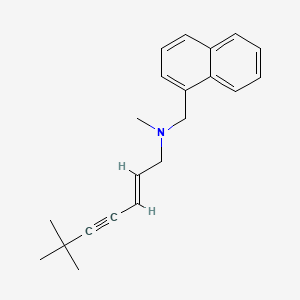

1. (e)-n-(6,6-dimethyl-2-heptenynyl)-n-methyl-1-naphthalenementhamin Hydrochloride
2. Da 5505
3. Lamisil
4. Sf 86 327
5. Sf 86-327
6. Sf 86327
7. Sf-86-327
8. Sf86327
9. Tdt 067
10. Tdt-067
11. Tdt067
12. Terbinafine Hydrochloride
13. Terbinafine, (z)-
14. Terbinafine, (z)-isomer
1. 91161-71-6
2. Lamisil
3. Lamasil
4. (e)-n,6,6-trimethyl-n-(naphthalen-1-ylmethyl)hept-2-en-4-yn-1-amine
5. Sf-86-327
6. Lamisil At
7. Sf 86-327
8. Terbinafin
9. Terbinex
10. (e)-n-(6,6-dimethyl-2-hepten-4-ynyl)-n-methyl-1-naphthalenemethylamine
11. Terbinafina
12. (e)-n-(6,6-dimethyl-2-hepten-4-ynyl)-n-methyl-1-naphthalene Methanamine
13. Terbinafine Free Base
14. Tdt-067
15. G7riw8s0xp
16. Chembl822
17. Chebi:9448
18. Lamisil Tablet
19. 91161-71-6 (free Base)
20. Terbinafinum
21. Zabel
22. 1-naphthalenemethanamine, N-(6,6-dimethyl-2-hepten-4-ynyl)-n-methyl-, (e)-
23. Ncgc00159346-02
24. (2e)-n,6,6-trimethyl-n-(1-naphthylmethyl)hept-2-en-4-yn-1-amine
25. (2e)-n,6,6-trimethyl-n-(naphthalen-1-ylmethyl)hept-2-en-4-yn-1-amine
26. Dsstox_cid_3640
27. N-[(2e)-6,6-dimethyl-2-hepten-4-yn-1-yl]-n-methyl-1-naphthalenemethanamine
28. Dsstox_rid_77123
29. Dsstox_gsid_23640
30. Lamasil (tn)
31. Cas-91161-71-6
32. Unii-g7riw8s0xp
33. Terbinafine (usan/inn)
34. Brn 4256376
35. Corbinal
36. Terbinafine [usan:inn:ban]
37. N,6,6-trimethyl-n-(1-naphthylmethyl)hept-2-en-4-yn-1-amine Hydrochloride
38. Erbinafine Hydrochloride
39. Terbinafine [mi]
40. Terbinafine, Sf-86-327, Lamisil, Tbnf
41. Terbinafine [inn]
42. Terbinafine [usan]
43. Ec 618-706-8
44. Terbinafine [vandf]
45. Terbinafine [mart.]
46. Schembl36794
47. Schembl37843
48. Terbinafine [who-dd]
49. Mls006011885
50. Bidd:gt0825
51. Dtxsid2023640
52. Terbinafine (lamisil, Terbinex)
53. Terbinafine [green Book]
54. Chebi:94705
55. Terbinafine [orange Book]
56. Hms2089b20
57. Hms3715l08
58. Albb-027269
59. Bcp22896
60. Osurnia Component Terbinafine
61. Zinc1530981
62. Tox21_111591
63. (e)-n,6,6-trimethyl-n-(1-naphthylmethyl)hept-2-en-4-yn-1-amine
64. Bbl010959
65. Bdbm50018518
66. Hy-17395a
67. Mfcd00242672
68. S1725
69. Stk802069
70. Akos001451917
71. Tox21_111591_1
72. Ac-8561
73. Ccg-221253
74. Cs-1944
75. Db00857
76. Gs-3099
77. Terbinafine Component Of Osurnia
78. (e)-n,6,6-trimethyl-n-(naphthalen-1
79. Ncgc00159346-03
80. Ncgc00159346-04
81. Ncgc00188975-01
82. Terbinafine [ema Epar Veterinary]
83. Sf86-327
84. Smr004703509
85. Sbi-0206829.p001
86. Sw197656-3
87. T3677
88. C08079
89. D02375
90. Ab00698510-07
91. Ab00698510-09
92. Ab00698510-10
93. Ab00698510-11
94. Ab00698510_12
95. Ab00698510_13
96. Ab00698510_14
97. 161t716
98. A843743
99. Q415259
100. Brd-k68132782-003-05-4
101. (6,6-dimethyl-hept-2-en-4-ynyl)-methyl-naphthalen-1-ylmethyl-amine
102. N,6,6-trimethyl-n-(1-naphthylmethyl)-2-heptene-4-yne-1-amine
103. Sf 86-327; Sf-86-327; Sf86-327; Lamasil; Lamisil At
104. ((e)-6,6-dimethyl-hept-2-en-4-ynyl)-methyl-naphthalen-1-ylmethyl-amine
105. 1n,6,6-trimethyl-1n-(1-naphthylmethyl)-(e)-2-hepten-4-yn-1-amine
106. (6,6-dimethyl-hept-2-en-4-ynyl)-methyl-naphthalen-1-ylmethyl-amine(terbinafine)
107. (6,6-dimethylhept-2-en-4-yn-1-yl)methyl(1-naphthylmethyl)amine Hydrochloride
108. [(2e)-6,6-dimethylhept-2-en-4-yn-1-yl](methyl)[(naphthalen-1-yl)methyl]amine
109. [(e)-6,6-dimethyl-hept-2-en-4-ynyl]-methyl-(naphthalen-1-yl-methyl)-amine
110. 1-naphthalenemethanamine, N-[(2e)-6,6-dimethyl-2-hepten-4-yn-1-yl]-n-methyl-
| Molecular Weight | 291.4 g/mol |
|---|---|
| Molecular Formula | C21H25N |
| XLogP3 | 5.6 |
| Hydrogen Bond Donor Count | 0 |
| Hydrogen Bond Acceptor Count | 1 |
| Rotatable Bond Count | 5 |
| Exact Mass | 291.198699802 g/mol |
| Monoisotopic Mass | 291.198699802 g/mol |
| Topological Polar Surface Area | 3.2 Ų |
| Heavy Atom Count | 22 |
| Formal Charge | 0 |
| Complexity | 428 |
| Isotope Atom Count | 0 |
| Defined Atom Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Undefined Atom Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Defined Bond Stereocenter Count | 1 |
| Undefined Bond Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Covalently Bonded Unit Count | 1 |
| 1 of 4 | |
|---|---|
| Drug Name | Lamisil |
| PubMed Health | Terbinafine |
| Drug Classes | Antifungal |
| Drug Label | Lamisil Tablets contain the synthetic allylamine antifungal compound terbinafine hydrochloride.Chemically, terbinafine hydrochloride is (E)-N-(6,6-dimethyl-2-hepten-4-ynyl)-N-methyl-1-naphthalenemethanamine hydrochloride. The empirical formula C21H26... |
| Active Ingredient | Terbinafine hydrochloride |
| Dosage Form | Tablet; Cream; Granule |
| Route | Oral; Topical |
| Strength | eq 187.5mg base/packet; 1%; eq 250mg base; eq 125mg base/packet |
| Market Status | Over the Counter; Prescription |
| Company | Novartis |
| 2 of 4 | |
|---|---|
| Drug Name | Lamisil at |
| Active Ingredient | Terbinafine hydrochloride; Terbinafine |
| Dosage Form | Spray; Gel; Solution |
| Route | Topical |
| Strength | 1% |
| Market Status | Over the Counter |
| Company | Novartis |
| 3 of 4 | |
|---|---|
| Drug Name | Lamisil |
| PubMed Health | Terbinafine |
| Drug Classes | Antifungal |
| Drug Label | Lamisil Tablets contain the synthetic allylamine antifungal compound terbinafine hydrochloride.Chemically, terbinafine hydrochloride is (E)-N-(6,6-dimethyl-2-hepten-4-ynyl)-N-methyl-1-naphthalenemethanamine hydrochloride. The empirical formula C21H26... |
| Active Ingredient | Terbinafine hydrochloride |
| Dosage Form | Tablet; Cream; Granule |
| Route | Oral; Topical |
| Strength | eq 187.5mg base/packet; 1%; eq 250mg base; eq 125mg base/packet |
| Market Status | Over the Counter; Prescription |
| Company | Novartis |
| 4 of 4 | |
|---|---|
| Drug Name | Lamisil at |
| Active Ingredient | Terbinafine hydrochloride; Terbinafine |
| Dosage Form | Spray; Gel; Solution |
| Route | Topical |
| Strength | 1% |
| Market Status | Over the Counter |
| Company | Novartis |
Terbinafine hydrochloride is indicated to treat fungal skin and nail infections caused by _Trichophyton_ species, _Microsporum canis_, _Epidermophyton floccosum_, and _Tinea_ species. Terbinafine hydrochloride also treats yeast infections of the skin caused by _Candida_ species and _Malassezia furfur_.
FDA Label
Terbinafine is an allylamine antifungal that inhibits squalene epoxidase (also known as squalene monooxygenase) to prevent the formation of ergosterol and cause an accumulation of squalene, weakening the cell wall of fungal cells. Terbinafine distributes into tissues and has a long terminal elimination half life, so the duration of action is long. Overdose with terbinafine is rare, even above the therapeutic dose, so the therapeutic index is wide. Patients taking oral terbinafine should have liver function tests performed prior to treatment to reduce the risk of liver injury.
Antifungal Agents
Substances that destroy fungi by suppressing their ability to grow or reproduce. They differ from FUNGICIDES, INDUSTRIAL because they defend against fungi present in human or animal tissues. (See all compounds classified as Antifungal Agents.)
Enzyme Inhibitors
Compounds or agents that combine with an enzyme in such a manner as to prevent the normal substrate-enzyme combination and the catalytic reaction. (See all compounds classified as Enzyme Inhibitors.)
D - Dermatologicals
D01 - Antifungals for dermatological use
D01A - Antifungals for topical use
D01AE - Other antifungals for topical use
D01AE15 - Terbinafine
D - Dermatologicals
D01 - Antifungals for dermatological use
D01B - Antifungals for systemic use
D01BA - Antifungals for systemic use
D01BA02 - Terbinafine
Absorption
Oral terbinafine is >70% absorbed but only 40% bioavailable after first pass metabolism, reaching a Cmax of 1g/mL with a Tmax of 2 hours an an AUC of 4.56g\*h/mL. Over the course of a week, 1% topical terbinafine's Cmax increases from 949-1049ng/cm2 and the AUC increases from 9694-13,492ng/cm2/h.
Route of Elimination
Terbinafine is approximately 80% eliminated in urine, while the remainder is eliminated in feces. The unmetabolized parent drug is not present in urine.
Volume of Distribution
A single 250mg oral dose of terbinafine has a volume of distribution at steady state of 947.5L or 16.6L/kg.
Clearance
A single 250mg oral dose of terbinafine has a clearance of 76L/h or 1.11L/h/kg.
Terbinafine can be deaminated to 1-naphthaldehyde by CYP2C9, 2B6, 2C8, 1A2, 3A4, and 2C19. 1-naphthaldehyde is then oxidized to 1-naphthoic acid or reduced to 1-naphthalenemethanol. Terbinafine can also be hydroxylated by CYP1A2, 2C9, 2C8, 2B6, and 2C19 to hydroxyterbinafine. Hydroxyterbinafine is then oxidized to carboxyterbinafine or N-demethylated by CYP3A4, 2B6, 1A2, 2C9, 2C8, and 2C19 to desmethylhydroxyterbinafine. Terbinafine can be N-demethylated to desmethylterbinafine. Desmethylterbinafine is then dihydroxylated to a desmethyldihydrodiol or hydroxylated to desmethylhydroxyterbinafine. Finally, terbinafine can be dihydroxylated to a dihydrodiol which is then N-demethylated to a desmethyldihydrodiol.
Terbinafine has known human metabolites that include 1-Naphtaldehyde, Hydroxyterbinafine, and N-Desmethylterbinafine.
S73 | METXBIODB | Metabolite Reaction Database from BioTransformer | DOI:10.5281/zenodo.4056560
Oral terbinafine has an effective half life of approximately 36 hours. However, the terminal half life ranges from 200-400 hours as it distributes into skin and adipose tissue. 1% topical terbinafine's half life increases over the first seven days from approximately 10-40 hours.
Terbinafine inhibits the enzyme squalene monooxygenase (also called squalene epoxidase), preventing the conversion of squalene to 2,3-oxydosqualene, a step in the synthesis of ergosterol. This inhibition leads to decreased ergosterol, which would normally be incorporated into the cell wall, and accumulation of squalene. Generation of a large number of squalene containing vesicles in the cytoplasm may leach other lipids away from, and further weaken, the cell wall.