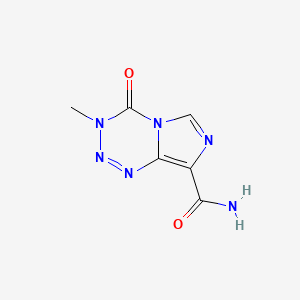

1. 8-carbamoyl-3-methylimidazo(5,1-d)-1,2,3,5-tetrazin-4(3h)-one
2. Ccrg 81045
3. Ccrg-81045
4. Ccrg81045
5. M And B 39831
6. M And B-39831
7. M And B39831
8. Methazolastone
9. Nsc 362856
10. Nsc-362856
11. Nsc362856
12. Temodal
13. Temodar
14. Temozolomide Hexyl Ester
15. Tmz Bioshuttle
16. Tmz-bioshuttle
17. Tmza-he
1. 85622-93-1
2. Methazolastone
3. Temodar
4. Temodal
5. Temozolamide
6. 3-methyl-4-oxo-3,4-dihydroimidazo[5,1-d][1,2,3,5]tetrazine-8-carboxamide
7. Sch 52365
8. Ccrg-81045
9. Temozolomidum [latin]
10. Temozolodida [spanish]
11. Temozolomidum
12. Ccrg 81045
13. Nsc 362856
14. Sch-52365
15. M&b 39831
16. M&b-39831
17. Nsc-362856
18. Ccris 8996
19. Mb 39831
20. 8-carbamoyl-3-methylimidazo(5,1-d)-1,2,3,5-tetrazin-4(3h)-one
21. M & B 39831
22. Brn 5547136
23. M-39831
24. 3,4-dihydro-3-methyl-4-oxoimidazo(5,1-d)-as-tetrazine-8-carboxamide
25. 3,4-dihydro-3-methyl-4-oxoimidazo(5,1-d)-1,2,3,5-tetrazine-8-carboxamide
26. 3-methyl-4-oxo-3,4-dihydroimidazo(5,1-d)(1,2,3,5)tetrazine-8-carboxamide
27. Nsc362856
28. 3-methyl-4-oxoimidazo[5,1-d][1,2,3,5]tetrazine-8-carboxamide
29. Chembl810
30. Mls002701861
31. Yf1k15m17y
32. Chebi:72564
33. Mk-7365
34. Imidazo[5,1-d]-1,2,3,5-tetrazine-8-carboxamide, 3,4-dihydro-3-methyl-4-oxo-
35. Tmz
36. Ncgc00167429-01
37. Temozolodida
38. 3-methyl-4-oxo-3h,4h-imidazo[4,3-d][1,2,3,5]tetrazine-8-carboxamide
39. 8-carbamoyl-3-methylimidazo[5,1-d]-1,2,3,5-tetrazin-4(3h)-one
40. Dsstox_cid_23714
41. Dsstox_rid_80068
42. Dsstox_gsid_43714
43. 3,4-dihydro-3-methyl-4-oxoimidazo[5,1-d]-1,2,3,5-tetrazine-8-carboxamide
44. 3-methyl-4-oxo-3,4-dihydroimidazo-[5,1-d][1,2,3,5]tetrazine-8-carboxamide
45. 3-methyl-4-oxo-3,4-dihydroimidazo[5,1-d][1,2,3,5]tetrazine-8-carboxamide.
46. 3-methyl-4-oxo-3,4-dihydro-imidazo[5,1-d][1,2,3,5]tetrazine-8-carboxylic Acid Amide
47. Smr000466338
48. Temodal (tn)
49. Temodar (tn)
50. Cas-85622-93-1
51. Temozolomide, Vetranal(tm), Analytical Standard
52. Sr-01000759347
53. Temozolomida
54. Unii-yf1k15m17y
55. Temozolomide (jan/usan/inn)
56. Temozolomide [usan:inn:ban]
57. Imidazo(5,1-d)-1,2,3,5-tetrazine-8-carboxamide, 3,4-dihydro-3-methyl-4-oxo-
58. Mfcd00866492
59. Temozolomide- Bio-x
60. Temozolomide [mi]
61. Temozolomide [inn]
62. Temozolomide [jan]
63. Temodar (tn) (schering)
64. Temozolomide [usan]
65. Schembl3739
66. 4-methyl-5-oxo-2,3,4,6,8-pentazabicyclo[4.3.0]nona-2,7,9-triene-9-carboxamide
67. Temozolomide [vandf]
68. Temozolomide [mart.]
69. Mls000759447
70. Mls001424028
71. Bidd:gt0204
72. Temozolomide [usp-rs]
73. Temozolomide [who-dd]
74. Gtpl7301
75. Temozolomide [ema Epar]
76. Dtxsid5043714
77. Temozolomide, >=98% (hplc)
78. Hms2051o12
79. Hms2090b08
80. Hms2232n13
81. Hms3264i14
82. Hms3269p05
83. Hms3372k13
84. Hms3393o12
85. Hms3413d06
86. Hms3654n05
87. Hms3677d06
88. Hms3713h16
89. Pharmakon1600-01502289
90. Temozolomide [orange Book]
91. Temozolomide [ep Monograph]
92. 3-methyl-4-oxo-imidazo[5,1-d][1,2,3,5]tetrazine-8-carboxamide
93. Albb-021358
94. Bcp03692
95. Zinc1482184
96. Temozolomide [usp Monograph]
97. Tox21_112433
98. Ac-758
99. Bdbm50034562
100. Dl-190
101. Nsc759883
102. S1237
103. Stk623541
104. 3,4-dihydro-3-methyl-4-oxoimidazo[5,1-d][1,2,3,5]tetrazine-8-carboxamide
105. 3-methyl-4-oxo-3,4-dihydroimidazo[5,1-d][1,2,3,5]tetraazine-8-carboxamide
106. Akos005557098
107. Tox21_112433_1
108. Ccg-100870
109. Cs-0943
110. Db00853
111. Ks-1216
112. Nc00120
113. Nsc-759883
114. Imidazo(5,1-d)(1,2,3,5)tetrazine-8-carboxamide, 3,4-dihydro-3-methyl-4-oxo-
115. Ncgc00167429-02
116. Ncgc00167429-04
117. Ncgc00167429-05
118. Bp-25388
119. Bt164447
120. Hy-17364
121. Nci60_003316
122. Bcp0726000154
123. Temozolomide 100 Microg/ml In Acetonitrile
124. Am20110227
125. Ft-0630936
126. Ft-0674845
127. Sw197500-4
128. T2744
129. D06067
130. Ab00639915-06
131. Ab00639915-08
132. Ab00639915-09
133. Ab00639915_10
134. Ab00639915_11
135. 622t931
136. A841386
137. Q425088
138. Q-201786
139. Sr-01000759347-4
140. Sr-01000759347-5
141. Brd-k32107296-001-04-5
142. Z1551429743
143. 3-methyl-4-oxo-8-imidazo[5,1-d][1,2,3,5]tetrazinecarboxamide
144. Temozolomide, United States Pharmacopeia (usp) Reference Standard
145. 3-methyl-4-oxidanylidene-imidazo[5,1-d][1,2,3,5]tetrazine-8-carboxamide
146. 3-methyl-8-aminocarbonyl-imidazo[5,1-d]-1,2,3,5-tetrazin-4(3h)-one
147. Imidazo[5,2,3,5-tetrazine-8-carboxamide, 3,4-dihydro-3-methyl-4-oxo-
148. {imidazo[5,1-d]-1,2,3,5-tetrazine-8-carboxamide,} 3, 4-dihydro-3-methyl-4-oxo-
149. Temozolomide, Pharmaceutical Secondary Standard; Certified Reference Material
150. 3-methyl-4-oxo-3,4-dihydro-imidazo[5,1-d][1,2,3,5]tetrazine-8-carboxylic Acid Amide (temozolomide)
151. 3-methyl-4-oxo-3,4-dihydro-imidazo[5,1-d][1,2,3,5]tetrazine-8-carboxylic Acid Amide(temozolomide)
| Molecular Weight | 194.15 g/mol |
|---|---|
| Molecular Formula | C6H6N6O2 |
| XLogP3 | -1.1 |
| Hydrogen Bond Donor Count | 1 |
| Hydrogen Bond Acceptor Count | 5 |
| Rotatable Bond Count | 1 |
| Exact Mass | 194.05522346 g/mol |
| Monoisotopic Mass | 194.05522346 g/mol |
| Topological Polar Surface Area | 106 Ų |
| Heavy Atom Count | 14 |
| Formal Charge | 0 |
| Complexity | 315 |
| Isotope Atom Count | 0 |
| Defined Atom Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Undefined Atom Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Defined Bond Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Undefined Bond Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Covalently Bonded Unit Count | 1 |
| 1 of 4 | |
|---|---|
| Drug Name | Temodar |
| PubMed Health | Temozolomide (Injection) |
| Drug Classes | Antineoplastic Agent |
| Drug Label | TEMODAR contains temozolomide, an imidazotetrazine derivative. The chemical name of temozolomide is 3,4-dihydro-3-methyl-4-oxoimidazo[5,1-d]-as-tetrazine-8-carboxamide. The structural formula is:The material is a white to light tan/light pink powder... |
| Active Ingredient | Temozolomide |
| Dosage Form | Capsule; Powder |
| Route | Oral; Intravenous |
| Strength | 180mg; 250mg; 140mg; 5mg; 100mg/vial; 100mg; 20mg |
| Market Status | Prescription |
| Company | Merck Sharp Dohme |
| 2 of 4 | |
|---|---|
| Drug Name | Temozolomide |
| PubMed Health | Temozolomide |
| Drug Classes | Antineoplastic Agent |
| Drug Label | TEMODAR contains temozolomide, an imidazotetrazine derivative. The chemical name of temozolomide is 3,4-dihydro-3-methyl-4-oxoimidazo[5,1-d]-as-tetrazine-8-carboxamide. The structural formula is:The material is a white to light tan/light pink powder... |
| Active Ingredient | Temozolomide |
| Dosage Form | Capsule |
| Route | Oral |
| Strength | 180mg; 250mg; 140mg; 5mg; 100mg; 20mg |
| Market Status | Prescription |
| Company | Sun Pharma Global; Barr |
| 3 of 4 | |
|---|---|
| Drug Name | Temodar |
| PubMed Health | Temozolomide (Injection) |
| Drug Classes | Antineoplastic Agent |
| Drug Label | TEMODAR contains temozolomide, an imidazotetrazine derivative. The chemical name of temozolomide is 3,4-dihydro-3-methyl-4-oxoimidazo[5,1-d]-as-tetrazine-8-carboxamide. The structural formula is:The material is a white to light tan/light pink powder... |
| Active Ingredient | Temozolomide |
| Dosage Form | Capsule; Powder |
| Route | Oral; Intravenous |
| Strength | 180mg; 250mg; 140mg; 5mg; 100mg/vial; 100mg; 20mg |
| Market Status | Prescription |
| Company | Merck Sharp Dohme |
| 4 of 4 | |
|---|---|
| Drug Name | Temozolomide |
| PubMed Health | Temozolomide |
| Drug Classes | Antineoplastic Agent |
| Drug Label | TEMODAR contains temozolomide, an imidazotetrazine derivative. The chemical name of temozolomide is 3,4-dihydro-3-methyl-4-oxoimidazo[5,1-d]-as-tetrazine-8-carboxamide. The structural formula is:The material is a white to light tan/light pink powder... |
| Active Ingredient | Temozolomide |
| Dosage Form | Capsule |
| Route | Oral |
| Strength | 180mg; 250mg; 140mg; 5mg; 100mg; 20mg |
| Market Status | Prescription |
| Company | Sun Pharma Global; Barr |
Temozolomide is indicated in adult patients for the treatment of newly diagnosed glioblastoma concomitantly with radiotherapy and for use as maintenance treatment thereafter. It is also indicated for the treatment of refractory anaplastic astrocytoma in adult patients who have experienced disease progression on a drug regimen containing nitrosourea and procarbazine.
FDA Label
For the treatment of adult patients with newly diagnosed glioblastoma multiforme concomitantly with radiotherapy (RT) and subsequently as monotherapy treatment.
For the treatment of children from the age of three years, adolescents and adult patients with malignant glioma, such as glioblastoma multiforme or anaplastic astrocytoma, showing recurrence or progression after standard therapy.
For the treatment of adult patients with newly diagnosed glioblastoma multiforme concomitantly with radiotherapy (RT) and subsequently as monotherapy treatment.
For the treatment of children from the age of three years, adolescents and adult patients with malignant glioma, such as glioblastoma multiforme or anaplastic astrocytoma, showing recurrence or progression after standard therapy.
Temodal hard capsules is indicated for the treatment of:
- adult patients with newly diagnosed glioblastoma multiforme concomitantly with radiotherapy and subsequently as monotherapy treatment;
- children from the age of three years, adolescents and adult patients with malignant glioma, such as glioblastoma multiforme or anaplastic astrocytoma, showing recurrence or progression after standard therapy.
Temomedac hard capsules is indicated for the treatment of:
- adult patients with newly diagnosed glioblastoma multiforme concomitantly with radiotherapy (RT) and subsequently as monotherapy treatment;
- children from the age of three years, adolescents and adult patients with malignant glioma, such as glioblastoma multiforme or anaplastic astrocytoma, showing recurrence or progression after standard therapy.
For the treatment of adult patients with newly diagnosed glioblastoma multiforme concomitantly with radiotherapy (RT) and subsequently as monotherapy treatment.
For the treatment of children from the age of three years, adolescents and adult patients with malignant glioma, such as glioblastoma multiforme or anaplastic astrocytoma, showing recurrence or progression after standard therapy.
Temozolomide Sun is indicated for the treatment of:
- adult patients with newly diagnosed glioblastoma multiforme concomitantly with radiotherapy (RT) and subsequently as monotherapy treatment;
- children from the age of three years, adolescents and adult patients with malignant glioma, such as glioblastoma multiforme or anaplastic astrocytoma, showing recurrence or progression after standard therapy.
For the treatment of adult patients with newly diagnosed glioblastoma multiforme concomitantly with radiotherapy (RT) and subsequently as monotherapy treatment.
For the treatment of children from the age of three years, adolescents and adult patients with malignant glioma, such as glioblastoma multiforme or anaplastic astrocytoma, showing recurrence or progression after standard therapy.
Treatment of malignant glioma
Temozolomide is a prodrug of the imidazotetrazine class that requires nonenzymatic hydrolysis at physiological pH _in vivo_ to perform alkylation of adenine/guanine residues, leading to DNA damage through futile repair cycles and eventual cell death. Temozolomide treatment is associated with myelosuppression, which is likely to be more severe in females and geriatric patients. Patients must have an ANC of 1.5 x 109/L and a platelet count of 100 x 109/L before starting therapy and must be monitored weekly during the concomitant radiotherapy phase, on days one and 22 of maintenance cycles, and weekly at any point where the ANC/platelet count falls below the specified values until recovery. Cases of myelodysplastic syndrome and secondary malignancies, including myeloid leukemia, have been observed following temozolomide administration. Pneumocystis pneumonia may occur in patients undergoing treatment, and prophylaxis should be provided for patients in the concomitant phase of therapy with monitoring at all stages. Severe hepatotoxicity has also been reported, and liver testing should be performed at baseline, midway through the first cycle, before each subsequent cycle, and approximately two to four weeks after the last dose. Animal studies suggest that temozolomide has significant embryo-fetal toxicity; male and female patients should practice contraception up to three and six months following the last dose of temozolomide, respectively.
Antineoplastic Agents, Alkylating
A class of drugs that differs from other alkylating agents used clinically in that they are monofunctional and thus unable to cross-link cellular macromolecules. Among their common properties are a requirement for metabolic activation to intermediates with antitumor efficacy and the presence in their chemical structures of N-methyl groups, that after metabolism, can covalently modify cellular DNA. The precise mechanisms by which each of these drugs acts to kill tumor cells are not completely understood. (From AMA, Drug Evaluations Annual, 1994, p2026) (See all compounds classified as Antineoplastic Agents, Alkylating.)
L01AX03
L01AX03
L01AX03
L01AX03
L01AX03
L01AX03
L01AX03
L01AX03
S76 | LUXPHARMA | Pharmaceuticals Marketed in Luxembourg | Pharmaceuticals marketed in Luxembourg, as published by d'Gesondheetskeess (CNS, la caisse nationale de sante, www.cns.lu), mapped by name to structures using CompTox by R. Singh et al. (in prep.). List downloaded from https://cns.public.lu/en/legislations/textes-coordonnes/liste-med-comm.html. Dataset DOI:10.5281/zenodo.4587355
L - Antineoplastic and immunomodulating agents
L01 - Antineoplastic agents
L01A - Alkylating agents
L01AX - Other alkylating agents
L01AX03 - Temozolomide
Absorption
Temozolomide is rapidly and completely absorbed in the gastrointestinal tract and is stable at both acidic and neutral pH. Therefore, temozolomide may be administered both orally and intravenously with a median Tmax of one hour. Following a single oral dose of 150 mg/m2, temozolomide and its active MTIC metabolite had Cmax values of 7.5 g/mL and 7.5 g/mL and AUC values of 23.4 g\*hr/mL and 864 ng\*hr/mL, respectively. Similarly, following a single 90-minute IV infusion of 150 mg/m2, temozolide and its active MTIC metabolite had Cmax values of 7.3 g/mL and 276 ng/mL and AUC values of 24.6 g\*hr/mL and 891 ng\*hr/mL, respectively. Temozolomide kinetics are linear over the range of 75-250 mg/m2/day. Oral temozolomide absorption is affected by food. Administration following a high-fat breakfast of 587 calories caused the mean Cmax and AUC to decrease by 32% and 9%, respectively, and the median Tmax to increase by 2-fold (from 1-2.25 hours).
Route of Elimination
Roughly 38% of administered temozolomide can be recovered over seven days, with 38% in the urine and only 0.8% in the feces. The recovered material comprises mainly metabolites: unidentified polar metabolites (17%), AIC (12%), and the temozolomide acid metabolite (2.3%). Only 6% of the recovered dose represents unchanged temozolomide.
Volume of Distribution
Temozolomide has a mean apparent volume of distribution (%CV) of 0.4 (13%) L/kg.
Clearance
Temozolomide has a clearance of approximately 5.5 L/hr/m2.
After absorption, temozolomide undergoes nonenzymatic chemical conversion to the active metabolite 5-(3-methyltriazen-1-yl) imidazole-4-carboxamide (MTIC) plus carbon dioxide and to a temozolomide acid metabolite, which occurs at physiological pH but is enhanced with increasing alkalinity. MTIC subsequently reacts with water to produce 5-aminoimidazole-4-carboxamide (AIC) and a highly reactive methyl diazonium cation, the active alkylating species. The cytochrome P450 system plays only a minor role in temozolomide metabolism. Relative to the AUC of temozolomide, the exposure to MTIC and AIC is 2.4% and 23%, respectively.
Temozolomide has a mean elimination half-life of 1.8 hours.
Glioblastoma (glioblastoma multiforme) is the most common and aggressive adult primary brain tumour, accounting for 45.6% of all primary malignant brain tumours. Primarily defined histopathologically by necrosis and microvascular proliferation (WHO grade IV classification), glioblastomas are commonly treated through radiotherapy and concomitant alkylation-based chemotherapy with temozolomide. Temozolomide (TMZ) is a small (194 Da) lipophilic alkylating agent of the imidazotetrazine class that is stable at acidic pH, allowing for both oral and intravenous dosing, and can cross the blood-brain barrier to affect CNS tumours. After absorption, TMZ undergoes spontaneous nonenzymatic breakdown at physiological pH to form 5-(3-methyltriazen-1-yl) imidazole-4-carboxamide (MTIC), which then reacts with water to produce 5-aminoimidazole-4-carboxamide (AIC) and a highly reactive methyl diazonium cation. Brain tumours such as glioblastoma typically possess a more alkaline pH than healthy tissue, favouring TMZ activation within tumour tissue. The methyl diazonium cation is highly reactive and methylates DNA at the N7 position of guanine (N7-MeG, 70%), the N3 position of adenine (N3-MeA, 9%), and the O6 position of guanine (O6-MeG, 6%). Although more prevalent, N7-MeG and N3-MeA are rapidly repaired by the base excision repair pathway and are not primary mediators of temozolomide toxicity, although N3-MeA lesions are lethal if not repaired. By comparison, repair of O6-MeG requires action by the suicide enzyme methylguanine-DNA methyltransferase (MGMT), which removes the methyl group to restore guanine. If not repaired by MGMT, O6-MeG mispairs with thymine, activating the DNA mismatch repair (MMR) pathway that removes the thymine (not the O6-MeG), resulting in futile cycles of repair and eventual DNA strand breaks leading to apoptosis. As MMR activity is crucial for temozolomide cytotoxicity, cells that have reduced or absent MGMT function and an intact MMR pathway are the most sensitive to temozolomide treatment. Glioblastomas that upregulate MGMT downregulate MMR or alter both are resistant to TMZ, leading to treatment failure. More recently, increased interest has also been shown in the immunomodulatory effects of TMZ, related to its myelosuppressive effects. Counterintuitively, lymphodepletion may enhance the antitumour effects of cellular immunotherapy and improve the dynamics of memory cells by altering tumour-specific versus tumour-tolerant populations. The depletion of tumour-localized immunosuppressive Treg cells may contribute to an improved response to immunotherapy. Hence, TMZ treatment may also form the backbone of immunotherapy strategies against glioblastoma in the future.