
1. Boltin
2. Livial
3. Liviella
4. Org Od 14
5. Org Od14
6. Tibilone
1. 5630-53-5
2. Liviella
3. Livial
4. Org Od 14
5. Tibolona
6. Tibolonum
7. Xyvion
8. Boltin
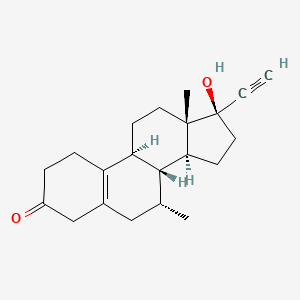
9. (7r,8r,9s,13s,14s,17r)-17-ethynyl-17-hydroxy-7,13-dimethyl-1,2,4,6,7,8,9,11,12,14,15,16-dodecahydrocyclopenta[a]phenanthren-3-one
10. 17-hydroxy-7alpha-methyl-19-nor-17alpha-pregn-5(10)-en-20-yn-3-one
11. Org-od 14
12. Chebi:32223
13. Ff9x0205v2
14. Nsc-759898
15. (1s,9r,10r,11s,14r,15s)-14-ethynyl-14-hydroxy-9,15-dimethyltetracyclo[8.7.0.0^{2,7}.0^{11,15}]heptadec-2(7)-en-5-one
16. Dsstox_cid_3667
17. (7alpha,17alpha)-17-hydroxy-7-methyl-19-norpregn-5(10)-en-20-yn-3-one
18. Dsstox_rid_77135
19. Dsstox_gsid_23667
20. 17alpha-ethynyl-17beta-hydroxy-7alpha-methylestr-5(10)-en-3-one
21. (17r)-17-hydroxy-7alpha-methyl-19-norpregn-5(10)-en-20-yn-3-one
22. (7alpha,17beta)-17-ethynyl-17-hydroxy-7-methylestr-5(10)en-3-one
23. Cas-5630-53-5
24. Tibolonum [inn-latin]
25. Tibolona [inn-spanish]
26. Tibolone [usan:inn:ban]
27. Tibofem
28. Unii-ff9x0205v2
29. 19-norpregn-5(10)-en-20-yn-3-one, 17-hydroxy-7-methyl-, (7.alpha.,17.alpha.)-
30. Ncgc00164632-01
31. Einecs 227-069-1
32. Tibolone [usan]
33. Org-od14
34. Tibolone [inn]
35. Tibolone [jan]
36. Tibolone [mi]
37. Tibolone [vandf]
38. Tibolone [mart.]
39. Tibolone [who-dd]
40. Schembl41172
41. Org Od 14;org Od14
42. Tibolone (jan/usan/inn)
43. Mls001424234
44. Tibolone [ep Impurity]
45. Gtpl9711
46. Tibolone [ep Monograph]
47. Chembl2103774
48. Dtxsid5023667
49. 17-hydroxy-7.alpha.-methyl-19-nor-17.alpha.-pregn-5(10)-en-20-yn-3-one
50. Hms2052k21
51. Hms2090b10
52. Hms2232b13
53. Hms3649j14
54. Hms3712j15
55. Zinc3812889
56. Tox21_112250
57. Kb-889
58. Akos015963197
59. Tox21_112250_1
60. Ccg-101148
61. Db09070
62. Gs-3562
63. Nc00398
64. Nsc 759898
65. Ncgc00164632-02
66. (7beta,8xi,9beta,13alpha,14beta,17alpha)-17-ethynyl-17-hydroxy-7-methylestr-5(10)-en-3-one
67. Ac-20036
68. Ac-31722
69. Cpd000469219
70. Smr000469219
71. D01639
72. T-3854
73. Ab00698273-05
74. 630t535
75. Q413805
76. Sr-01000763531
77. Sr-01000946727
78. Sr-01000763531-3
79. Sr-01000946727-1
80. 17.alpha.-hydroxy-7.alpha.-methyl-19-norpregn-5(10)-en-20-yn-3-one
81. 19-norpregn-5(10)-en-20-yn-3-one, 17-hydroxy-7-methyl-, (7alpha,17alpha)-
| Molecular Weight | 312.4 g/mol |
|---|---|
| Molecular Formula | C21H28O2 |
| XLogP3 | 2.4 |
| Hydrogen Bond Donor Count | 1 |
| Hydrogen Bond Acceptor Count | 2 |
| Rotatable Bond Count | 1 |
| Exact Mass | 312.208930132 g/mol |
| Monoisotopic Mass | 312.208930132 g/mol |
| Topological Polar Surface Area | 37.3 Ų |
| Heavy Atom Count | 23 |
| Formal Charge | 0 |
| Complexity | 636 |
| Isotope Atom Count | 0 |
| Defined Atom Stereocenter Count | 6 |
| Undefined Atom Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Defined Bond Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Undefined Bond Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Covalently Bonded Unit Count | 1 |
For the relief of post-menopausal symptoms and for the prevention of osteoporosis.
Tibolone prevents bone loss and treating post-menopausal symptoms without stimulating the endometrial tissues, which may lead to malignancy. Typical, drugs that treat post-menopausal symptoms such as estrogen, have a proliferative effect on the endometrium, increasing the risk of endometrial carcinoma. The effects on the bone, brain and vaginal tissues can be explained by the estrogenic activity of tibolone. It is important to note that activity is not expressed in the endometrium. Tibolone behaves differently from estrogen plus progesterone combinations on the breast. Therefore, tibolone can be characterized as a selective estrogen activity regulator. Tibolone has been demonstrated to be an effective agent in treating symptoms associated with menopause. A 16 week trial in 1189 women examined the effect of tibolone 2.5 mg once daily on climacteric symptoms. Women treated with tibolone showed improvement from baseline in typical menopausal symptoms including hot flashes, sweating, insomnia, and anxiety.
Anabolic Agents
These compounds stimulate anabolism and inhibit catabolism. They stimulate the development of muscle mass, strength, and power. (See all compounds classified as Anabolic Agents.)
Androgen Antagonists
Compounds which inhibit or antagonize the biosynthesis or actions of androgens. (See all compounds classified as Androgen Antagonists.)
Antihypertensive Agents
Drugs used in the treatment of acute or chronic vascular HYPERTENSION regardless of pharmacological mechanism. Among the antihypertensive agents are DIURETICS; (especially DIURETICS, THIAZIDE); ADRENERGIC BETA-ANTAGONISTS; ADRENERGIC ALPHA-ANTAGONISTS; ANGIOTENSIN-CONVERTING ENZYME INHIBITORS; CALCIUM CHANNEL BLOCKERS; GANGLIONIC BLOCKERS; and VASODILATOR AGENTS. (See all compounds classified as Antihypertensive Agents.)
Estrogen Receptor Modulators
Substances that possess antiestrogenic actions but can also produce estrogenic effects as well. They act as complete or partial agonist or as antagonist. They can be either steroidal or nonsteroidal in structure. (See all compounds classified as Estrogen Receptor Modulators.)
Antineoplastic Agents, Hormonal
Antineoplastic agents that are used to treat hormone-sensitive tumors. Hormone-sensitive tumors may be hormone-dependent, hormone-responsive, or both. A hormone-dependent tumor regresses on removal of the hormonal stimulus, by surgery or pharmacological block. Hormone-responsive tumors may regress when pharmacologic amounts of hormones are administered regardless of whether previous signs of hormone sensitivity were observed. The major hormone-responsive cancers include carcinomas of the breast, prostate, and endometrium; lymphomas; and certain leukemias. (From AMA Drug Evaluations Annual 1994, p2079) (See all compounds classified as Antineoplastic Agents, Hormonal.)
G03CX01
S76 | LUXPHARMA | Pharmaceuticals Marketed in Luxembourg | Pharmaceuticals marketed in Luxembourg, as published by d'Gesondheetskeess (CNS, la caisse nationale de sante, www.cns.lu), mapped by name to structures using CompTox by R. Singh et al. (in prep.). List downloaded from https://cns.public.lu/en/legislations/textes-coordonnes/liste-med-comm.html. Dataset DOI:10.5281/zenodo.4587355
G - Genito urinary system and sex hormones
G03 - Sex hormones and modulators of the genital system
G03C - Estrogens
G03CX - Other estrogens
G03CX01 - Tibolone
Absorption
Tibolone is extensively and rapidly absorbed after oral administration. The parent drug undergoes extensive metabolism, with. Greater than 80% of a radioactive dose excreted from the body as metabolites, which suggests very low plasma concentrations of tibolone. Plasma concentrations of the metabolites appear within 30 minutes and peak within 11.5 hours.2,7 The plasma concentrations of the hydroxymetabolites are higher than those of the 4-isomer. Food does not appear to have an effect on the absorption of this drug.
Route of Elimination
Excreted in the urine and feces in the form of sulfated metabolites,. The predominant route of elimination of tibolone is via the feces, although some excretion occurs via the urine.
Clearance
Elimination of tibolone is not dependent renal function.
Tibolone is metabolized mainly in the liver. The cytochrome P450 isoenzyme system is involved in minor hydroxylation of tibolone. Tibolone is rapidly converted into three major metabolites: 3 alpha- and 3 beta-hydroxy-tibolone, which have oestrogenic effects, and the Delta(4)-isomer, which has both progestogenic and androgenic effects. The 3-hydroxy metabolites are present in the circulation, predominantly in their inactive sulfated form.
The elimination half-life is approximately 45 h.
This drug's effects are owed to the activity of its metabolites in various tissues. Upon ingestion, tibolone is quickly converted into three major metabolites: _3 alpha- and 3 beta-hydroxy-tibolone_, which have oestrogenic effects, and the _Delta(4)-isomer_, which has progestogenic and androgenic effects. The specific tissue-selective effects of tibolone occur due to the metabolism, regulation of enzymes and receptor activation that varies in different tissues of the body. The bone-conserving effects occur due to estradiol receptor activation, while the progesterone and androgen receptors are not involved in this process. Breast tissue of monkeys is not found to be stimulated after tibolone administration, as occurs with estrogen plus progesterone used in combination. This is explained by the fact that tibolone and its metabolites inhibit _sulphatase and 17 beta-hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase_ (HSD) type I and _stimulate sulphotransferase and 17 beta-HSD type II_. The combined effects of this process prevent the conversion to active estrogens. In the uterus, the progestogenic activity of the _Delta(4)-metabolite_ and the effect on estrogen-inactivating enzymes prevent estrogenic stimulation. The mammary gland is not stimulated in currently used animal models. Tibolone has been shown to regulate estrogenic activity in several tissue types by influencing the availability of estrogenic compounds for the estradiol receptor in a selective manner. Additionally, tibolone modulates cellular homeostasis in the breast by preventing breast tissue proliferation and stimulating cell apoptosis. Tibolone does not stimulate the endometrium because of the action of its highly stable progestogenic metabolite (Delta(4)-isomer) in combination with an effect on the sulfatase (inhibition)-sulfotransferase (stimulation) system. The estrogenic metabolites of tibolone have direct, favorable effects on the cardiovascular system and, in animal models, this drug has shown no adverse consequences. The tissue-selective effects of tibolone are the result of metabolism, enzyme regulation and receptor activation that vary in different tissues. The bone-preserving effects of tibolone are the result of estradiol receptor activation, while other steroid receptors, mainly the progesterone and androgen receptors, are not involved in this process. In a study of monkeys, breast tissue was not stimulated, which occurs with estrogen and progesterone, because tibolone and its metabolites inhibit _sulfatase and 17 beta-hydroxysteroid _dehydrogenase (HSD) type I and stimulate _sulfotransferase and 17 beta-HSD type II_. The simultaneous effects of this process halt conversion to active estrogens. Additionally, tibolone affects cellular homeostasis in the breast by preventing proliferation and stimulating apoptosis. Tibolone does not stimulate the endometrium due to the action of the highly stable progestogenic metabolite (Delta(4)-isomer) in combination with an effect on the sulphatase (inhibition)-sulphotransferase (stimulation) pathway. The levels of tibolone metabolites and the alteration of hormonal activities vary according to the tissue type. In endometrial tissue the _4-isomer_ functions as a progestagen, however, in the brain and liver, it shows androgenic effects. In breast tissue, the primary actions of tibolone are strong inhibition of sulfatase activity and weak inhibition of 17-hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase activity, which leads to blocking the conversion estrone sulfate to E2.