


1. Amethocaine
2. Ametop
3. Dicaine
4. Hydrochloride, Tetrracaine
5. Pantocaine
6. Pontocaine
7. Tetracaine Monohydrochloride
8. Tetrakain
9. Tetrracaine Hydrochloride
1. 94-24-6
2. Amethocaine
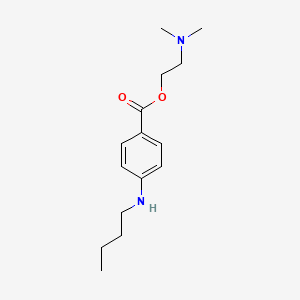
3. 2-(dimethylamino)ethyl 4-(butylamino)benzoate
4. Pontocaine
5. Dicaine
6. Laudocaine
7. Metraspray
8. Tetrakain
9. Anetain
10. Contralgin
11. Meethobalm
12. Mucaesthin
13. Tetracaina
14. Tetracainum
15. Uromucaesthin
16. Fissucain
17. Intercain
18. Medicaine
19. Niphanoid
20. Rexocaine
21. Dicain
22. Dikain
23. Medihaler-tetracaine
24. 2-(dimethylamino)ethyl P-(butylamino)benzoate
25. P-butylaminobenzoyl-2-dimethylaminoethanol
26. Benzoic Acid, 4-(butylamino)-, 2-(dimethylamino)ethyl Ester
27. Diaethylaminoaethanol Ester Der P-butylaminobenzoesaeure
28. 4-(butylamino)benzoic Acid 2-(dimethylamino)ethyl Ester
29. Dimethylaminoethyl P-butyl-aminobenzoate
30. Chebi:9468
31. P-(butylamino)benzoic Acid, 2-(dimethylamino)ethyl Ester
32. Mfcd00053787
33. Chembl698
34. Benzoic Acid, P-(butylamino)-, 2-(dimethylamino)ethyl Ester
35. 2-dimethylaminoethylester Kyseliny P-butylaminobenzoove
36. Tetracaine Base
37. 0619f35cgv
38. Butylocaine
39. Tetrakain [czech]
40. Tetracainum [inn-latin]
41. Tetracaina [inn-spanish]
42. P-(butylamino)benzoic Acid Beta-(dimethylamino)ethyl Ester
43. Amethocaine (tn)
44. Tetracaine (usp/inn)
45. Ncgc00016049-02
46. Cas-136-47-0
47. Einecs 202-316-6
48. Brn 2216051
49. Landocaine
50. Tetracaine [usp:inn:ban]
51. Unii-0619f35cgv
52. Amethocaine Hcl
53. 2-dimethylaminoethylester Kyseliny P-butylaminobenzoove [czech]
54. Diaethylaminoaethanol Ester Der P-butylaminobenzoesaeure [german]
55. Te4
56. Spectrum_001032
57. Pantocaine (salt/mix)
58. Tetracaine [inn]
59. 100311-22-6
60. Prestwick0_000571
61. Prestwick1_000571
62. Prestwick2_000571
63. Prestwick3_000571
64. Spectrum2_001328
65. Spectrum3_000562
66. Spectrum4_000351
67. Spectrum5_001072
68. Lopac-t-7508
69. Tetracaine [vandf]
70. Epitope Id:174843
71. Tetracaine [mart.]
72. Tetracaine [usp-rs]
73. Tetracaine [who-dd]
74. Lopac0_001211
75. Schembl34714
76. Bspbio_000382
77. Bspbio_001944
78. Kbiogr_000781
79. Kbioss_001512
80. 4-14-00-01172 (beilstein Handbook Reference)
81. Divk1c_000607
82. Spbio_001455
83. Spbio_002601
84. Bpbio1_000422
85. Tetracaine [green Book]
86. Tetracaine, >=98% (tlc)
87. Dtxsid1043883
88. Tetracaine [orange Book]
89. Kbio1_000607
90. Kbio2_001512
91. Kbio2_004080
92. Kbio2_006648
93. Kbio3_001444
94. Tetracaine [ep Monograph]
95. Ninds_000607
96. Synera Component Tetracaine
97. Bcpp000048
98. Tetracaine [usp Monograph]
99. Act04765
100. Albb-025902
101. Bcp04777
102. Hy-a0079
103. Zinc1530811
104. Bdbm50017659
105. Stl483844
106. Tetracaine Component Of Synera
107. Akos015889234
108. Ac-3480
109. Ccg-205285
110. Db09085
111. Sdccgsbi-0051178.p005
112. Idi1_000607
113. Ncgc00016049-01
114. Ncgc00016049-03
115. Ncgc00016049-04
116. Ncgc00016049-14
117. Ncgc00162367-01
118. As-81743
119. Sy066710
120. Bcp0726000001
121. Sbi-0051178.p004
122. Ab00053549
123. Ft-0656378
124. T2789
125. Tetracaine, Meets Usp Testing Specifications
126. .beta.-dimethylaminoethyl P-butylaminobenzoate
127. 2-(dimethylamino)ethyl4-(n-butylamino)benzoate
128. C07526
129. D00551
130. 2-(dimethylamino)ethyl 4-(butylamino)benzoate #
131. Ab00053549-11
132. Ab00053549_12
133. Ab00053549_13
134. Q419608
135. Q-201805
136. Brd-k45071273-003-05-8
137. Brd-k45071273-003-15-7
138. Tetracaine, United States Pharmacopeia (usp) Reference Standard
139. Benzoic Acid, 4-(butylamino)-, 2-(dimethylamino)ethyl Ester ,hydrochloride
140. Benzoic Acid,4-butylamino,2-dimethylaminoethyl Ester Pantocain Base
| Molecular Weight | 264.36 g/mol |
|---|---|
| Molecular Formula | C15H24N2O2 |
| XLogP3 | 3.7 |
| Hydrogen Bond Donor Count | 1 |
| Hydrogen Bond Acceptor Count | 4 |
| Rotatable Bond Count | 9 |
| Exact Mass | 264.183778013 g/mol |
| Monoisotopic Mass | 264.183778013 g/mol |
| Topological Polar Surface Area | 41.6 Ų |
| Heavy Atom Count | 19 |
| Formal Charge | 0 |
| Complexity | 249 |
| Isotope Atom Count | 0 |
| Defined Atom Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Undefined Atom Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Defined Bond Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Undefined Bond Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Covalently Bonded Unit Count | 1 |
Ophthalmic tetracaine is indicated for the for procedures requiring a rapid and short- acting topical ophthalmic anesthetic. The combination lidocaine and tetracaine patch is indicated for local dermal analgesia for superficial dermatological procedures and superficial venous access. The combination lidocaine and tetracaine cream is intended to provide topical local analgesia for superficial dermatological procedures.
FDA Label
Anesthetics, Local
Drugs that block nerve conduction when applied locally to nerve tissue in appropriate concentrations. They act on any part of the nervous system and on every type of nerve fiber. In contact with a nerve trunk, these anesthetics can cause both sensory and motor paralysis in the innervated area. Their action is completely reversible. (From Gilman AG, et. al., Goodman and Gilman's The Pharmacological Basis of Therapeutics, 8th ed) Nearly all local anesthetics act by reducing the tendency of voltage-dependent sodium channels to activate. (See all compounds classified as Anesthetics, Local.)
S01HA03
S76 | LUXPHARMA | Pharmaceuticals Marketed in Luxembourg | Pharmaceuticals marketed in Luxembourg, as published by d'Gesondheetskeess (CNS, la caisse nationale de sante, www.cns.lu), mapped by name to structures using CompTox by R. Singh et al. (in prep.). List downloaded from https://cns.public.lu/en/legislations/textes-coordonnes/liste-med-comm.html. Dataset DOI:10.5281/zenodo.4587355
C - Cardiovascular system
C05 - Vasoprotectives
C05A - Agents for treatment of hemorrhoids and anal fissures for topical use
C05AD - Local anesthetics
C05AD02 - Tetracaine
D - Dermatologicals
D04 - Antipruritics, incl. antihistamines, anesthetics, etc.
D04A - Antipruritics, incl. antihistamines, anesthetics, etc.
D04AB - Anesthetics for topical use
D04AB06 - Tetracaine
N - Nervous system
N01 - Anesthetics
N01B - Anesthetics, local
N01BA - Esters of aminobenzoic acid
N01BA03 - Tetracaine
S - Sensory organs
S01 - Ophthalmologicals
S01H - Local anesthetics
S01HA - Local anesthetics
S01HA03 - Tetracaine
Absorption
Systemic absorption of anaesthetic from the combination cream is directly related to the duration and surface area of application. Although peak plasma concentrations for lidocaine were measured, plasma levels for tetracaine could not be determined due to low levels (<0.9 ng/mL)
Volume of Distribution
Tetracaine is rapidly hydrolyzed in the plasma; therefore, volume of distribution could not be determined.
Clearance
Tetracaine is hydrolyzed rapidly in the plasma; therefore, clearance has not been determined.
Tetracaine is rapidly hydrolyzed by plasma esterases to the following primary metabolites: para-aminobenzoic acid and diethylaminoethanol. The activity of both metabolites is unspecified.
Tetracaine is hydrolyzed rapidly in the plasma; therefore, half-life has not been determined.
Tetracaine is an ester-type anesthetic and produces local anesthesia by blocking the sodium ion channels involved in initiation and conduction of neuronal impulses.
