


1. Av 951
2. Av-951
3. Av951 Cpd
4. Fotivda
5. Krn 951
6. Krn-951
7. Krn951
1. 475108-18-0
2. Av-951
3. Tivozanib (av-951)
4. Krn-951
5. Av 951
6. Av951
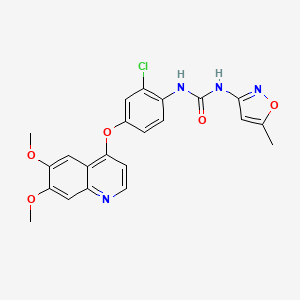
7. 1-(2-chloro-4-((6,7-dimethoxyquinolin-4-yl)oxy)phenyl)-3-(5-methylisoxazol-3-yl)urea
8. Krn951
9. Fotivda
10. Kil8951
11. Krn 951
12. N-[2-chloro-4-[(6,7-dimethoxy-4-quinolyl)oxy]phenyl]-n'-(5-methyl-3-isoxazolyl)urea
13. Kil-8951
14. Chembl1289494
15. Av-951;krn951
16. 1-(2-chloro-4-(6,7-dimethoxyquinolin-4-yloxy)phenyl)-3-(5-methylisoxazol-3-yl)urea
17. 1-[2-chloro-4-(6,7-dimethoxyquinolin-4-yl)oxyphenyl]-3-(5-methyl-1,2-oxazol-3-yl)urea
18. 172030934t
19. 1-(2-chloro-4-((6,7-dimethoxyquinolin-4-yl)-oxy)phenyl)-3-(5-methylisoxazol-3-yl)urea
20. N-(2-chloro-4-((6,7-dimethoxy-4-quinolyl)oxy)phenyl)-n'-(5-methyl-3-isoxazolyl)urea
21. Urea, N-(2-chloro-4-((6,7-dimethoxy-4-quinolinyl)oxy)phenyl)-n'-(5-methyl-3-isoxazolyl)-
22. Tivozanib [usan]
23. Asp-4130
24. Tivozanib [usan:inn]
25. 4ase
26. N-{2-chloro-4-[(6,7-dimethoxy-4-quinolyl)oxy]phenyl}-n'-(5-methyl-3-isoxazolyl)urea
27. Av9
28. Unii-172030934t
29. Av-951,tivozanib
30. Tivozanib(av-951)
31. Tivozanib [inn]
32. Av951 Cpd
33. Tivozanib (usan/inn)
34. Tivozanib - Av-951
35. Tivozanib [who-dd]
36. Mls006011287
37. Schembl172883
38. Gtpl6058
39. Chebi:91327
40. Dtxsid20963865
41. Ex-a472
42. Hms3229o09
43. Hms3244c19
44. Hms3244c20
45. Hms3244d19
46. Hms3265a11
47. Hms3265a12
48. Hms3265b11
49. Hms3265b12
50. Hms3654g22
51. Hms3745c05
52. Amy39975
53. Bcp01980
54. Zinc1489430
55. Vegfr Tyrosine Kinase Inhibitor Iv
56. Bdbm50331095
57. Mfcd15146788
58. Nsc758007
59. Nsc800952
60. S1207
61. Akos022177607
62. Av951 (krn951, Tivozanib)
63. Bcp9000343
64. Ccg-206805
65. Cs-0103
66. Db11800
67. Ex-8600
68. Nsc-758007
69. Nsc-800952
70. Pb28569
71. Ncgc00249390-01
72. Ncgc00249390-05
73. Ncgc00249390-12
74. Ac-24702
75. As-16997
76. Bt160380
77. Hy-10977
78. Smr004703037
79. Ft-0700315
80. Sw219364-1
81. A24970
82. D09683
83. 108k180
84. J-502964
85. Q7810457
86. Brd-k53414658-001-01-7
87. 1-{2-chloro-4-[(6,7-dimethoxyquinolin-4-yl)oxy]phenyl}-3-(5-methyl-1,2-oxazol-3-yl)urea
88. N-{2-chloro-4-[(6,7-dimethoxy-4-quinolyl)-oxy]phenyl}-n'-(5-methyl-3-isoxazolyl)urea
89. 1-(2-chloro-4-(6,7-dimethoxyquinolin-4-yloxy)phenyl)-3-(5-methylisoxazol-3-yl)urea;av-951
90. 1-{2-chloro-4-[(6,7-dimethoxyquinolin-4-yl)oxy]phenyl}-3-[(3e)-5-methylisoxazol-3(2h)-ylidene]urea
91. N-(2-chloro-4-((6,7-dimethoxyquinolin-4-yl)oxy)phenyl)-n'-(5-methylisoxazol-3-yl)urea
| Molecular Weight | 454.9 g/mol |
|---|---|
| Molecular Formula | C22H19ClN4O5 |
| XLogP3 | 4 |
| Hydrogen Bond Donor Count | 2 |
| Hydrogen Bond Acceptor Count | 7 |
| Rotatable Bond Count | 6 |
| Exact Mass | 454.1043974 g/mol |
| Monoisotopic Mass | 454.1043974 g/mol |
| Topological Polar Surface Area | 108 Ų |
| Heavy Atom Count | 32 |
| Formal Charge | 0 |
| Complexity | 631 |
| Isotope Atom Count | 0 |
| Defined Atom Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Undefined Atom Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Defined Bond Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Undefined Bond Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Covalently Bonded Unit Count | 1 |
Tivozanib is approved in the USA for the treatment of relapsed or refractory renal cell carcinoma in adult patients who have undergone two or more systemic therapies. In the UK and other countries, is indicated as first line therapy of adults with advanced renal cell carcinoma (RCC) and VEGFR and mTOR pathway inhibitor-nave patients after disease progression following one previous treatment with cytokine therapy for advanced disease.
Fotivda is indicated for the first line treatment of adult patients with advanced renal cell carcinoma (RCC) and for adult patients who are VEGFR and mTOR pathway inhibitor-nave following disease progression after one prior treatment with cytokine therapy for advanced RCC.
Treatment of advanced renal cell carcinoma.
Tivozanib inhibits growth factor receptors, treating renal cell carcinoma. In mice and rats, tivozanib inhibits tumour angiogenesis, tumour growth, and vascular permeability. Tivozanib was shown to frequently cause hypertension in clinical trials; hypertension must be managed before initiating therapy. Cardiac QT segment prolongation was reported in a tivozanib cardiac safety study, however the reactions were not considered clinically serious. In clinical studies, levels of serum soluble VEGFR2 (sVEGFR2) decreased with time and this effect increased with tivozanib exposure, and sVEGFR2 may serve as a pharmacodynamic marker of VEGFR inhibition.
Protein Kinase Inhibitors
Agents that inhibit PROTEIN KINASES. (See all compounds classified as Protein Kinase Inhibitors.)
L01EK03
L - Antineoplastic and immunomodulating agents
L01 - Antineoplastic agents
L01E - Protein kinase inhibitors
L01EK - Vascular endothelial growth factor receptor (vegfr) tyrosine kinase inhibitors
L01EK03 - Tivozanib
Absorption
The median Tmax of tivozanib is 10 hours, however, can range from 3 to 24 hours. A pharmacokinetic study in 8 healthy subjects revealed a Cmax and AUC for radiolabeled tivozanib of 12.1 5.67 ng/mL and 1084 417.0 ngh/mL, respectively. Steady-state tivozanib concentrations are achieved at concentrations 6-7 times higher the normal dose.
Route of Elimination
Tivozanib is primarily excreted in the feces. After oral ingestion of a radiolabeled 1.34 mg dose of tivozanib in healthy volunteers, 79% of the administered dose was found in the feces (with 26% unchanged) and 12% was found in the urine solely as metabolites.
Volume of Distribution
Tivozanib has an apparent volume of distribution (V/F) of 123 L.
Clearance
The apparent clearance (CL/F) of tivozanib is approximately 0.75 L/h.
Tivozanib is primarily metabolized by CYP3A4. After oral ingestion of a radiolabeled 1.34 mg dose of tivozanib in healthy volunteers, unchanged tivozanib accounted for 90% of the radioactive drug detected in serum.
The half-life of tivozanib is about 111 hours according to prescribing information. Information from clinical studies reveals a half-life of 4-5 days.
The VHL mutation-HIF upregulation-VEGF transcription is the main pathway implicated in the growth of renal cell carcinoma. Vascular endothelial growth factor receptors (VEGFR receptors) are important targets for tyrosine kinase inhibitors, which halt the growth of tumours. Tivozanib is a tyrosine kinase inhibitor that exerts its actions by inhibiting the phosphorylation of vascular endothelial growth factor receptor (VEGFR)-1, VEGFR-2 and VEGFR-3 and inhibits other kinases such as c-kit and platelet derived growth factor beta (PDGFR ). The above actions inhibit tumour growth and progression, treating renal cell carcinoma.
