials are hyperpolarized - making it more difficult or less likely for action potentials to fire, ultimately resulting in less excitation of the neurons. Subsequently, benzodiazepines like temazepam can bind to benzodiazepine receptors that are components of various varieties of GABA(a) receptors. This binding acts to enhance the effects of GABA by increasing GABA affinity for the GABA(a) receptor, which ultimately enhances GABA ligand binding at the receptors. This enhanced ligand binding of the inhibitory neurotransmitter GABA to the receptors increases the aforementioned chloride ion conduction (perhaps reportedly via an increase in the frequency of the chloride channel opening), resulting in a hyperpolarized cell membrane that prevents further excitation of the associated neuron cells. Combined with the notion that such benzodiazepine receptor associated GABA(a) receptors exist both peripherally and in the CNS, this activity consequently facilitates various effects like sedation, hypnosis, skeletal muscle relaxation, anticonvulsant activity, and anxiolytic action.