

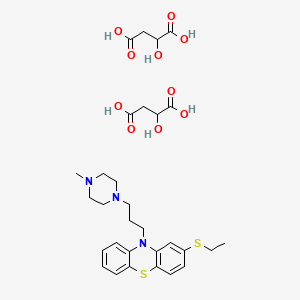

1. Norzine
2. Thiethylperazine
3. Thiethylperazine Maleate (2:1)
4. Torecan
1. Thiethylperazine Dimalate
2. 52239-63-1
3. Torecan
4. Thietylperazine Malate
5. Hp46xk89xb
6. 2-(ethylthio)-10-(3-(4-methyl-1-piperazinyl)propyl)phenothiazine Malate (1:2)
7. 2-ethylsulfanyl-10-[3-(4-methylpiperazin-1-yl)propyl]phenothiazine;2-hydroxybutanedioic Acid
8. Thiethylperazine Malate (jan)
9. Norzine Ampuls
10. Thiethylperazine Malate [jan]
11. 10h-phenothiazine, 2-(ethylthio)-10-(3-(4-methyl-1-piperazinyl)propyl)-, 2-hydroxy-1,4-butanedioate (1:2)
12. Malic Acid, Compound With 2-(ethylthio)-10-[3-(4-methylpiperazin-1-yl)propyl]-10h-phenothiazine (2:1)
13. Ncgc00017115-01
14. Cas-52239-63-1
15. Unii-hp46xk89xb
16. Thiethylperazine Malate [usp]
17. Malic Acid, Compound With 2-(ethylthio)-10-(3-(4-methylpiperazin-1-yl)propyl)-10h-phenothiazine (2:1)
18. Einecs 257-780-2
19. Torecan (tn)
20. Dsstox_cid_25586
21. Dsstox_rid_80982
22. Dsstox_gsid_45586
23. Schembl466913
24. Chembl2359670
25. Dtxsid1045586
26. Hms1571e18
27. Hms2098e18
28. Hms3715e18
29. Tox21_110784
30. Thiethylperazine Dimalate [mi]
31. Ccg-221068
32. Thiethylperazine Malate [mart.]
33. Thiethylperazine Malate [orange Book]
34. D02610
35. Sr-01000841243
36. Sr-01000841243-2
37. Q27280042
38. 2-(ethylthio)-10-[3-(4-methyl-1-piperazinyl)propyl]-10h-phenothiazine Hydroxybutanedioate (1:2)
39. Butanedioic Acid, Hydroxy-, Compd. With 2-(ethylthio)-10-(3-(4-methyl-1-piperazinyl)propyl)-10h-phenothiazine (2:1)
40. Hydroxybutanedioic Acid Compd. With 2-(ethylthio)-10-[3-(4-methyl-1-piperazinyl)propyl]-10h-phenothiazine (2:1)
| Molecular Weight | 667.8 g/mol |
|---|---|
| Molecular Formula | C30H41N3O10S2 |
| Hydrogen Bond Donor Count | 6 |
| Hydrogen Bond Acceptor Count | 15 |
| Rotatable Bond Count | 12 |
| Exact Mass | 667.22333686 g/mol |
| Monoisotopic Mass | 667.22333686 g/mol |
| Topological Polar Surface Area | 250 Ų |
| Heavy Atom Count | 45 |
| Formal Charge | 0 |
| Complexity | 584 |
| Isotope Atom Count | 0 |
| Defined Atom Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Undefined Atom Stereocenter Count | 2 |
| Defined Bond Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Undefined Bond Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Covalently Bonded Unit Count | 3 |
Antiemetics
Drugs used to prevent NAUSEA or VOMITING. (See all compounds classified as Antiemetics.)
Dopamine Antagonists
Drugs that bind to but do not activate DOPAMINE RECEPTORS, thereby blocking the actions of dopamine or exogenous agonists. Many drugs used in the treatment of psychotic disorders (ANTIPSYCHOTIC AGENTS) are dopamine antagonists, although their therapeutic effects may be due to long-term adjustments of the brain rather than to the acute effects of blocking dopamine receptors. Dopamine antagonists have been used for several other clinical purposes including as ANTIEMETICS, in the treatment of Tourette syndrome, and for hiccup. Dopamine receptor blockade is associated with NEUROLEPTIC MALIGNANT SYNDROME. (See all compounds classified as Dopamine Antagonists.)