
1. Bacteriostat
2. Disulfide, Tetramethylthiuram
3. Disulfide, Tmt
4. Nobecutan
5. Sadoplon 75
6. Tetramethylthiuram Disulfide
7. Thiuram
8. Thiuram D
9. Tmt Disulfide
10. Tmtd
1. Tetramethylthiuram Disulfide
2. 137-26-8
3. Thiuram
4. Rezifilm
5. Tmtd
6. Pomarsol
7. Thirame
8. Arasan
9. Fernasan
10. Nobecutan
11. Thioscabin
12. Thirasan
13. Aapirol
14. Tersan
15. Tetrathiuram Disulfide
16. Tetramethylthiuram
17. Falitiram
18. Formalsol
19. Hexathir
20. Kregasan
21. Mercuram
22. Normersan
23. Sadoplon
24. Spotrete
25. Tetrasipton
26. Thillate
27. Thiramad
28. Aatiram
29. Atiram
30. Fermide
31. Fernide
32. Hermal
33. Pomasol
34. Puralin
35. Thiosan
36. Thiotox
37. Thiulin
38. Thiulix
39. Heryl
40. Pomarsol Forte
41. Methyl Tuads
42. Polyram Ultra
43. Accelerator T
44. Methyl Thiram
45. Fernasan A
46. Tetramethylthiuram Disulphide
47. Nocceler Tt
48. Arasan-m
49. Bis(dimethylthiocarbamoyl) Disulfide
50. Thiram B
51. Arasan-sf
52. Cyuram Ds
53. Ekagom Tb
54. Hermat Tmt
55. Tetramethylenethiuram Disulfide
56. Accel Tmt
57. Accelerator Thiuram
58. Aceto Tetd
59. Radothiram
60. Royal Tmtd
61. Tetramethyl-thiram Disulfid
62. Fernacol
63. Sadoplon 75
64. Tetramethylthiuram Bisulfide
65. Tetrapom
66. Thioknock
67. Thirampa
68. Thiramum
69. Anles
70. Arasan-sf-x
71. Aules
72. Thimer
73. Panoram 75
74. Tetramethylthiouram Disulfide
75. Tetramethylthiurane Disulfide
76. Arasan 70
77. Arasan 75
78. Tersan 75
79. Thiram 75
80. Thiram 80
81. Spotrete-f
82. Tmtds
83. Arasan 70-s Red
84. Tetramethylthioperoxydicarbonic Diamide
85. Methylthiuram Disulfide
86. N,n-tetramethylthiuram Disulfide
87. Metiurac
88. Micropearls
89. Nomersan
90. Thianosan
91. Cunitex
92. Delsan
93. Thimar
94. Teramethylthiuram Disulfide
95. Tersantetramethyldiurane Sulfide
96. Pol-thiuram
97. Arasan 42-s
98. Tetramethylthiurum Disulfide
99. Disulfure De Tetramethylthiourame
100. Tetrathiuram Disulphide
101. Sranan-sf-x
102. Hy-vic
103. Sq 1489
104. Chipco Thiram 75
105. Bis(dimethyl-thiocarbamoyl)-disulfid
106. Orac Tmtd
107. Tetramethylthioramdisulfide
108. Tetramethyldiurane Sulphite
109. Thiotox (fungicide)
110. Disulfide, Bis(dimethylthiocarbamoyl)
111. Bis((dimethylamino)carbonothioyl) Disulfide
112. Fermide 850
113. Tetramethyl Thiuramdisulfide
114. Tetramethylthiocarbamoyldisulphide
115. Thiuramyl
116. Thylate
117. Methyl Thiuramdisulfide
118. Bis(dimethylthiocarbamyl) Disulfide
119. Tetramethyl Thiurane Disulfide
120. Bis(dimethyl Thiocarbamoyl)disulfide
121. Thirame [inn-french]
122. Thiramum [inn-latin]
123. Thiuram D
124. Disolfuro Di Tetrametiltiourame
125. Tetramethyl Thiurane Disulphide
126. Tetramethylenethiuram Disulphide
127. N,n'-(dithiodicarbonothioyl)bis(n-methylmethanamine)
128. Rcra Waste Number U244
129. Flo Pro T Seed Protectant
130. Tetramethylthiuram Bisulphide
131. Tetramethylthiuran Disulphide
132. Tetramethylthiurum Disulphide
133. Nsc-1771
134. Tetramethyl Thiuram Disulfide
135. Alpha,alpha'-dithiobis(dimethylthio)formamide
136. Thiotex
137. Thiurad
138. Tirampa
139. Tiuramyl
140. Trametan
141. Tridipam
142. Tripomol
143. Tyradin
144. Tuads
145. Tutan
146. Vulkacit Mtic
147. N,n,n',n'-tetramethylthiuram Disulfide
148. N,n-tetramethylthiuram Disulphide
149. Vulkacit Thiuram
150. Thioperoxydicarbonic Diamide, Tetramethyl-
151. Thiuram M
152. Vulkacit Th
153. Tetramethylthioramdisulfide [dutch]
154. Vulcafor Tmt
155. Vulcafor Tmtd
156. Bis((dimethylamino)carbonothioyl) Disulphide
157. Fmc 2070
158. Bis(dimethylthiocarbamoyl) Disulphide
159. Tetramethyl-thiram Disulfid [german]
160. Formamide, 1,1'-dithiobis(n,n-dimethylthio-
161. Dimethylcarbamothioylsulfanyl N,n-dimethylcarbamodithioate
162. Zaprawa Nasienna T
163. [me2nc(s)s]2
164. Vancida Tm-95
165. Disulfuro Di Tetrametiltiourame
166. Arasan 42s
167. Tuex
168. Disolfuro Di Tetrametiltiourame [italian]
169. Disulfuro Di Tetrametiltiourame [italian]
170. Disulfure De Tetramethylthiourame [french]
171. Nsc1771
172. Bis(dimethyl-thiocarbamoyl)-disulfid [german]
173. Vuagt-i-4
174. Nsc-49512
175. Thioperoxydicarbonic Diamide ([(h2n)c(s)]2s2), Tetramethyl-
176. Nsc-622696
177. [disulfanediylbis(carbonothioylnitrilo)]tetramethane
178. Thiuram M Rubber Accelerator
179. Mls000069752
180. Mls002702972
181. 0d771is0fh
182. Chebi:9495
183. Thiuram Disulfide, Tetramethyl-
184. Dtxsid5021332
185. Thiuram-m
186. Thioperoxydicarbonic Diamide (((h2n)c(s))2s2), Tetramethyl-
187. Nsc49512
188. Ccg-35460
189. Nsc-59637
190. Nsc622696
191. Tntd
192. Sq-1489
193. Ncgc00091563-01
194. Smr000059023
195. Thioperoxydicarbonic Diamide ((h2n)c(s))2s2, Tetramethyl-
196. [dithiobis(carbonothioylnitrilo)]tetramethane
197. Dsstox_cid_1332
198. Dsstox_rid_76087
199. .alpha.,.alpha.'-dithiobis(dimethylthio)formamide
200. Dsstox_gsid_21332
201. Caswell No. 856
202. Granuflo
203. Thiuramin
204. N,n',n'-tetramethylthiuram Disulfide
205. Thioperoxydicarbonic Diamide (((h2n)c(s))2s2), N,n,n',n'-tetramethyl-
206. Cas-137-26-8
207. Formamide,1'-dithiobis(n,n-dimethylthio-
208. Bis[(dimethylamino)carbonothioyl] Disulfide
209. Attack [antifungal]
210. Thiram [iso]
211. Nsc59637
212. Ccris 1282
213. Hsdb 863
214. Ent 987
215. Wln: 1n1 & Yus & Ssyus & N1 & 1
216. Nsc 1771
217. Einecs 205-286-2
218. Nsc 49512
219. Nsc 59637
220. Rcra Waste No. U244
221. Epa Pesticide Chemical Code 079801
222. Nsc 622696
223. Brn 1725821
224. Tiramo
225. Unii-0d771is0fh
226. Basultra
227. Betoxin
228. Tiradin
229. Accelerant T
230. Ai3-00987
231. Arasan M
232. Vulkazam S
233. Thioperoxydicarbonic Diamide ([(h2n)c(s)]2s2), N,n,n',n'-tetramethyl-
234. Vanguard Gf
235. Vancide Tm
236. Akrochem Tmtd
237. Perkacit Tmtd
238. Vulkacit Dtmt
239. Robac Tmt
240. Thiram (tmtd)
241. Rezifilm (tn)
242. Arasan 50 Red
243. Spotrete Wp 75
244. Mfcd00008325
245. Vancide Tm-95
246. Naftocit Thiuram 16
247. Spectrum_001687
248. Thiram (usan/inn)
249. Agrichem Flowable Thiram
250. Thiram [hsdb]
251. Thiram [iarc]
252. Thiram [inci]
253. Thiram [usan]
254. Thiram [inn]
255. Spectrum2_001554
256. Spectrum3_001592
257. Spectrum4_000860
258. Spectrum5_001653
259. Thiram [who-dd]
260. Thiram [mi]
261. Thiram [mart.]
262. Bmse000928
263. Ec 205-286-2
264. Ncimech_000272
265. Cid_5455
266. Nciopen2_007854
267. Schembl21144
268. Bspbio_003184
269. Kbiogr_001499
270. Kbioss_002167
271. 4-04-00-00242 (beilstein Handbook Reference)
272. Bidd:er0359
273. Divk1c_000741
274. Spectrum1503322
275. Spbio_001428
276. Chembl120563
277. Thiram [usan:inn:bsi:iso]
278. Bdbm43362
279. Hms502f03
280. Kbio1_000741
281. Kbio2_002167
282. Kbio2_004735
283. Kbio2_007303
284. Kbio3_002684
285. Kuazqdvkqlnfpe-uhfffaoysa-
286. Ent-987
287. Ninds_000741
288. Hms1922a12
289. Hms2093e03
290. Hms2234b08
291. Hms3374c05
292. Pharmakon1600-01503322
293. Tetramethylthiuram Disulfide, 97%
294. Thiram 100 Microg/ml In Ethanol
295. Zinc1532176
296. Tox21_111150
297. Tox21_201569
298. Tox21_301102
299. Nsc758454
300. S2431
301. Stl264104
302. (dimethylamino){[(dimethylamino)thioxomethyl]disulfanyl}methane-1-thione
303. Akos000120200
304. Bis (dimethyl Thiocarbamoyl) Disulfide
305. Bis(dimethylaminothiocarbonyl)disulfide
306. Tox21_111150_1
307. Bis(dimethylaminothiocarbonyl) Disulfide
308. Db13245
309. Ks-5354
310. Nsc-758454
311. Idi1_000741
312. Qtl1_000082
313. Ncgc00091563-02
314. Ncgc00091563-03
315. Ncgc00091563-04
316. Ncgc00091563-05
317. Ncgc00091563-06
318. Ncgc00091563-07
319. Ncgc00091563-08
320. Ncgc00091563-09
321. Ncgc00091563-10
322. Ncgc00091563-12
323. Ncgc00255002-01
324. Ncgc00259118-01
325. Nci60_001477
326. Nci60_006736
327. Sbi-0051813.p002
328. Thiram, Pestanal(r), Analytical Standard
329. Db-042384
330. B0486
331. Cs-0012858
332. Ft-0631799
333. 37t268
334. D06114
335. D97716
336. Ab00052345_10
337. Q416572
338. Sr-01000736911
339. J-006992
340. J-524968
341. Sr-01000736911-2
342. Thiram, Certified Reference Material, Tracecert(r)
343. Brd-k29254801-001-06-3
344. F0001-0468
345. Tetramethylthioperoxydicarbonic Acid [(h2n)c(s)]2s2
346. N,n-dimethyl[(dimethylcarbamothioyl)-disulfanyl]carbothioamide
347. N,n-dimethyl[(dimethylcarbamothioyl)disulfanyl]carbothioamide
348. 1-(dimethylthiocarbamoyldisulfanyl)-n,n-dimethyl-methanethioamide
349. N,n-dimethylcarbamodithioic Acid (dimethylthiocarbamoylthio) Ester
350. N(1),n(1),n(3),n(3)-tetramethyl-2-dithioperoxy-1,3-dithiodicarbonic Diamide
351. N,n-dimethylcarbamodithioic Acid [[dimethylamino(sulfanylidene)methyl]thio] Ester
352. Tetramethylthioperoxydicarbonic Diamide ((((ch(sub 3))(sub 2)n)c(s))(sub 2)s(sub 2))
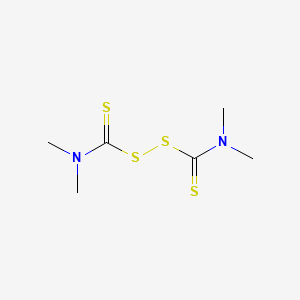
| Molecular Weight | 240.4 g/mol |
|---|---|
| Molecular Formula | C6H12N2S4 |
| XLogP3 | 1.7 |
| Hydrogen Bond Donor Count | 0 |
| Hydrogen Bond Acceptor Count | 4 |
| Rotatable Bond Count | 3 |
| Exact Mass | 239.98833309 g/mol |
| Monoisotopic Mass | 239.98833309 g/mol |
| Topological Polar Surface Area | 121 Ų |
| Heavy Atom Count | 12 |
| Formal Charge | 0 |
| Complexity | 158 |
| Isotope Atom Count | 0 |
| Defined Atom Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Undefined Atom Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Defined Bond Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Undefined Bond Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Covalently Bonded Unit Count | 1 |
Anti-Infective Agents, Local; Antifungal Agents; Carcinogens; Enzyme Inhibitors; Fungicides, Industrial; Mutagens
National Library of Medicine's Medical Subject Headings online file (MeSH, 1999)
Has wide spectrum of antibacterial activity ... also effective against several dermatophytes. Serum does not appear to suppress its activity. ... marketed only as component of plastic film that is sprayed onto dry surgical wounds for purpose of preventing post operative infections. ... film containing 0.5% thiram.
Osol, A. and J.E. Hoover, et al. (eds.). Remington's Pharmaceutical Sciences. 15th ed. Easton, Pennsylvania: Mack Publishing Co., 1975., p. 1104
Antifungal (topical)
Budavari, S. (ed.). The Merck Index - Encyclopedia of Chemicals, Drugs and Biologicals. Rahway, NJ: Merck and Co., Inc., 1989., p. 1476
Used in antiseptic sprays.
Association of American Railroads. Emergency Handling of Hazardous Materials in Surface Transportation. Washington, DC: Association of American Railroads, Bureau of Explosives, 1994., p. 1051
Mutagens
Chemical agents that increase the rate of genetic mutation by interfering with the function of nucleic acids. A clastogen is a specific mutagen that causes breaks in chromosomes. (See all compounds classified as Mutagens.)
Fungicides, Industrial
Chemicals that kill or inhibit the growth of fungi in agricultural applications, on wood, plastics, or other materials, in swimming pools, etc. (See all compounds classified as Fungicides, Industrial.)
P - Antiparasitic products, insecticides and repellents
P03 - Ectoparasiticides, incl. scabicides, insecticides and repellents
P03A - Ectoparasiticides, incl. scabicides
P03AA - Sulfur containing products
P03AA05 - Thiram
Tetramethylthiuramdisulfide appears to be readily absorbed through the intestinal tract and the lungs and is quickly and widely distributed throughout the body.
O'Donoghue, J.L. (ed.). Neurotoxicity of Industrial and Commercial Chemicals. Volume II. Boca Raton, FL: CRC Press, Inc., 1985., p. 48
In 2 days following its ingestion, bis(dimethylthiocarbamoyl) disulfide (TMTD) is found in the liver and spleen together with its metabolites: amine salt dimethyldithiocarbamic acid (DDCA) and tetramethylthiourea, and in the lungs, carbon disulfide and the amine salt of DDCA. TMTD is known to form N-nitrosodimethylamine by reaction with nitrite in mildly acid solution. TMTD and the amine salt of DDCA are excreted from the body in the urine and feces, and as carbon disulfide via the lungs.
Sheftel, V.O.; Indirect Food Additives and Polymers. Migration and Toxicology. Lewis Publishers, Boca Raton, FL. 2000., p. 551
After absorption (respiratory, dermal, gastrointestinal), thiram is distributed in all organs and is mainly excreted unchanged in urine and feces. Some metabolism exists; carbon dioxide is exhaled and dithiocarbamate is excreted in urine.
American Conference of Governmental Industrial Hygienists. Documentation of Threshold Limit Values for Chemical Substances and Physical Agents and Biological Exposure Indices for 2001. Cincinnati, OH. 2001., p. 3
In studies with ruminant animals fed corn treated with thiram, rumen microorganisms degraded thiram to carbon disulfide and probably hydrogen sulfide and dimethylamine. ... some unchanged thiram was also observed in feces /and/ urine.
Menzie, C.M. Metabolism of Pesticides. U.S. Department of the Interior, Bureau of Sport Fisheries and Wildlife, Publication 127. Washington, DC: U.S. Government Printing Office, 1969., p. 310
Pesticides and nitrites in food may be a hazard to man, since many pesticides are secondary or tertiary amines, which form nitroso compounds in the presence of nitrite under conditions resembling those in the human stomach. Compounds were incubated for 4 hours at 37 C in the presence of excess nitrite at pH 3. Thiram converted to the carcinogen dimethylnitrosamine at a yield of 9%.
PMID:7518 Egert G, Greim H; Food Cosmet Toxicol 14 (3): 193-5 (1976)
The major metabolite in plants is ethylene thiourea, followed by ethylene thiuram monosulfide and presumably ethylene thiuram disulfide and sulfur.
Hartley, D. and H. Kidd (eds.). The Agrochemicals Handbook. 2nd ed. Lechworth, Herts, England: The Royal Society of Chemistry, 1987., p. A399/Aug 87
The hepatotoxic effects of thiram metabolism to carbon disulfide were investigated in rats. Male Sprague-Dawley rats were administered 15, 30 or 60 mg/kg thiram ip. Activities of serum glutamic oxaloacetic transaminase and sorbitol dehydrogenase were measured in the blood to assess the extent of liver injury. Detectable amounts of carbon disulfide appeared after 1.5 to 2 hr of treatment; 5 hr were required for complete recovery of carbon disulfide produced from 60 mg/kg thiram. A 2 fold increase in the dose of thiram from 15 to 30 mg/kg resulted in a 10 fold increase in the amount of carbon disulfide in expired air. Increasing the thiram dose 4 times to 60 mg/kg resulted in a 40 fold increase in carbon disulfide production over that from a 15 mg/kg thiram dose. The microsomal inhibitor SKF-525A inhibited the formation of carbon disulfide from thiram; phenobarbital treatment increased the formation of carbon disulfide. Thiram caused a significant loss of cytochrome P450 and benzphetamine-N-demethylase activity at 24 hr following treatment. Five hours after 60 mg/kg thiram treatment, there was an increase in sorbitol dehydrogenase activity 47%; serum glutamic oxaloacetic transaminase activity increased by 41 and 40% during 5 and 24 hr, respectively. /It was/ concluded that carbon disulfide is an in vivo metabolite of thiram and may be responsible for hepatotoxicity.
PMID:3953292 Dalvi RR, Deoras DP; Acta Pharmacologica et Toxicologica 58 (1): 38-42 (1986)
For more Metabolism/Metabolites (Complete) data for THIRAM (6 total), please visit the HSDB record page.
Inhibition of hepatic dehydrogenases results in an acetaldehyde reaction on exposure to ethanol. Other effects may result from the known reactions of dithiocarbamates with metals, sulfhydryl-containing enzymes, or metabolism to reactive metabolites including carbon disulfide.
O'Donoghue, J.L. (ed.). Neurotoxicity of Industrial and Commercial Chemicals. Volume II. Boca Raton, FL: CRC Press, Inc., 1985., p. 48
...Ingestion of the fungicide thiram (125 mg/kg)... /has/ been reported to evoke ovarian atrophy and cessation of egg laying in hens, presumably through inhibition of dopamine beta-hydroxylase.
Shore R.F., Rattner BA. Ecotoxicology of Wild Mammals. Ecological & Environmental Toxicology Series 2001. John Wiley & Sons, New York, N.Y. 2001, p. 12
... /It was/ previously demonstrated that Disulfiram impairs the permeability of inner mitochondrial membrane (IMM). In this report, the effect of Disulfiram and its structural analogue thiram (Th) on mitochondrial functions was studied in detail. /It was/ found that mitochondria metabolize thiram disulfide compounds (TDs) in a NAD(P)H- and GSH-dependent manner. At the concentration above characteristic threshold, TDs induced irreversible oxidation of NAD(P)H and glutathione (GSH) pools, collapse of transmembrane potential, and inhibition of oxidative phosphorylation. The presence of Ca(2+) and exhaustion of mitochondrial glutathione (GSH+GSSG) decreased the threshold concentration of TDs. ... TDs induced the mitochondrial permeability transition (MPT).
PMID:11714485 Balakirev MY, Zimmer G; Chem Biol Interact 138 (3): 299-311 (2001)