


1. 2 Mercaptopropionylglycine
2. 2 Thiol Propionamido Acetic Acid
3. 2 Thiolpropionamidoacetic Acid
4. 2-mercaptopropionylglycine
5. 2-thiol-propionamido-acetic Acid
6. 2-thiolpropionamidoacetic Acid
7. Acadione
8. Acid, 2-thiol-propionamido-acetic
9. Acid, 2-thiolpropionamidoacetic
10. Alpha Mercaptopropionylglycine
11. Alpha-mercaptopropionylglycine
12. Captimer
13. Meprin
14. Mercaptopropionylglycine
15. Thiola
16. Thiopronine
17. Tiopronine
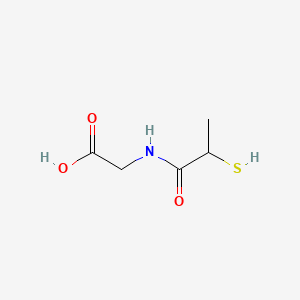
1. 1953-02-2
2. N-(2-mercaptopropionyl)glycine
3. Acadione
4. Captimer
5. Thiopronine
6. Mucolysin
7. Capen
8. Thiola
9. Tiopronine
10. Epatiol
11. 2-(2-sulfanylpropanoylamino)acetic Acid
12. Thiosol
13. Glycine, N-(2-mercapto-1-oxopropyl)-
14. Tiopronin (thiola)
15. A-mercaptopropionyl Glycine
16. 2-(2-mercaptopropanamido)acetic Acid
17. Nsc-760416
18. Chembl1314
19. C5w04go61s
20. N-(2-mercaptopropanoyl)glycine
21. Thiopronin
22. Chebi:32229
23. 2-(2-sulfanylpropanamido)acetic Acid
24. Ncgc00159422-02
25. Ncgc00159422-04
26. Sutilan
27. Dsstox_cid_3678
28. Glycine, N-(2-mercapto-1-oxopropyl)- (9ci)
29. Dsstox_rid_77142
30. Dsstox_gsid_23678
31. Thiolpropionamidoacetic Acid
32. Tioglis
33. Vincol
34. Cas-1953-02-2
35. Meprin (detoxicant)
36. N-(2-mercapto-1-oxopropyl)glycine
37. Tiopronine [inn-french]
38. Tioproninum [inn-latin]
39. Tiopronino [inn-spanish]
40. (2-mercaptopropionyl)glycine
41. Tiopronin [inn:dcf:jan]
42. Tiopronino
43. Tioproninum
44. Ccris 1935
45. (s)-2-(2-mercaptopropanamido)acetic Acid
46. Einecs 217-778-4
47. Thiola (tn)
48. Brn 1859822
49. Thiola Ec
50. Tiopronin (jan/inn)
51. Tiopronin [inn]
52. Tiopronin [jan]
53. Tiopronin [mi]
54. Glycine, N-(2-mercaptopropionyl)-
55. Tiopronin [vandf]
56. 2-mercapto-propionylglycine
57. Tiopronin [mart.]
58. Tiopronin [who-dd]
59. (2-mercaptopropanoyl)glycine
60. Unii-c5w04go61s
61. Schembl19989
62. Mls006010632
63. Alpha-mercaptopropionyl Glycine
64. Mercaptopropionylglycine-
65. N-(2-sulfanylpropanoyl)glycine
66. Tiopronin [orange Book]
67. Dtxsid4023678
68. N-(2-mercaptopropionyl) Glycine
69. N-(2-mercaptopropanoyl) Glycine
70. Acadione; Capen; Epatiol; Vincol
71. Hms3264b11
72. Hms3655l15
73. Pharmakon1600-01506190
74. Amy39003
75. Bcp13354
76. Hy-b0373
77. 2-(2-mercaptopropanamido)aceticacid
78. Tox21_111654
79. Bdbm50020805
80. Mfcd00004861
81. Mfcd30157366
82. Nsc760416
83. S2062
84. (2-mercaptopropionylamino)acetic Acid
85. Akos015895408
86. N-(2-mercaptopropionyl)glycine, 99%
87. Tox21_111654_1
88. Ac-2087
89. Ccg-214007
90. Db06823
91. Nsc 760416
92. (2-mercapto-propionylamino)-acetic Acid
93. Ncgc00159422-03
94. As-12522
95. Smr001550282
96. Sy262996
97. Ft-0603530
98. Ft-0653686
99. Sw219206-1
100. T2614
101. Tiopronin, Vetranal(tm), Analytical Standard
102. C73708
103. D01430
104. Ab00376096_02
105. 953t022
106. A813794
107. Q414456
108. Sr-01000942263
109. J-012651
110. Sr-01000942263-1
111. Tiopronin, Dextiopronin, Tiopronin (n-2-mercaptopropionyl Glycine)
| Molecular Weight | 163.20 g/mol |
|---|---|
| Molecular Formula | C5H9NO3S |
| XLogP3 | -0.1 |
| Hydrogen Bond Donor Count | 3 |
| Hydrogen Bond Acceptor Count | 4 |
| Rotatable Bond Count | 3 |
| Exact Mass | 163.03031432 g/mol |
| Monoisotopic Mass | 163.03031432 g/mol |
| Topological Polar Surface Area | 67.4 Ų |
| Heavy Atom Count | 10 |
| Formal Charge | 0 |
| Complexity | 148 |
| Isotope Atom Count | 0 |
| Defined Atom Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Undefined Atom Stereocenter Count | 1 |
| Defined Bond Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Undefined Bond Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Covalently Bonded Unit Count | 1 |
Tiopronin is indicated for the prevention of kidney stone formation in patients with severe homozygous cystinuria consisting of a urinary cystine concentration greater than 500 mg/day, and who have failed treatment with non-pharmacological measures of increased fluid intake, decreased sodium and protein intake, and urine alkalinization.
G - Genito urinary system and sex hormones
G04 - Urologicals
G04B - Urologicals
G04BX - Other urologicals
G04BX16 - Tiopronin
Absorption
Tiopronin undergoes slow absorption, reaching peak plasma concentration 3-6 hours after ingestion. In a study of healthy subjects, the bioavailability of total and unbound tiopronin was found to be 63% and 40%, respectively.
Route of Elimination
Tiopronin is 100% excreted in urine.
Volume of Distribution
The volume of distribution of tiopronin is high at 455 L, indicating that a large portion of the drug is bound to tissues outside plasma.
Clearance
Total renal clearance for the total and unbound fractions of tiopronin were found to be 3.3 and 13.3 L/h respectively.
The principle metabolite of tiopronin is 2-mercaptopropionic acid (2-MPA). Between 10-15% of the drug is metabolized to 2-MPA via hydrolysis.
Tiopronin has a long terminal half life of 53 hours in healthy subjects. However, the unbound drug fraction of tiopronin is eliminated much more rapidly from plasma with a calculated half life of 1.8 hours.
Kidney stones form when the solubility limit is exceeded and urine becomes supersaturated with endogenous cystine. Tiopronin is an active reducing agent which undergoes a thiol-disulfide exchange with cystine to form a water-soluble mixed disulfide complex. Thus, the amount of sparingly soluble cystine is reduced. By reducing urinary cystine concentrations below the solubility limit, tiopronin helps reduce cystine stone formation.