

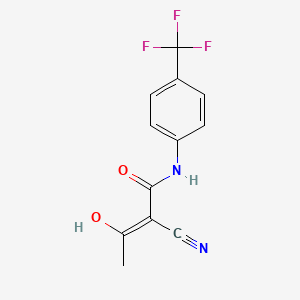

1. (2z)-2-cyano-3-hydroxy-n-(4-(trifluoromethyl)phenyl)-2-butenamide
2. (z)-2-cyano-3-hydroxy-n-(4-(trifluoromethyl)phenyl)-2-butenamide
3. 2-cyano-3-hydroxy-n-(4-(trifluoromethyl)phenyl)-2-butenamide
4. 2-hydroxyethylidene-cyanoacetic Acid-4-trifluoromethyl Anilide
5. A 1726
6. A 771726
7. A-771726
8. A77 1726
9. A771726
10. Aubagio
11. Hmr-1726
12. Hmr1726
13. Rs 61980
1. 163451-81-8
2. 108605-62-5
3. Aubagio
4. Flucyamide
5. A77 1726
6. Hmr1726
7. Hmr-1726
8. (z)-2-cyano-3-hydroxy-n-(4-(trifluoromethyl)phenyl)but-2-enamide
9. Hmr 1726
10. A 771726
11. A-771726
12. Su 20
13. A771726
14. Teriflunomide(random Configuration)
15. (z)-2-cyano-3-hydroxy-n-[4-(trifluoromethyl)phenyl]but-2-enamide
16. A 77-1726
17. Leflunomide Related Compound B
18. (e/z)-teriflunomide
19. Chebi:68540
20. 2-cyano-3-hydroxy-n-(4-(trifluoromethyl)phenyl)-2-butenamide
21. (2z)-2-cyano-3-hydroxy-n-[4-(trifluoromethyl)phenyl]but-2-enamide
22. (z)-2-cyano-alpha,alpha,alpha-trifluoro-3-hydroxy-p-crotonotoluidide
23. 2-butenamide, 2-cyano-3-hydroxy-n-[4-(trifluoromethyl)phenyl]-, (2z)-
24. 1c058ikg3b
25. A77-1726
26. Teriflunomide (usan)
27. Teriflunomide [inn]
28. 2-butenamide, 2-cyano-3-hydroxy-n-(4-(trifluoromethyl)phenyl)-
29. Teriflunomide [usan]
30. 2-cyano-3-oh-n-(4-trifluoromethylphenyl)croton Amide
31. 2-butenamide, 2-cyano-3-hydroxy-n-[4-(trifluoromethyl)phenyl]-
32. (z)-2-cyano-3-hydroxy-n-(4-(trifluoromethyl)phenyl)but-2-enamide.
33. Mfcd00910058
34. Rs 61980
35. Teriflunomide [usan:inn]
36. Teriflunomida
37. Teriflunomidum
38. Unii-1c058ikg3b
39. 2-cyano-3-hydroxy-n-[4-(trifluoromethyl)phenyl]-2-butenamide
40. Malononitrilamide
41. N-(4-trifluoromethylphenyl)-2-cyano-2-hydroxycrotonamide
42. 2-hydroxyethylidene-cyanoacetic Acid-4-trifluoromethyl Anilide
43. 2-butenamide, 2-cyano-3-hydroxy-n-(4-(trifluoromethyl)phenyl)-, (2z)-
44. A 1726
45. A26
46. Aubagio (tn)
47. Su-0020
48. Leflunomide Impurity B
49. Rs-61980
50. Leflunomide Ep Impurity B
51. Teriflunomide [mi]
52. (2z)-2-[hydroxy-[4-(trifluoromethyl)anilino]methylidene]-3-oxobutanenitrile
53. Dimethyl Aprobarbital
54. Schembl22661
55. Teriflunomide [vandf]
56. Teriflunomide(a-771726)
57. Teriflunomide, A77 1726
58. Teriflunomide [who-dd]
59. Gtpl6844
60. Dtxsid80893457
61. Leflunomide Related Compound B Rs
62. A77 1726 (e/z) Mixture
63. Teriflunomide [orange Book]
64. Teriflunomide [ep Monograph]
65. Bdbm50018011
66. Nsc766118
67. S4169
68. Zinc13512456
69. Akos015994773
70. Ccg-267145
71. Db08880
72. Le-0275
73. Nsc-766118
74. Ncgc00263218-07
75. Ncgc00263218-13
76. Ac-26446
77. Hy-110159
78. Cs-0033021
79. Leflunomide Impurity B [ep Impurity]
80. Sw219377-1
81. T3287
82. Leflunomide-d4 Metabolite (teriflunomide-d4)
83. D10172
84. Leflunomide Related Compound B [usp-rs]
85. Ab01565775_02
86. A801897
87. A882574
88. J-010046
89. Q3077133
90. Leflunomide Related Compound B [usp Impurity]
91. N-(4-trifluoromethylphenyl)-2-cyano-3-hydroxycrotonamide
92. N-[4-(trifluoromethyl)phenyl]-2-cyano-3-hydroxycrotonamide
93. 2-cyano-3-hydroxy-n-[4-(trifluoromethyl)phenyl]-2z-butenamide
94. (z)-2-cyano-3-hydroxy-n-[4-(trifluoromethyl)phenyl]-2-butenamide
95. 163451-81-8 (z Isomer) , 108605-62-5 (e/z Mixture)
96. 2-butenamide, 2-cyano-3-hydroxy-n-(4-(trifluoromethyl)phenyl)-, (z)-
97. A 77-1726;a771726;hmr1726;cas# 108605-62-5
98. (2z)-2-cyano-3-hydroxy-n-[4-(trifluoromethyl)phenyl]but-2-enamide (teriflunomide)
99. 2-cyano-3-hydroxy-n-(4-(trifluoromethyl)phenyl)but-2-enamide (e/z)-mixture
100. Leflunomide Related Compound B, United States Pharmacopeia (usp) Reference Standard
101. A 1726, A77-1726, A771726, Flucyamide, Hmr 1726, N-(4-trifluoromethylphenyl)-2-cyano-3-hydroxycrotoamide, Su 20
102. Teriflunomide; Leflunomide Usp Rc B; Cyano Keto Leflunomide Impurity; N-(4-trifluoromethylphenyl)-2-cyano-3-hydroxycrotonamide; 2-cyano-3-hydroxy-n-[4-(trifluoromethyl)phenyl]-2-beuteamide
| Molecular Weight | 270.21 g/mol |
|---|---|
| Molecular Formula | C12H9F3N2O2 |
| XLogP3 | 3.3 |
| Hydrogen Bond Donor Count | 2 |
| Hydrogen Bond Acceptor Count | 6 |
| Rotatable Bond Count | 2 |
| Exact Mass | 270.06161202 g/mol |
| Monoisotopic Mass | 270.06161202 g/mol |
| Topological Polar Surface Area | 73.1 Ų |
| Heavy Atom Count | 19 |
| Formal Charge | 0 |
| Complexity | 426 |
| Isotope Atom Count | 0 |
| Defined Atom Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Undefined Atom Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Defined Bond Stereocenter Count | 1 |
| Undefined Bond Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Covalently Bonded Unit Count | 1 |
| 1 of 2 | |
|---|---|
| Drug Name | Aubagio |
| PubMed Health | Teriflunomide (By mouth) |
| Drug Classes | Central Nervous System Agent, Immune Modulator |
| Active Ingredient | Teriflunomide |
| Dosage Form | Tablet |
| Route | Oral |
| Strength | 14mg; 7mg |
| Market Status | Prescription |
| Company | Sanofi Aventis Us |
| 2 of 2 | |
|---|---|
| Drug Name | Aubagio |
| PubMed Health | Teriflunomide (By mouth) |
| Drug Classes | Central Nervous System Agent, Immune Modulator |
| Active Ingredient | Teriflunomide |
| Dosage Form | Tablet |
| Route | Oral |
| Strength | 14mg; 7mg |
| Market Status | Prescription |
| Company | Sanofi Aventis Us |
Used in the treatment of relapsing forms of multiple sclerosis (MS).
FDA Label
AUBAGIO is indicated for the treatment of adult patients and paediatric patients aged 10 years and older with relapsing remitting multiple sclerosis (MS) (please refer to section 5. 1 for important information on the population for which efficacy has been established).
Teriflunomide is an immunomodulatory agent that decreases the amount of activated CNS lymphocytes, which results in anti-inflammatory and antiproliferative effects.
Anti-Inflammatory Agents, Non-Steroidal
Anti-inflammatory agents that are non-steroidal in nature. In addition to anti-inflammatory actions, they have analgesic, antipyretic, and platelet-inhibitory actions. They act by blocking the synthesis of prostaglandins by inhibiting cyclooxygenase, which converts arachidonic acid to cyclic endoperoxides, precursors of prostaglandins. Inhibition of prostaglandin synthesis accounts for their analgesic, antipyretic, and platelet-inhibitory actions; other mechanisms may contribute to their anti-inflammatory effects. (See all compounds classified as Anti-Inflammatory Agents, Non-Steroidal.)
Immunosuppressive Agents
Agents that suppress immune function by one of several mechanisms of action. Classical cytotoxic immunosuppressants act by inhibiting DNA synthesis. Others may act through activation of T-CELLS or by inhibiting the activation of HELPER CELLS. While immunosuppression has been brought about in the past primarily to prevent rejection of transplanted organs, new applications involving mediation of the effects of INTERLEUKINS and other CYTOKINES are emerging. (See all compounds classified as Immunosuppressive Agents.)
L04AA31
L04AA31
S76 | LUXPHARMA | Pharmaceuticals Marketed in Luxembourg | Pharmaceuticals marketed in Luxembourg, as published by d'Gesondheetskeess (CNS, la caisse nationale de sante, www.cns.lu), mapped by name to structures using CompTox by R. Singh et al. (in prep.). List downloaded from https://cns.public.lu/en/legislations/textes-coordonnes/liste-med-comm.html. Dataset DOI:10.5281/zenodo.4587355
L - Antineoplastic and immunomodulating agents
L04 - Immunosuppressants
L04A - Immunosuppressants
L04AA - Selective immunosuppressants
L04AA31 - Teriflunomide
Absorption
After oral administration of teriflunomide, maximum plasma concentrations are reached, on average, in 1-4 hours.
Route of Elimination
Teriflunomide is eliminated unchanged and mainly through bile. Specifically 37.5% is eliminated in the feces and 22.6% in urine.
Volume of Distribution
After a single intravenous dose, the volume of distribution is 11 L.
Clearance
After a single IV dose, teriflunomide has a total body clearance of 30.5 mL/h.
Teriflunomide mainly undergoes hydrolyis to minor metabolites. Other minor metabolic pathways include oxidation, N-acetylation and sulfate conjugation. Teriflunomide is not metabolized by CYP450 or flavin monoamine oxidase.
The median half-life is 18 to 19 days.
The exact mechanism by which teriflunomide acts in MS is not known. What is known is that teriflunomide prevents pyrimidine synthesis by inhibiting the mitochondrial enzyme dihydroorotate dehydrogenase, and this may be involved in its immunomodulatory effect in MS.